Abstract
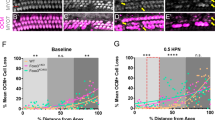
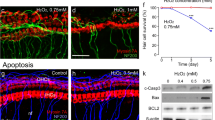
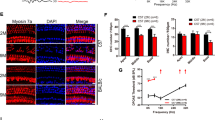
We investigated oxidative stress and antioxidant response in the p62/Sqstm1-Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in C57BL/6 mice cochleae during age-related hearing loss (ARHL) and noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL), and the function of full-length and variant p62 in the regulation of Nrf2 activation. Groups of young (2 months), old (13–14 months), control, and acoustic trauma (AT) mice were examined cochlear damage and oxidative stress as follows: auditory brainstem response and hair cell counts; malondialdehyde (MDA) levels measured by assay kit and 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG) detected by immunohistochemistry. Full-length and variant p62 were examined for expression in cochleae, hippocampus (HIP), and auditory cortex (AC) using immunoblotting. Keap1-Nrf2 pathway activation was based on immunoblotting of nuclear Nrf2 and quantitative real-time PCR of Nrf2 target genes HO-1/NQO-1. The oxidative function of full-length and variant p62 was examined in HEI-OC-1 cells by flow cytometry. The results showed hearing loss, and cochlear hair cell loss was associated with MDA accumulation and 8-oxoG expression during ARHL and NIHL. Nrf2 showed no obvious changes in nuclear protein. Expression levels mRNA for HO-1 and NQO1 were lower in old mice and mildly greater in AT Mice. The expression of p62 splicing variant lacking the Keap1-interacting region was greater than full-length p62 in cochleae. However, the expression of p62 splicing variant was lesser than full-length p62 in HIP and AC. For HEI-OC-1 cells, overexpression of full-length p62 decreased ROS levels induced by H2O2. Oxidative stress is closely related to ARHL and NIHL. Changing the ratio of full-length to variant p62 protein expression may be a new target to reduce the level of oxidative stress in cochleae.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The data is available upon request.
Abbreviations
- ARHL:
-
Age-related hearing loss
- NIHL:
-
Noise-induced hearing loss
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- ABR:
-
Auditory brainstem response
- 8-oxoG:
-
7,8-Dihydro-8-oxoguanine
- HIP:
-
Hippocampus
- AC:
-
Auditory cortex
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
References
Bjorkoy G, Lamark T, Brech A, Outzen H, Perander M, Overvatn A, Stenmark H, Johansen T (2005) p62/SQSTM1 forms protein aggregates degraded by autophagy and has a protective effect on huntingtin-induced cell death. J Cell Biol 171:603–614
Brewton DH, Kokash J, Jimenez O, Pena ER, Razak KA (2016) Age-related deterioration of perineuronal nets in the primary auditory cortex of mice. Front Aging Neurosci 8
Chen W, Sun Z, Wang X, Jiang T, Huang Z, Fang D, Zhang DD (2009) Direct interaction between Nrf2 and p21Cip1/WAF1 upregulates the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Mol Cell 34:663–673
Fetoni AR, Paciello F, Rolesi R, Eramo SLM, Mancuso C, Troiani D, Paludetti G (2015) Rosmarinic acid up-regulates the noise-activated Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and protects against noise-induced injury in rat cochlea. Free Radical Biol Med 85:269–281
Fetoni AR, Paciello F, Rolesi R, Paludetti G, Troiani D (2019) Targeting dysregulation of redox homeostasis in noise-induced hearing loss: oxidative stress and ROS signaling. Free Radical Biol Med 135:46–59
Frisina RD (2009) Age-related hearing loss. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1170:708–717
Harder B, Jiang T, Wu T, Tao S, de la Vega MR, Tian W, Chapman E, Zhang DD (2015) Molecular mechanisms of Nrf2 regulation and how these influence chemical modulation for disease intervention. Biochem Soc Trans 43:680–686
Honkura Y, Matsuo H, Murakami S, Sakiyama M, Mizutari K, Shiotani A, Yamamoto M, Morita I, Shinomiya N, Kawase T, Katori Y, Motohashi H (2016) NRF2 is a key target for prevention of noise-induced hearing loss by reducing oxidative damage of cochlea. Sci Rep 6
Hoshino T, Tabuchi K, Nishimura B, Tanaka S, Nakayama M, Ishii T, Warabi E, Yanagawa T, Shimizu R, Yamamoto M, Hara A (2011) Protective role of Nrf2 in age-related hearing loss and gentamicin ototoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 415:94–98
Hosokawa K, Hosokawa S, Ishiyama G, Ishiyama A, Lopez IA (2018) Immunohistochemical localization of Nrf2 in the human cochlea. Brain Res 1700:1–8
Jain A, Lamark T, Sjøttem E, Bowitz Larsen K, Atesoh Awuh J, Øvervatn A, McMahon M, Hayes JD, Johansen T (2010) p62/SQSTM1 is a target gene for transcription factor NRF2 and creates a positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response element-driven gene transcription. J Biol Chem 285:22576–22591
Johnson KR, Tian C, Gagnon LH, Jiang H, Ding D, Salvi R (2017) Effects of Cdh23 single nucleotide substitutions on age-related hearing loss in C57BL/6 and 129S1/Sv mice and comparisons with congenic strains. Sci Rep 7
Kageyama S, Saito T, Obata M, Koide RH, Ichimura Y, Komatsu M (2018) Negative regulation of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway by a p62/Sqstm1 splicing variant. Mol Cell Biol 38
Kalinec GM, Park C, Thein P, Kalinec F (2016) Working with auditory HEI-OC1 cells. J Vis Exp: JoVE 115
Kalinec GM, Webster P, Lim DJ, Kalinec F (2003) A cochlear cell line as an in vitro system for drug ototoxicity screening. Audiology and Neurotology 8:177–189
Katsuragi Y, Ichimura Y, Komatsu M (2015) p62/SQSTM1 functions as a signaling hub and an autophagy adaptor. FEBS J 282:4672–4678
Kim S, Ho Hur J, Park C, Kim H, Oh G, Lee JN, Yoo S, Choe S, So H, Lim DJ, Moon SK, Park R (2015) Bucillamine prevents cisplatin-induced ototoxicity through induction of glutathione and antioxidant genes. Exp Mol Med 47:e142–e142
Kobayashi A, Kang M, Okawa H, Ohtsuji M, Zenke Y, Chiba T, Igarashi K, Yamamoto M (2004) Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol 24:7130–7139
Komatsu M, Kurokawa H, Waguri S, Taguchi K, Kobayashi A, Ichimura Y, Sou Y, Ueno I, Sakamoto A, Tong KI, Kim M, Nishito Y, Iemura S, Natsume T, Ueno T, Kominami E, Motohashi H, Tanaka K, Yamamoto M (2010) The selective autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of Keap1. Nat Cell Biol 12:213–223
Kong L, Chen G, Zhou X, McGinnis JF, Li F, Cao W (2009) Molecular mechanisms underlying cochlear degeneration in the tubby mouse and the therapeutic effect of sulforaphane. Neurochem Int 54:172–179
Lau A, Wang X, Zhao F, Villeneuve NF, Wu T, Jiang T, Sun Z, White E, Zhang DD (2010) A noncanonical mechanism of Nrf2 activation by autophagy deficiency: direct interaction between Keap1 and p62. Mol Cell Biol 30:3275–3285
Lee D, Ko W, Song B, Son I, Kim D, Kang D, Lee H, Oh H, Jang J, Kim Y, Kim S (2016) The herbal extract KCHO-1 exerts a neuroprotective effect by ameliorating oxidative stress via heme oxygenase-1 upregulation. Mol Med Rep 13:4911–4919
Lee S, Han JJ, Lee S, Jung G, Min HJ, Song J, Koo J (2020) Outcomes of peptide vaccine GV1001 treatment in a murine model of acute noise-induced hearing loss. Antioxidants 9:112
Li P, Bing D, Wang S, Chen J, Du Z, Sun Y, Qi F, Zhang Y, Chu H (2019) Sleep deprivation modifies noise-induced cochlear injury related to the stress hormone and autophagy in female mice. Front Neurosci 13
Liu W, Xu Z, Yang T, Deng Y, Xu B, Feng S, Li Y (2014) The protective role of tea polyphenols against methylmercury-induced neurotoxic effects in rat cerebral cortex via inhibition of oxidative stress. Free Radical Res 48:849–863
Matlin AJ, Clark F, Smith CWJ (2005) Understanding alternative splicing: towards a cellular code. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:386–398
Menardo J, Tang Y, Ladrech S, Lenoir M, Casas F, Michel C, Bourien J, Ruel J, Rebillard G, Maurice T, Puel J, Wang J (2012) Oxidative stress, inflammation, and autophagic stress as the key mechanisms of premature age-related hearing Loss in SAMP8 mouse cochlea. Antioxid Redox Signal 16:263–274
Pan J, Sun Y, Jiang Y, Bott AJ, Jaber N, Dou Z, Yang B, Chen J, Catanzaro JM, Du C, Ding W, Diaz-Meco MT, Moscat J, Ozato K, Lin RZ, Zong W (2016) TRIM21 ubiquitylates SQSTM1/p62 and suppresses protein sequestration to regulate redox homeostasis. Mol Cell 61:720–733
Rogov V, Dotsch V, Johansen T, Kirkin V (2014) Interactions between autophagy receptors and ubiquitin-like proteins form the molecular basis for selective autophagy. Mol Cell 53:167–178
Wang B, Cao P, Wang Z, Li Z, Wang Z, Ma J, Liao B, Deng Y, Long X, Xu K, Wang H, Wang H, Zeng M, Lu X, Liu Z (2017) Interferon-γ-induced insufficient autophagy contributes to p62-dependent apoptosis of epithelial cells in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Allergy 72:1384–1397
Wilson MI, Gill DJ, Perisic O, Quinn MT, Williams RL (2003) PB1 domain-mediated heterodimerization in NADPH oxidase and signaling complexes of atypical protein kinase C with Par6 and p62. Mol Cell 12:39–50
Wu F, Xiong H, Sha S (2020) Noise-induced loss of sensory hair cells is mediated by ROS/AMPKα pathway. Redox Biol 29:101406
Xiong H, Chen S, Lai L, Yang H, Xu Y, Pang J, Su Z, Lin H, Zheng Y (2019) Modulation of miR-34a/SIRT1 signaling protects cochlear hair cells against oxidative stress and delays age-related hearing loss through coordinated regulation of mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis. Neurobiol Aging 79:30–42
Yamasoba T, Lin FR, Someya S, Kashio A, Sakamoto T, Kondo K (2013) Current concepts in age-related hearing loss: epidemiology and mechanistic pathways. Hear Res 303:30–38
Yasuda SP, Seki Y, Suzuki S, Ohshiba Y, Hou X, Matsuoka K, Wada K, Shitara H, Miyasaka Y, Kikkawa Y (2020) c.753A>G genome editing of a Cdh23 allele delays age-related hearing loss and degeneration of cochlear hair cells in C57BL/6J mice. Hear Res 389:107926
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Hao Xiong for donating HEI-OC1 cell lines to us.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81500794, 81771004, and 81500791).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dan Bing and Hanqi Chu designed and conceived the experiments. Pengjun Li, Xiaodi Zhang, Zhihui Du, Yanbo Sun, and Fan Qi performed the experiments. Pengjun Li wrote the manuscript. Chen Jin performed tissue preparation and immunohistochemistry. Xiaodi Zhang was mainly responsible for cell culture. Dan Bing and Hanqi Chu interpreted the data and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Care of the animals and experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Research and Ethics Committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science, and Technology, China.
Consent for Publication
Consent.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Bing, D., Wang, X. et al. New Target of Oxidative Stress Regulation in Cochleae: Alternative Splicing of the p62/Sqstm1 Gene. J Mol Neurosci 72, 830–840 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-01969-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-01969-0