Abstract
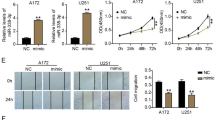
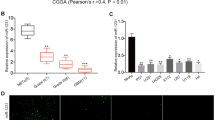
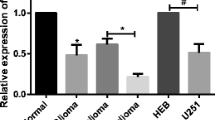
Increasing evidence has demonstrated the miRNAs’ action in cancerogenesis and tumor progression. Here, we explored the role and underlying mechanism of miR-3918 during glioma malignancy. miR-3918 and EGFR expression was detected in glioma tissues and tissues by RT-qPCR. The proliferative and migratory rate of glioma cells was assessed through CCK8 and Scratch wound-healing migration assay. Xenograft tumor mouse models were established for in vivo verification. A series of bioinformatics analysis coupled with luciferase reporter assays verified the targeted binding between miR-3918 and EGFR. Expression analyses demonstrated that miR-3918 was poorly expressed in glioma tissues while EGFR abundantly expressed. MiR-3918 overexpression impaired the proliferative and migratory capacities of glioma cells by inactivating PI3K/AKT and ERK pathways. Meanwhile, miR-3918 overexpression also retarded the growth of glioma xenograft. Mechanically, miR-3918 targeted EGFF which was further validated by the correlation of miR-3918 and EGFR expression in glioma tissues. When overexpressed, EGFR can restore the inactivated PI3K/AKT and ERK pathways caused by miR-3918 and influence the glioma cell proliferation and migration. Our findings are the first report that miR-3918/EGFR axis arrested the tumorigenesis of glioma via regulating PI3K/AKT and ERK pathways.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Acunzo M, Romano G, Wernicke D, Croce CM (2015) MicroRNA and cancer–a brief overview. Adv Biol Regul 57:1–9
Alzahrani AS (2019) PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: at the bench and bedside. Semin Cancer Biol 59:125–132
Biswas S (2018) MicroRNAs as therapeutic agents: the future of the battle against cancer. Curr Top Med Chem 18(30):2544–2554
Colquhoun A (2017) Cell biology-metabolic crosstalk in glioma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 89:171–181
Chen H, Zhou L, Wu X et al (2016) The PI3K/AKT pathway in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark edition) 21:1084–1091
Chai C, Song LJ, Han SY, Li XQ, Li M (2018) MicroRNA-21 promotes glioma cell proliferation and inhibits senescence and apoptosis by targeting SPRY1 via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther 24(5):369–380
Correia De Sousa M, Gjorgjieva M, Dolicka D, Sobolewski C, Foti M (2019) Deciphering miRNAs' Action through miRNA Editing. Int J Mol Sci 20(24)
Ciardiello F, Tortora G (2008) EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. New England J Med 358(11):1160–1174
Dong ZQ, Guo ZY, Xie J (2019) The lncRNA EGFR-AS1 is linked to migration, invasion and apoptosis in glioma cells by targeting miR-133b/RACK1. Biomed Pharmacother 118:109292
Fu T, Ji K, Jin L et al (2021) ASB16-AS1 up-regulated and phosphorylated TRIM37 to activate NF-κB pathway and promote proliferation, stemness, and cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer. Gastric cancer: official journal of the International Gastric Cancer Association and the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association 24(1):45–59
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, De Castro J, Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C, González-Barón M (2004) PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 30(2):193–204
Gusyatiner O, Hegi ME (2018) Glioma epigenetics: from subclassification to novel treatment options. Semin Cancer Biol 51:50–58
Harrison PT, Vyse S, Huang PH (2020) Rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 61:167–179
Li X, Wu C, Chen N et al (2016) PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and targeted therapy for glioblastoma. Oncotarget 7(22):33440–33450
Lee YS, Dutta A (2009) MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 4:199–227
Liu Y, Yang L, Liao F, Wang W, Wang ZF (2020) MiR-450a-5p strengthens the drug sensitivity of gefitinib in glioma chemotherapy via regulating autophagy by targeting EGFR. Oncogene 39(39):6190–6202
Nan Y, Guo H, Guo L et al (2018) MiRNA-451 inhibits glioma cell proliferation and invasion through the mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway by targeting CAB39 Human gene therapy. Clin Dev 29(3):156–166
Nicholson RI, Gee JM (2001) MEEGFR Harper cancer prognosis. European journal of cancer Oxford, England, 1990 37(Suppl 4)S 9–15
Pan DS, Cao P, Li JJ, Fan D, Song ZQ (2019) MicroRNA-374b inhibits migration and invasion of glioma cells by targeting EGFR. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(10):4254–4263
Ribeiro De Souza AL, Marra K, Gunn J et al (2018) Optimizing glioma detection using an EGFR-targeted fluorescent affibodY. Photochem Photobiol 94(6):1167-1171
Saadeh FS, Mahfouz R, Assi HI (2018) EGFR as a clinical marker in glioblastomas and other gliomas. Int J Biol Markers 33(1):22–32
Xu S, Tang L, Li X, Fan F, Liu Z (2020) Immunotherapy for glioma: current management and future application. Cancer Lett 476:1–12
Yang G, Wang X, Liu B et al (2019) circ-BIRC6, a circular RNA, promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting the miR-3918/Bcl2 axis. Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 18(9):976–989
Zhao L, Tang X, Luo R, Duan J, Wang Y, Yang B (2018) MicroRNA-490-5P targets CCND1 to suppress cellular proliferation in glioma cells and tissue through cell cycle arrest. Curr Neurovasc Res 15(3):246–255
Zhang X, Niu W, Mu M, Hu S, Niu C (2020) Long non-coding RNA LPP-AS2 promotes glioma tumorigenesis via miR-7-5p/EGFR/PI3K/AKT/c-MYC feedback loop. J Exp Clin Cancer Res: CR 39(1):196
Zhang LX, Jin W, Zheng J et al (2018) MicroRNA-375 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of glioma cancer cells by inhibiting CTGF-EGFR signaling pathway. Bratislavske lekarske listy 119(1):17–21
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YH and HMW performed the experiments and data analysis. YH and HMW conceived and designed the study. YH and HMW made the acquisition of data. YH did the analysis and interpretation of data. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Wuhan Red Cross Hospital (Wuhan, China). The processing of clinical tissue samples is in strict compliance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients signed written informed consent.
Consent to Participate
All patients signed written informed consent.
Consent for Publication
Consent for publication was obtained from the participants.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Y., Wang, H. MiR-3918 Inhibits Tumorigenesis of Glioma via Targeting EGFR to Regulate PI3K/AKT and ERK Pathways. J Mol Neurosci 72, 433–440 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01952-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01952-1