Abstract
Data from preclinical studies propose nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) as a neuroprotective and bioenergetics stimulant agent to treat Alzheimer’s disease (AD); however, there seems to be inconsistency between behavioral and molecular outcomes. We performed this systematic review to provide a better understanding of the effects of NAD+ in rodent AD models and to summarize the literature.
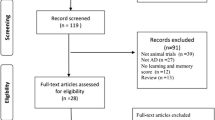
Studies were identified by searching PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, Google Scholar, and the reference lists of relevant review articles published through December 2020. The search strategy was restricted to articles about NAD+, its derivatives, and their association with cognitive function in AD rodent models. The initial search yielded 320 articles, of which 11 publications were included in our systematic review.
Based on the primary outcomes, it was revealed that NAD+ improves learning and memory. The secondary endpoints also showed neuroprotective effects of NAD+ on different AD models. The proposed neuroprotective mechanisms included, but were not limited to, the attenuation of the oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis, while enhancing the mitochondrial function.
The current systematic review summarizes the preclinical studies on NAD+ precursors and provides evidence favoring the pro-cognitive effects of such components in rodent models of AD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alano CC, Ying W, Swanson RA (2004) Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-mediated cell death in astrocytes requires NAD+ depletion and mitochondrial permeability transition. J Biol Chem 279:18895-18902
Bonda DJ, Wang X, Perry G, Smith MA, Zhu X (2010) Mitochondrial dynamics in Alzheimer’s disease Drugs & aging 27:181–192
Bostancıklıoğlu M (2019) An update on the interactions between Alzheimer's disease, autophagy and inflammation. Gene 705:157-166
Butterfield DA, Halliwell B (2019) Oxidative stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 20:148-160
Cassidy L, Fernandez F, Johnson JB, Naiker M, Owoola AG, Broszczak DA (2020) Oxidative stress in alzheimer’s disease: A review on emergent natural polyphenolic therapeutics. Complement Ther Med 49:102294
Chen X-Q, Mobley WC (2019) Exploring the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease in basal forebrain cholinergic neurons: Converging insights from alternative hypotheses. Front Neurosci 13:446
Costello DA, Herron CE (2004) The role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in the Aβ-mediated impairment of LTP and regulation of synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 46:655–662
Davila A et al (2018) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is transported into mammalian mitochondria Elife 7:e33246
Dong M et al (2019) Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Detect & Prevent-presymptomatic AD detection and prevention
Fang EF et al (2014) Defective mitophagy in XPA via PARP-1 hyperactivation and NAD+/SIRT1 reduction. Cell 157:882-896
Flannery PJ, Trushina E (2019) Mitochondrial dynamics and transport in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Cell Neurosci 98:109–120
Gong B, Chen F, Pan Y, Arrieta‐Cruz I, Yoshida Y, Haroutunian V, Pasinetti GM (2010) SCFFbx2‐E3‐ligase‐mediated degradation of BACE1 attenuates Alzheimer’s disease amyloidosis and improves synaptic function. Aging Cell 9:1018-1031
Gong B et al (2013) Nicotinamide riboside restores cognition through an upregulation of proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α regulated β-secretase 1 degradation and mitochondrial gene expression in Alzheimer's mouse models. Neurobiol Aging 34:1581-1588
Green KN, Steffan JS, Martinez-Coria H, Sun X, Schreiber SS, Thompson LM, LaFerla FM (2008) Nicotinamide restores cognition in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice via a mechanism involving sirtuin inhibition and selective reduction of Thr231-phosphotau. J Neurosci 28:11500-11510
Grozio A et al (2019) Slc12a8 is a nicotinamide mononucleotide transporter. Nat Metab 1:47-57
Guglielmotto M, Monteleone D, Giliberto L, Fornaro M, Borghi R, Tamagno E, Tabaton M (2011) Amyloid-β 42 activates the expression of BACE1 through the JNK pathway. J Alzheimers Dis 27:871-883
Hosseini L, Farokhi-Sisakht F, Badalzadeh R, Khabbaz A, Mahmoudi J, Sadigh-Eteghad S (2019) Nicotinamide mononucleotide and melatonin alleviate aging-induced cognitive impairment via modulation of mitochondrial function and apoptosis in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Neuroscience 423:29–37
Hou Y et al (2018) NAD+ supplementation normalizes key Alzheimer’s features and DNA damage responses in a new AD mouse model with introduced DNA repair deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci 115:E1876-E1885
Hu JP et al (2011) Valproate reduces tau phosphorylation via cyclin-dependent kinase 5 and glycogen synthase kinase 3 signaling pathways. Brain Res Bull 85:194-200
Kandimalla R, Manczak M, Yin X, Wang R, Reddy PH (2018) Hippocampal phosphorylated tau induced cognitive decline, dendritic spine loss and mitochondrial abnormalities in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Human Mol Gen 1;27(1):30-40
Kaur H, Patro I, Tikoo K, Sandhir R (2015) Curcumin attenuates inflammatory response and cognitive deficits in experimental model of chronic epilepsy. Neurochem Int 89:40–50
Killick R et al (2014) Clusterin regulates β-amyloid toxicity via Dickkopf-1-driven induction of the wnt–PCP–JNK pathway. Mol Psychiatry 19:88-98
Kim D et al (2007) SIRT1 deacetylase protects against neurodegeneration in models for Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. EMBO J 26:3169-3179
Kim EJ, Yang SJ (2017) Nicotinamide reduces amyloid precursor protein and presenilin 1 in brain tissues of amyloid beta-tail vein injected mice. Clin Nutr Res 6:130-135
Kim SH, Smith CJ, Van Eldik LJ (2004) Importance of MAPK pathways for microglial pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β production. Neurobiol Aging 25:431-439
Kwak YD, Wang R, Li JJ, Zhang YW, Xu H, Liao FF (2011) Differential regulation of BACE1 expression by oxidative and nitrosative signals. Mol Neurodegener 6:17
Lesné S et al (2006) A specific amyloid-β protein assembly in the brain impairs memory. Nature 440:352–357
Li N, Liu Y, Li W, Zhou L, Li Q, Wang X, He P (2016) A UPLC/MS-based metabolomics investigation of the protective effect of ginsenosides Rg1 and Rg2 in mice with Alzheimer's disease. J Ginseng Res 40:9-17
Liu D et al (2013) Nicotinamide forestalls pathology and cognitive decline in Alzheimer mice: evidence for improved neuronal bioenergetics and autophagy procession. Neurobiol Aging 34:1564–1580
Liu D, Pitta M, Mattson MP (2008) Preventing NAD+ depletion protects neurons against excitotoxicity: bioenergetic effects of mild mitochondrial uncoupling and caloric restriction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1147:275
Long AN, Owens K, Schlappal AE, Kristian T, Fishman PS, Schuh RA (2015) Effect of nicotinamide mononucleotide on brain mitochondrial respiratory deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease-relevant murine model. BMC Neurol 15:19
Luongo TS et al (2020) SLC25A51 is a mammalian mitochondrial NAD+ transporter. Nature 588:174-179
Manczak M, Kandimalla R, Yin X, Reddy PH (2018) Hippocampal mutant APP and amyloid beta-induced cognitive decline, dendritic spine loss, defective autophagy, mitophagy and mitochondrial abnormalities in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 27:1332-1342
Mandir AS et al (2000) NMDA but not non-NMDA excitotoxicity is mediated by Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. J Neurosci 20:8005-8011
Martire S, Mosca L, d’Erme M (2015) PARP-1 involvement in neurodegeneration: a focus on Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Mech Ageing Dev 146:53-64
Mehan S, Meena H, Sharma D, Sankhla R (2011) JNK: a stress-activated protein kinase therapeutic strategies and involvement in Alzheimer’s and various neurodegenerative abnormalities. J Mol Neurosci 43:376-390
Mericskay M (2016) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide homeostasis and signalling in heart disease: Pathophysiological implications and therapeutic potential. Arch Cardiovasc Dis 109:207–215
Minogue AM, Schmid AW, Fogarty MP, Moore AC, Campbell VA, Herron CE, Lynch MA (2003) Activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling cascade mediates the effect of amyloid-β on long term potentiation and cell death in hippocampus a role for Interleuken-1β? J Biol Chem 278:27971–27980
Onyango IG, Dennis J, Khan SM (2016) Mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease and the rationale for bioenergetics based therapies. Aging Dis 7:201
Popugaeva E, Pchitskaya E, Bezprozvanny I (2017) Dysregulation of neuronal calcium homeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease–A therapeutic opportunity? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 483:998–1004
Pugazhenthi S, Wang M, Pham S, Sze C-I, Eckman CB (2011) Downregulation of CREB expression in Alzheimer’s brain and in Aβ-treated rat hippocampal neurons Molecular neurodegeneration 6:60
Rahman M, Zhang Z, Mody AA, Su D-M, Das HK (2012) Intraperitoneal injection of JNK-specific inhibitor SP600125 inhibits the expression of presenilin-1 and Notch signaling in mouse brain without induction of apoptosis. Brain Res 1448:117-128
Sadigh-Eteghad S, Sabermarouf B, Majdi A, Talebi M, Farhoudi M, Mahmoudi J (2015) Amyloid-beta: a crucial factor in Alzheimer's disease. Med Princ Pract 24:1-10
Sclip A et al (2014) c-Jun N-terminal kinase has a key role in Alzheimer disease synaptic dysfunction in vivo. Cell Death Dis 5:e1019-e1019
Su S et al (2014) Sesamin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: involvement of Sirt1 and Mn-SOD pathway. Toxicol Lett 224:257-263
Sultana R, Butterfield DA (2010) Role of oxidative stress in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 19:341–353
Sultana R, Perluigi M, Butterfield DA (2006) Protein oxidation and lipid peroxidation in brain of subjects with Alzheimer’s disease: insights into mechanism of neurodegeneration from redox proteomics. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:2021–2037
Ton AMM et al (2020) Oxidative stress and dementia in alzheimer’s patients: Effects of synbiotic supplementation. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2020
Turunc Bayrakdar E, Uyanikgil Y, Kanit L, Koylu E, Yalcin A (2014) Nicotinamide treatment reduces the levels of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and PARP-1 activity in Aβ (1–42)-induced rat model of Alzheimer's disease. Free Radic Res 48:146-158
Vakilinezhad MA, Amini A, Javar HA, Zarandi BFBaB, Montaseri H, Dinarvand R (2018) Nicotinamide loaded functionalized solid lipid nanoparticles improves cognition in Alzheimer’s disease animal model by reducing Tau hyperphosphorylation DARU. J Pharm Sci 26:165–177
Vogel J, Anand V, Ludwig B, Nawoschik S, Dunlop J, Braithwaite S (2009) The JNK pathway amplifies and drives subcellular changes in tau phosphorylation. Neuropharmacology 57:539–550
Waetzig V et al (2005) c‐Jun N‐terminal kinases (JNKs) mediate pro‐inflammatory actions of microglia. Glia 50:235-246
Wang S, Colonna M (2019) Microglia in Alzheimer’s disease: a target for immunotherapy. J Leukoc Biol 106:219–227
Wang W et al (2017) Inhibition of mitochondrial fragmentation protects against Alzheimer’s disease in rodent model. Hum Mol Genet 26:4118–4131
Wang X, Hu X, Yang Y, Takata T, Sakurai T (2015) Systemic pyruvate administration markedly reduces neuronal death and cognitive impairment in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 271:145–154
Wang X, Hu X, Yang Y, Takata T, Sakurai T (2016) Nicotinamide mononucleotide protects against β-amyloid oligomer-induced cognitive impairment and neuronal death. Brain Res 15;1643:1-9
Wang X, Su B, Lee HG, Li X, Perry G, Smith MA, Zhu X (2009) Impaired balance of mitochondrial fission and fusion in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 29:9090–9103
Wei CC et al (2017) NAD replenishment with nicotinamide mononucleotide protects blood–brain barrier integrity and attenuates delayed tissue plasminogen activator‐induced haemorrhagic transformation after cerebral ischaemia. Br J Pharmacol 174:3823-3836
Wilkinson BL, Landreth GE (2006) The microglial NADPH oxidase complex as a source of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 3:30
Xie C, Soeda Y, Shinzaki Y, In Y, Tomoo K, Ihara Y, Miyasaka T (2015) Identification of key amino acids responsible for the distinct aggregation properties of microtubule‐associated protein 2 and tau. J Neurochem 135:19-26
Xie X, Gao Y, Zeng M, Wang Y, Wei T-F, Lu Y-B, Zhang W-P (2019) Nicotinamide ribose ameliorates cognitive impairment of aged and Alzheimer’s disease model mice. Metab Brain Dis 34:353–366
Yao Z, Yang W, Gao Z, Jia P (2017) Nicotinamide mononucleotide inhibits JNK activation to reverse Alzheimer disease. Neurosci Lett 647:133–140
Ying W (2008) NAD+/NADH and NADP+/NADPH in cellular functions and cell death: regulation and biological consequences. Antioxid Redox Signal 10:179-206
Yoon SO et al (2012) JNK3 perpetuates metabolic stress induced by Aβ peptides. Neuron 75:824-837
Zhang TT, Li W, Meng G, Wang P, Liao W (2016) Strategies for transporting nanoparticles across the blood–brain barrier. Biomater Sci 4:219-229
Zhu X, Perry G, Smith MA, Wang X (2013) Abnormal mitochondrial dynamics in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 33:S253–S262
Zhu X, Raina AK, Rottkamp CA, Aliev G, Perry G, Boux H, Smith MA (2001) Activation and redistribution of c-jun N-terminal kinase/stress activated protein kinase in degenerating neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 76:435–441
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LH, JM, and SS-E designed the project. FP and HS-P performed the literature review and extracted data. LH and S S-E wrote the manuscript. S S-E supervised the work. JM and S S-E edited the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for Publication
The authors give the publisher permission to publish the work.
Competing Interests
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini, L., Mahmoudi, J., Pashazadeh, F. et al. Protective Effects of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide and Related Precursors in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies. J Mol Neurosci 71, 1425–1435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01842-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01842-6