Abstract
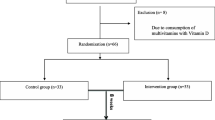
The aims of this study are to compare serum ubiquinone levels in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) with healthy controls and to investigate the correlation between ubiquinone levels of children with ADHD and their ADHD symptoms. Twenty-seven children who are 6–12 years old age with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder having clinically normal intelligence and 23 children with clinically normal intelligence and no psychiatric disorder of similar age and sex who referred to Ankara University School of Medicine Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry were included in this study. All children were diagnosed by same researcher using the Semi-Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Scale for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia Interview for School Children-Now and for the Life-Long Version (K-SADS-PL). Parents and teachers of the children completed the Conners Parent Rating Scale Revised Long Form (CPRS-LF) and Conners Teacher Rating Scale Revised Long Form (CTRS-LF). There were no statistically significant differences regarding the age, gender, and sociodemographic data of the groups. Serum ubiquinone levels of the ADHD group were significantly lower than the control group. We did not find any correlation between ubiquinone levels and clinical values. Since ubiquinone levels are lower in children with ADHD compared with controls, we suggest that decreased antioxidant levels may play a role in ADHD pathogenesis by disrupting oxidative balance.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Abdelraouf ER, Kilany A, Hashish AF, Gebril OH, Helal SI, Hasan HM, Nashaat NH (2018) Investigating the influence of ubiquinone blood level on the abilities of children with specific learning disorder. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatr Neurosurg 54(1):39
APA-American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5. American Psychiatric Association Publishing, Arlington
Bulut M, Selek S, Gergerlioglu H, Savas H, Yilmaz H, Yuce M (2007) Malondialdehyde levels in adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Psychiatry Neurosci 32(6):435–438
Dvoráková M, Sivonová M, Trebatická J, Skodácek I, Waczuliková I, Muchová J (2006) The effect of polyphenolic extract from pine bark, pycnogenol on the level of glutathione in children suffering from attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Redox Rep 11(4):163–172
Gvozdjáková A, Kucharská J, Ostatníková D, Babinská K, Nakládal D, Crane FL (2014) Ubiquinol improves symptoms in children with autism. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2014
Ikonomıdou C, Kaındl AM (2011) Neuronal death and oxidative stress in the developing brain. Antioxid Redox Signal 14(8):1535–1550
Imagawa M (1989) Low erythrocyte coenzyme Q10 level in schizophrenic patients. Jpn J Psy- chiatry Neurol 43(2):143–145
Joseph N, Zhang-James Y, Perl A, Faraone SV (2015) Oxidative stress and ADHD: a meta-analysis. J Atten Disord 19(11):915–924
Kandemir H, Abuhandan M, Aksoy N, Savik E, Kaya C (2013) Oxidative imbalance in child and adolescent patients with obsessive compulsive disorder. J Psychiatr Res 47(11):1831–1834
Kodydková J, Vávrová L, Zeman M, Jirák R, Macášek J, Staňková B, Žák A (2009) Antioxidative enzymes and increased oxidative stress in depressive women. Clin Biochem 42(13–14):1368–1374
Mehrpooya M, Yasrebifar F, Haghighi M, Mohammadi Y, Jahangard L (2018) Evaluating the effect of coenzyme Q10 augmentation on treatment of bipolar depression: a double-blind controlled clinical trial. J Clin Psychopharmacol 38:460–466
Millichap JG (2008) Etiologic classification of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 121(2):E358–E365
Mousavinejad E, Ghaffari MA, Riahi F, Hajmohammadi M, Tiznobeyk Z, Mousavinejad M (2018) Coenzyme Q10 supplementation reduces oxidative stress and decreases antioxidant enzyme activity in children with autism spectrum disorders. Psychiatry Res 265:62–69
Oztop D, Altun H, Baskol G, Ozsoy S (2012) Oxidative stress in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Clin Biochem 45(10–11):745–748
Polanczyk G, De Lima MS, Horta BL, Biederman J, Rohde LA (2007) The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: a systematic review and metaregression analysis. Am J Psychiatry 164(6):942–948
Polanczyk G, Rohde LA (2007) Epidemiology of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder across the lifespan. Curr Opin Psychiatry 20(4):386–392
Rose S, Melnyk S, Pavliv O, Bai S, Nick TG, Frye RE (2012) Evidence of oxidative damage and inflammation associated with low glutathione redox status in the autism brain. Transl Psychiatry 2:134
Selek S, Savas HA, Gergerlioglu HS, Bulut M, Yilmaz HR (2008) Oxidative imbalance in adult attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychol 79(2):256–259
Sezen H, Kandemir H, Savik E, Basmacı Kandemir S, Kilicaslan F, Bilinc H, Aksoy N (2016) Increased oxidative stress in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Redox Rep 21(6):248–253
Spahis S, Vanasse M, Bélanger SA, Ghadirian P, Grenier E, Levy E (2008) Lipid profile, fatty acid composition and pro and antioxidant status in pediatric patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 79(1–2):47–53
Tripp G, Wickens JR (2009) Neurobiology of ADHD. Neuropharmacology 57(7–8):579–589
Tsaluchidu S, Cocchi M, Tonello L, Puri BK (2008) Fatty acids and oxidative stress in psychiatric disorders. Bmc Psychiatry 8(Suppl. 1):S5
Tsang AH, Chung KK (2009) Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress in Parkinson's Disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1792.7: 643–650
Yen GC, Hsıeh CL (1997) Antioxidant effects of dopamine and related compounds. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61(10):1646–1649
Young J, McKinney SB, Ross BM, Wahle KW, Boyle SP (2007) Biomarkers of oxidative stress in schizophrenic and control subjects. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 76(2):73–85
Yumru M, Savaş H, Kalenderoglu A, Bulut M, Çelik H, Erel Ö (2009) Oxidative imbalance in bipolar disorder subtypes: a comparative study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:1070–1074
Funding
The research budget was met by the researcher and no financial support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept: Y.S.K., D.B.Ö., B.G.K.; design: Y.S.K., Ö.D., S.E., B.G.K.; supervision: Y.S.K., D.B.Ö., S.E., B.G.K.; funding: Y.S.K., Ö.D., S.E., B.G.K.; materials: Y.S.K., Ö.D.; data collection and/or processing: Y.S.K., Ö.D., B.G.K.; analysis and/or interpretation: Y.S.K., B.G.K.; literature review: Y.S.K; writing: Y.S.K., B.G.K.; critical review: Y.S.K., Ö.D., S.E., D.B.Ö., B.G.K.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The study was approved by the Ankara University Faculty of Medicine Ethics Board (14.10.2019 decision no: I5—179-19).
Consent for Publication
Allowed for publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karagöz, Y., Doğan, Ö., Elgün, S. et al. Ubiquinone Levels as a Marker of Antioxidant System in Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. J Mol Neurosci 71, 2173–2178 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01763-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01763-w