Abstract
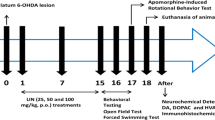
Previous evidence has shown a link between neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson's disease (PD), and melatonin. The data in the literature about the impact of the hormone under different experimental PD conditions are quite controversial, and its effect on memory impairment in the disease is very poorly explored. The current research was aimed at investigating the role of melatonin pretreatment on memory and motor behavior in healthy rats and those with the partial 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) model of PD. All rodents were pretreated with melatonin (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneally) for 5 days. At 24 h and 7 days after the first treatment for healthy rats, and at the second and third week post-lesion for those with PD, the animals were tested behaviorally (apomorphine-induced rotations, rotarod, and passive avoidance tests). The neurochemical levels of dopamine (DA), acetylcholine (ACh), noradrenaline (NA), and serotonin (Sero) in the brain were also determined. The results showed that in healthy animals, melatonin pretreatment had amnestic and motor-suppressive effects and did not change the levels of measured brain neurotransmitters. In animals with PD, melatonin pretreatment exerted a neuroprotective effect, manifested as a significantly decreased number of apomorphine-induced rotations, reduced number of falls in the rotarod test, and improved memory performance. The brain DA and ACh concentrations in the same animals were restored to the control levels, and those of NA and Sero did not change. Our results demonstrate a beneficial effect of melatonin on memory and motor disturbance in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This manuscript has not been submitted to any other journal for simultaneous consideration and has never been published elsewhere in any form or language.
References
Adi N, Mash C, Ali Y, Singer C, Shehadeh L, Papapetropoulos S (2010) Melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptor expression in Parkinson’s disease. Med Sci Monitor 16:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3472032
Aguiar LMV, Vasconcelos SMM, Sousa FCF, Viana GSB (2002) Melatonin reverses neurochemical alterations inducedby 6-OHDA in rat striatum. Life Sci 70(9):1041–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-3205(01)01480-1
Araghi-Nikham M, Lane M, Watson RR (1999) Modification of physical movement in old C57BL/6 mice by DHEA and melatonin supplementation (44404). PSEMB 221:193–197. https://doi.org/10.3181/00379727-221-44404
Arushanyan EB, Ovanesov KB (1989) Peculiarities of psychotropic effect of melatonin depending on dose and time of day. Farmakol Toksikol 52:33–37 https://europepmc.org/article/med/2625143
Bassani TB, Gradowski RW, Zaminelli T et al (2014) Neuroprotective and antidepressant-like effects of melatonin in a rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease model in rats. Brain Res 1593:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.09.068
Bertaina-Anglade V, Drieu-La-Rochelle C, MocaЁer E, Seguin L (2011) Memory facilitating effects of agomelatine in the novelobject recognition memory paradigm in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 98(4):511–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2011.02.015
Blandini F, Levandis G, Bazzini E, Nappi G, Armentero MT (2007) Time-course of nigrostriatal damage, basal ganglia metabolic changes and behavioural alterations following intrastriatal injection of 6-hydroxydopamine in the rat: new clues from an old model. Eur J Neurosci 25:397–405. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05285.x
Blum D, Torch S, Lambeng N, Nissou M, Sadoul BAL, R, Verna JM, (2001) Molecular pathways involvedin the neurotoxicity of 6-OHDA, dopamine and MPTP:contribution to the apoptotic theory in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 65:135–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-0082(01)00003-x
Bondy SC, Campbell A (2020) Melatonin and Regulation of Immune Function: Impact on Numerous Diseases. Curr Aging Sci Jul 11. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874609813666200711153223. Online ahead of print
Bonito-Oliva A, Masini D, Fisone G (2014) A mouse model of non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: focus on pharmacological interventions targeting affective dysfunctions. Front Behav Neurosci 8(290):1-12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00290
Borah A et al (2009) Melatonin inhibits 6-hydroxydopamine production in the brain to protect against experimental parkinsonism in rodents. J Pineal Res 47:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00713.x
Bordet R, Devos D, Brique S et al (2003) Study of circadian melatonin secretion pattern at different stages of Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 26:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002826-200303000-00005
Bove J, Prou D, Perier C, Przedborski S (2005) Toxin-Induced Models of Parkinson’s Disease. J Am Soc Exp NeuroTherapeutics 2:484–494. https://doi.org/10.1602/neurorx.2.3.484
Braak H, Braak E (1996) Development of Alzheimer-related neurofibrillary changes in the neocortex inversely recapitulates cortical myelogenesis. Acta Neuropathol 92:197–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010050508
Bradbury AJ, Kelly ME, Smith JA (1985) Melatonin action in the midbrain can regulate forebrain dopamine function both behaviorally and biochemically. Brown GM, Wainwright SD (ed). The pineal gland: endocrine aspects, Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 327–332
Burton S, Daya S, Potgeiter B (1991) Melatonin modulates apomorphine-induced rotational behaviour. Experientia 47:466–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01959946
Cadet JL, Brannock C (1998) Free radicals and the pathobiology of brain dopamine systems. Neurochem Int 32:117–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0197-0186(97)00031-4
Capitelli C, Sereniki A, Lima MM, Reksidler AB, Tufik S, Vital MA (2008) Melatonin attenuates tyrosine hydroxylase loss and hypolocomotion in MPTP-lesioned rats. Eur J Pharmacol 594(1–3):101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.07.022 (Epub 2008 Jul 17)
Chang KH, Chen CM (2020) The Role of Oxidative Stress in Parkinson’s Disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 9(7):E597. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9070597
Chaudhuri KR, Schapira AH (2009) Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: dopaminergic pathophysiology and treatment. Lancet Neurol 8(5):464–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70068-7
Chuang JL, Lin MT (1994) Pharmacological effects of melatonin treatment on both locomotor activity and brain serotonin release in rats. J Pineal Res 17(1):11–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079x.1994.tb00107.x
Clinical trials.gov (2020) https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04287543
Dabbeni-Sala F, Di Santo S, Franceschini D, Skaper SD, Giusti P (2001) Melatonin protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in rats: a role for mitochondrial complex I activity. FASEB J 15(1):164–170. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.00-0129com
Datieva VK, Rosinskaya AV, Levin OS (2013) The use of melatonin in the treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome andcircadian rhythm disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr 113(7):77–81
Ding W, Ding L-J, Li F-F, Han Y, Mu L (2015) Neurodegeneration and cognition in Parkinson’s disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19(12):2275–2281
Dowling G, Mastick J, Colling E, Carter J, Singer C, Aminoff M (2005) Melatonin for sleep disturbances in Parkinson’s disease. Sleep Med 6(5):459–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2005.04.004
Fertl E, Auff E, Doppelbauer A, Waldhauser F (1991) Circadian secretion pattern of melatonin in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 3(1):41–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02251135
García J, Remires D, Leiva A, González R (2000) Depletion of brain glutathione potentiates the effect of 6-hydroxydopamine in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. J Mol Neurosci 14(3):147–153. https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:14:3:147
Garfinkle D, Laudon M, Dudai S, Karasic A, Nof D, Zisapel N (1995) Drug-induced sleep disturbances in the elderly: effects of melatonin therapy. Sleep Res 24:521
Gupta Y, Gupta M, Kohli K (2003) Neuroprotective role of melatonin in oxidative stress vulnerable brain Indian. J Physiol Pharmacol 47:373–386
Gutierrez-Valdez AL, Anaya-Martґınez V, Ordo˜nez-Librado JL, et al (2012) Effect of chronic L-dopa or melatonin treatments after dopamine deafferentation in rats: dyskinesia, motor performance, and cytological analysis. ISRN Neurology 360379:16. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/360379
Haimov I, Lavie P, Laudon M, Herer P, Vigder C, Zisapel N (1995) Melatonin replacement therapy of elderly insomniacs. Sleep 18(7):598–603. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/18.7.598
Hardeland R (2016) Melatonin and Synthetic Melatoninergic Agonists in Psychiatric and Age-associated Disorders: Successful and Unsuccessful Approaches. Curr Pharm Des 22(8):1086–1101. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612822666151214125543
Hershey LA, Coleman-Jackson R (2019) Pharmacological Management of Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Drugs Aging 36(4):309–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-018-00636-7
Hughes R, Sack R, Lewy A (1998) The role of melatonin and circadian phase in age-related sleep-maintenance insomnia: assessment in a clinical trial of melatonin replacement. Sleep 21(1):52–66. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/21.1.52
Jacobowitz D, Richardson J (1978) Method for the rapid determination of norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin in the same brain region. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 8:515–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-3057(78)90380-5
Jarvik M, Kopp R (1967) An improved one-trial passive avoidance learning situation. Psychol Rep 21(1):221–224. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.1967.21.1.221
Kirik D, Rosenblad C, Bjorklund A (1998) Characterization of behavioral and neurodegenerative changes following partial lesions of the nigrostriatal dopamine system induced by intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine in the rat. Exp Neurol 152:259–277. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.1998.6848
Кoзлoв BA, Уфyкoвa AЮ, Toлмaчeв AC (1999) Cпocoб oпpeдeлeния aцeтилxoлинa Пpиopитeт, №2159433 https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=37858322
Lees AJ, Hardy J, Revesz T (2009) Parkinson’s disease. The Lancet 373(9680):2055–2066. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60492-X
Lee CS, Sauer H, Bjorklund A (1996) Dopaminergic neuronal degeneration and motor impairments following axon terminal lesion by instrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine in the rat. Neuroscience 72:641–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(95)00571-4
Ma J, Shaw VE, Mitrofanis J (2009) Does melatonin help save dopaminergic cells inMPTP-treated mice? Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 15(4):307–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.07.008
Macchi M, Bruce JN (2004) Human pineal physiology and functional significance of melatonin. Front Neuroendocrinol 25:177–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2004.08.001
Mack JM, Schamne MG, Sampaio TB, Pértile RAN, Fernandes PA, Markus RP, Prediger RD (2016) Melatoninergic system in Parkinson’s Disease from neuroprotection to the management of motor and nonmotor symptoms. Oxid Med Cell Longev, Article ID 3472032:31. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3472032
Mayo J, Sainz R, Tan D, Antolín I, Rodríguez C, Reiter R (2005) Melatonin and Parkinson’s disease. Endocrine 27:169–178. https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:27:2:169
Mayo JC, Sainz RM, Uria H, Antolin I, Esteban MM, Rodriguez C (1998) Melatonin prevents apoptosis induced by 6-hydroxydopamine in neuronal cells: implications for Parkinson’s disease. J Pineal Res 24:179–192. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079x.1998.tb00531.x
Medeiros CAM, Carvalhedo de Bruin PF, Lopes LA, Magalh˜aes MS, Seabra M, Sales de BruinVM (2007) Effect of exogenousmelatonin on sleep andmotor dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. A randomized, double blind, placebocontrolled study. J Neurol 254(4):459–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0390-x
Mijatović S, Savić-Radojević A, Plješa-Ercegovac M, Simić T, Nicoletti F, Maksimović-Ivanić D (2020) The Double-Faced Role of Nitric Oxide and Reactive Oxygen Species in Solid Tumors. Antioxidants (Basel) 9(5):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050374
Minneman KP, Lynck H, Wurtman RJ (1976) Relationship between environmental light intensity and retinal-mediated suppression of rat pineal serotonin-N-acetyltransferase. Life Sci 15:1791–1796. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(74)90180-5
Nicola SM, Surmeier J, Malenka RC (2000) Dopaminergic modulation of neuronalexcitability in the striatum and nucleus accumbens. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:185–215. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.23.1.185
Paus S, Schmitz-Hübsch T, Wüllner U, Vogel A, Klockgether T, Abele M (2007) Bright light therapy in Parkinson’s disease: a pilot study. Mov Disord 22:1495–1498. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21542
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press New York NY USA, ISBN: 9780125476126.https://www.elsevier.com/books/the-rat-brain-in-stereotaxic-coordinates/paxinos/978-0-12-374121-9
Przedborski S, Levivier M, Jiang H, Ferreira M, Jackson-Lewis V, Donaldson D et al (1995) Dose-dependent lesions of the dopaminergic nigrostriatal pathway induced by intrastriatal injection of 6-hydroxydopamine. Neuroscience 67:631–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(95)00066-r
Ran D, Xie B, Gan Z, Sun X, Gu H, Yang J (2018) Melatonin attenuates hLRRK2-induced long-term memory deficit in a Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Biomed Rep 9(3):221–226. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2018.1125
Reis M, Davis RH, Sideman MB, Plichta ES (1963) Pineal gland and spontaneous activity in rats. J Endocrinol 28:127–128. https://doi.org/10.1677/joe.0.0280127
Rodriguez M, Sosa J, Hernandez G, Mas M (1984) Pineal indoles and testosterone affect exploratory activity of male rats. Experientia 40:397–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01952573
Roghani M, Niknam A, Jalali-Nadoushan M, Kiasalari Z, Khalili M, Baluchnejadmojarad T (2010) Oral pelargonidin exerts dose-dependent neuroprotection in 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of hemi-parkinsonism. Brain Res Bull 82:279–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2010.06.004
Sharma R, McMillan CR, Tenn CC, Niles LP (2006) Physiological neuroprotection by melatonin in a 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1068(1):230–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2005.10.084
Shapiro R, Glick S, Camarota N (1987) A two-population model of rat rotational behavior: effects of unilateral nigrostriatal 6-hydroxydopamine on striatal neurochemistry and amphetamine-induced rotation. Brain Res 426:323–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(87)90885-7
Sauer H, Oertel WH (1994) Progressive degeneration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons following intrastriatal terminal lesions with 6-hydroxydopamine: a combined retrograde tracing and immunocytochemical study in the rat. Neuroscience 59:401–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(94)90605-x
Schwarting R, Huston J (1997) Behavioral and neurochemical dynamic of meso-striatal dopamine lesions. Neurotoxicology 18:689–708
Singh S, Ahmed R, Sagar RK, Krishana B (2006) Neuroprotection of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons by melatonin in hemiparkinsonium rat. Indian J Med Res 124:419–426
Singhal N, Srivastava G, Patel D, Jain S, Singh M (2011) Melatonin or silymarin reduces maneb- and paraquat-induced Parkinson’s disease phenotype in the mouse. J Pineal Res 50:97–109. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00819.x
Srinivasan V, Pandi-Perumal SR, Maestroni GJ, Esquifino AI, Hardeland R, Cardinali DP (2005) Role of melatonin in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurotox Res 7:293–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033887
Tomás-Zapico C, Coto-Montes A (2007) Melatonin as antioxidant under pathological processes. Recent Patents Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov 1:63–82. https://doi.org/10.2174/187221407779814561
Yildirim FB, Ozsoy O, Tanriover G et al (2014) Mechanism of the beneficial effect of melatonin in experimental Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 79:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2014.09.005
Von Gall C, Weaver DR, Moek J, Jilg A, Stehle JH, Korf HW (2005) Melatonin plays a crucial role in the regulation of rhythmic clock gene expression in the mouse pars tuberalis. Ann NY Acad Sci 1040:508–511. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1327.105
Videnovic A, Noble C, Reid KJ et al (2014) Circadian melatonin rhythm and excessive daytime sleepiness in Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurology 71(4):463–469. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.6239
Wang LM, Suthana NA, Chaudhury D, Weaver DR, Colwell CS (2005) Melatonin inhibits hippocampal long-termpotentiation. Eur J Neurosci 22(9):2231–2237. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04408.x
Willis GL, Armstrong SM (1999) A therapeutic role for melatonin antagonism in experimental models of Parkinson’s disease. Physiol Behav 66:785–795. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9384(99)00023-2
Willis GL (2008) Intraocular microinjections repair experimental Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1217:119–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.03.083
Willis GL, Robertson AD (2004) Recovery of experimental Parkinson’s disease with the melatonin analogues ML-23 and S-20928 in a chronic, bilateral 6-OHDA model: a new mechanism involving antagonism of the melatonin receptor. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 79:413–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2004.08.011
Wongprayoon P, Govitrapong P (2020) Melatonin receptor as a drug target for neuroprotection. Curr Mol Pharmacol. Apr 21. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874467213666200421160835. Online ahead of print
Zaitone SA, Hammad LN, Farag NE (2013) Antioxidant potential of melatonin enhances the response to L-dopa in 1-methyl 4-phenyl 1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-parkinson mice. Pharmacol. Rep 65(5):1213–1226. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1734-1140(13)71479-8
Acknowledgements
Proper acknowledgements to other works is given.
Funding
This study was made possible with the financial support of the Institute of Neurobiology at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization—Lyubka Tancheva, Luciano Saso; Funding acquisition—Reni Kalfin; Investigation—Maria Lazarova, Lyubka Tancheva, Miroslava Stefanova, Diamara Uzunova; Validation—Atanas G. Atanasov; Resources—Reni Kalfin; Visualization—Maria Lazarova; Writing of original draft—Lyubka Tancheva, Maria Lazarova; Writing of review & editing—Reni Kalfin.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests
Ethical Approval
All experiments with laboratory animals have been performed strictly according to the national regulations and European Communities Council Directive (86/609/EEC) and the “Principles of laboratory animal care” (NIH publication No. 85–23) concerning the protection of animals used for scientific and experimental purposes.
Consent to Participate and Publication
All authors declare consent to participate and consent for publication
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tancheva, L., Lazarova, M., Saso, L. et al. Beneficial Effect of Melatonin on Motor and Memory Disturbances in 6-OHDA-Lesioned Rats. J Mol Neurosci 71, 702–712 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01760-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01760-z