Abstract
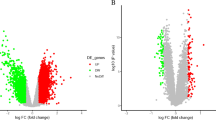
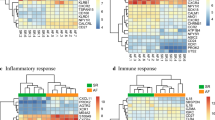
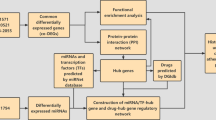
Atherosclerotic plaque instability is a major cause of ischemic stroke. Researchers must develop novel strategies for the detection and treatment of unstable atherosclerotic plaque (UAP)-related stroke. We aimed to identify potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets of UAP-related stroke. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of UAP, ischemic stroke and smoking were identified by microarray analyses from the Gene Expression Omnibus. Gene Ontology (GO) and pathway functional enrichment analyses of DEGs were performed to analyze plaque destabilization and ischemic stroke physiopathology. An integrative analysis of UAP, ischemic stroke and smoking DEGs and functional annotations was performed to identify the underlying physiopathology and hub genes in UAP-related stroke and the relationship with smoking. Online search databases were applied to confirm hub gene biofunctions and their relationships with atherosclerosis and cerebrovascular diseases. Following integrative analysis, 18 co-DEGs of UAP and ischemic stroke, including 17 upregulated and one downregulated, were identified. Inflammation, immunity, extracellular matrix degradation, blood coagulation, apoptosis and nerve degeneration were the primary physiopathological processes in UAP-related stroke. Hub genes included MMP9, ITGAM, CCR1, NCF2 and CD163, among which MMP9 and ITGAM were top 10 genes for both UAP and stroke. Smoking may upregulate MMP9, NCF2, C5AR1 and ANPEP to accelerate plaque destabilization and UAP-related stroke. MMP9, ITGAM, CCR1, NCF2, CD163, hsa-miR-3123 and hsa-miR-144-3p are potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of UAP-related stroke. MMP9 and ITGAM are potential therapeutic targets of UAP-related stroke, which will contribute to the development of novel management strategies.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The data used in this study were downloaded from the GEO database. The data used to support the findings of this study are available from corresponding websites upon request.
References
Abu-Saleh N, Aviram M, Hayek T (2016) Aqueous or Lipid Components of Atherosclerotic Lesion Increase Macrophage Oxidation and Lipid Accumulation. Life Sci 154:1–14
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam J, Bartel DP (2015) Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 4:e05005
Banerjee C, Chimowitz MI (2017) Stroke Caused by Atherosclerosis of the Major Intracranial Arteries. Circ Res 120(3):502–513
Barrett T, Troup DB, Wilhite SE et al (2007) NCBI GEO: Mining Tens of Millions of Expression Profiles--Database and Tools Update. Nucleic Acids Res 35(Database):D760–D765
Badimon L, Vilahur G (2014) Thrombosis Formation on Atherosclerotic Lesions and Plaque Rupture. J Intern Med 276(6):618–632
Carbon S, Ireland A, Mungall CJ et al (2009) AmiGO: Online Access to Ontology and Annotation Data. Bioinformatics 25(2):288–289
Chaturvedi M, Kaczmarek L (2014) Mmp-9 Inhibition: A Therapeutic Strategy in Ischemic Stroke. Mol Neurobiol 49(1):563–573
Chen YH, Wang XW (2020) miRDB: An Online Database for Prediction of Functional microRNA Targets. Nucleic Acids Res 48(D1):D127–D131
Cotto KC, Wagner AH, Feng YY et al (2018) DGIdb 3.0: A Redesign and Expansion of the Drug-Gene Interaction Database. Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D1068–D1073
Chen LL, Yang QH, Ding R, Liu D, Chen ZJ (2018) Carotid Thickness and Atherosclerotic Plaque Stability, Serum Inflammation, Serum MMP-2 and MMP-9 Were Associated With Acute Cerebral Infarction. Exp Ther Med 16(6):5253–5257
Davis AP, Grondin CJ, Johnson RJ et al (2019) The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database: Update 2019. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D948–D954
Elkind MSV (2010) Infectious Burden: A New Risk Factor and Treatment Target for Atherosclerosis. Infect Disord Drug Targets 10(2):84–90
Fuster V, Badimon L, Badimon JJ, Chesebro JH (1992) The Pathogenesis of Coronary Artery Disease and the Acute Coronary Syndromes (2). N Engl J Med 326(5):310–318
Finn AV, Nakano M, Polavarapu R et al (2012) Hemoglobin Directs Macrophage Differentiation and Prevents Foam Cell Formation in Human Atherosclerotic Plaques. J Am Coll Cardiol 59(2):166–177
Guo L, Akahori H, Harari E et al (2018) CD163+ Macrophages Promote Angiogenesis and Vascular Permeability Accompanied by Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest 128(3):1106–1124
Gorur A, Celik A, Yildirim DD, Yildirim DD, Gundes A, Tamer L (2019) Investigation of Possible Effects of microRNAs Involved in Regulation of Lipid Metabolism in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Mol Biol Rep 46(1):909–920
Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM et al (2004) Bioconductor: Open Software Development for Computational Biology and Bioinformatics. Genome Biol 5(10):R80
Grubb RL Jr, Derdeyn CP, Fritsch SM et al (1998) Importance of Hemodynamic Factors in the Prognosis of Symptomatic Carotid Occlusion. JAMA 280(12):1055–1060
Galis ZS, Khatri JJ (2002) Matrix Metalloproteinases in Vascular Remodeling and Atherogenesis: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Circ Res 90(3):251–262
Gorelick PB, Wong KS, Bae HJ, Pandey DK (2008) Large Artery Intracranial Occlusive Disease: A Large Worldwide Burden but a Relatively Neglected Frontier. Stroke 39(8):2396–2399
Hazen SL (2010) Neutrophils, Hypercholesterolemia, and Atherogenesis. Circulation 122(18):1786–1788
Han H, Cho JW, Lee S et al (2018) TRRUST v2: An Expanded Reference Database of Human and Mouse Transcriptional Regulatory Interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D380–D386
Hermus L, Tielliu IFJ, Wallis de Vries BM, van den Dungen JJAM, Zeebregts CJ (2010) Imaging the Vulnerable Carotid Artery Plaque. Acta Chir Belg 110(2):159–164
Johnson JL (2017) Metalloproteinases in Atherosclerosis. Eur J Pharmacol 816:93–106
Karagkouni D, Paraskevopoulou MD, Chatzopoulos S et al (2018) DIANA-TarBase v8: A Decade-Long Collection of Experimentally Supported miRNA-gene Interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D239–D245
Lijnen HR (2002) Extracellular Proteolysis in the Development and Progression of Atherosclerosis. Biochem Soc Trans 30(2):163–167
Linton MF, Babaev VR, Huang J, Linton EF, Tao H, Yancey PG (2016) Macrophage Apoptosis and Efferocytosis in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Circ J 80(11):2259–2268
Lindsberg PJ, Grau AJ (2003) Inflammation and Infections as Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 34(10):2518–2532
Libby P, Loscalzo JL, Ridker PM et al (2018) Inflammation, Immunity, and Infection in Atherothrombosis. JACC Review Topic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol 72(17):2071–2081
Liapis CD, Kakisis JD, Kostakis AG (2001) Carotid Stenosis: Factors Affecting Symptomatology. Stroke 32(12):2782–2786
Mazighi M, Labreuche J, Gongora-Rivera F, Duyckaerts C, Hauw JJ, Amarenco P (2008) Autopsy Prevalence of Intracranial Atherosclerosis in Patients With Fatal Stroke. Stroke 39(4):1142–1147
Mazzone A, Mazzucchelli I, Fossati G et al (1996) Iloprost Effects on Phagocytes in Patients Suffering From Ischaemic Diseases: In Vivo Evidence for Down-Regulation of Alpha M Beta 2 Integrin. Eur J Clin Invest 26(10):860–866
Offner H, Subramanian S, Parker SM, Afentoulis ME, Vandenbark AA, Hurn PD (2006) Experimental Stroke Induces Massive, Rapid Activation of the Peripheral Immune System. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26(5):654–665
Powers WJ (1991) Cerebral Hemodynamics in Ischemic Cerebrovascular Disease. Ann Neurol 29(3):231–240
Potteaux S, Combadière C, Esposito B et al (2005) Chemokine Receptor CCR1 Disruption in Bone Marrow Cells Enhances Atherosclerotic Lesion Development and Inflammation in Mice. Mol Med 11(1–12):16–20
Paraskevopoulou MD, Georgakilas G, Kostoulas N et al (2013) DIANA-microT Web Server v5.0: Service Integration Into miRNA Functional Analysis Workflows. Nucleic Acids Res 41(Web Server issue):W169–W173
Rombouts M, Ammi R, Brussel IV et al (2016) Linking CD11b (+) Dendritic Cells and Natural Killer T Cells to Plaque Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Mediators Inflamm 2016:6467375
Rao NM, Capri J, Cohn W et al (2017) Peptide Composition of Stroke Causing Emboli Correlate With Serum Markers of Atherosclerosis and Inflammation. Front Neurol 8:427
Rothwell PM, Gibson R, Warlow CP (2000) Interrelation Between Plaque Surface Morphology and Degree of Stenosis on Carotid Angiograms and the Risk of Ischemic Stroke in Patients With Symptomatic Carotid Stenosis. On Behalf of the European Carotid Surgery Trialists' Collaborative Group. Stroke 31(3):615–621
Su EJ, Cao CZ, Fredriksson L et al (2017) Microglial-mediated PDGF-CC Activation Increases Cerebrovascular Permeability During Ischemic Stroke. Acta Neuropathol 134(4):585–604
Sluimer JC, Daemen MJ (2009) Novel Concepts in Atherogenesis: Angiogenesis and Hypoxia in Atherosclerosis. J Pathol 218(1):7–29
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S et al (2015) STRING v10: Protein-Protein Interaction Networks, Integrated Over the Tree of Life. Nucleic Acids Res 43(Database issue):D447–D452
Safian RD, Gelbfish JS, Erny RE, Schnitt SJ, Schmidt DA, Baim DS (1990) Coronary Atherectomy. Clinical, Angiographic, and Histological Findings and Observations Regarding Potential Mechanisms. Circulation 82(1):69–79
Shibata K, Hashimoto T, Nobe K, Hasumi K (2011) Neuroprotective Mechanisms of SMTP-7 in Cerebral Infarction Model in Mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 384(1):103–108
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O et al (2003) Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504
Sata M, Saiura A, Kunisato A et al (2002) Hematopoietic Stem Cells Differentiate Into Vascular Cells That Participate in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Nat Med 8(4):403–409
Tokar T, Pastrello C, Rossos AEM et al (2018) mirDIP 4.1-integrative Database of Human microRNA Target Predictions. Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D360–D370
Tuttolomondo A, Raimondo DD, Pecoraro R, Arnao V, Pinto A, Licata G (2012) Atherosclerosis as an Inflammatory Disease. Curr Pharm Des 18(28):4266–4288
Turner RJ, Sharp FR (2016) Implications of MMP9 for Blood Brain Barrier Disruption and Hemorrhagic Transformation Following Ischemic Stroke. Front Cell Neurosci 10:56
Vlachos IS, Zagganas K, Paraskevopoulou MD et al (2015) DIANA-miRPath v3.0: Deciphering microRNA Function With Experimental Support. Nucleic Acids Res 43(W1):W460–W466
Wolf D, Ley K (2019) Immunity and Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Circ Res 124(2):315–327
Zirlik A, Maier C, Gerdes N et al (2007) CD40 Ligand Mediates Inflammation Independently of CD40 by Interaction With Mac-1. Circulation 115(12):1571–1580
Zheng LK, Xiong Y, Liu JF et al (2019) MMP-9-Related microRNAs as Prognostic Markers for Hemorrhagic Transformation in Cardioembolic Stroke Patients. Front Neurol 10:945
Zhou YY, Zhou B, Pache L et al (2019) Metascape Provides a Biologist-Oriented Resource for the Analysis of Systems-Level Datasets. Nat Commun 10(1):1523
Acknowledgments
This study used the GEO database as a data source. The interpretation and reporting of these data are the sole responsibility of the authors. The authors acknowledge the efforts of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) for the creation and distribution of the GEO database.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shaojiong Zhou and Shuo Liu analyzed and interpreted the data. Xiaoqiang Liu participated in the study. Shaojiong Zhou and Shuo Liu wrote the manuscript. Shaojiong Zhou and Xiaoqiang Liu conceived and designed the study. Weiduan Zhuang supervised the study and provided financial support. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Code Availability
The code that supports the findings of this study is available on request from the corresponding author.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Material 1
Gene Ontology term enrichment analyses of UAP-DEGs, ischemic stroke-DEGs and smoking-DEGs. (XLSX 24 kb)
Supplementary Material 2
Pathways enrichment analyses of UAP-DEGs, ischemic stroke-DEGs and smoking-DEGs. (XLSX 51 kb)
Supplementary Material 3
Functional enrichment analyses of co-DEGs of UAP and ischemic stroke. (XLSX 16 kb)
Supplementary Material 4
Gene Ontology Consortium annotations of hub genes of UAP-related stroke. (XLSX 20 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, S., Liu, S., Liu, X. et al. Bioinformatics Gene Analysis of Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Unstable Atherosclerotic Plaque-Related Stroke. J Mol Neurosci 71, 1031–1045 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01725-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01725-2