Abstract
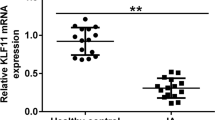
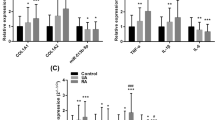
The proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) are involved in the pathogenesis of intracranial aneurysm (IA) formation and rupture. Interleukin enhancer binding factor 2 (ILF2) is known as the nuclear factor of activated T cells and regulates cell growth. This study was aimed to explore the effects of ILF2 on IA progression. Human brain VSMCs (hBVSMCs) were transfected with pCDNA3.1(+), pCDNA3.1(+)-ILF2, siRNA-negative control, and siRNA-ILF2. The transfection efficiency was then evaluated by determining ILF2 expression. The cell viability and apoptosis were determined using Cell Counting Kit-8 and Annexin V-FITC cell apoptosis assay kit, respectively. Real-time quantification PCR (RT-qPCR) was applied to measure the expression levels of apoptosis-related and inflammation-related genes. Finally, western blot was used to detect the expression level of Fas cell surface death receptor 95 (CD95) and Caspase 8. Overexpression of ILF2 could significantly increase cell viability and decrease cell apoptosis (P < 0.05), while knock-down of ILF2 showed opposite trends for hBVSMCs on cell viability and apoptosis (P < 0.05). RT-qPCR results showed that ILF2 knock-down downregulated the expression levels of BCL2 apoptosis regulator (BCL2), transcriptional regulator Myc-like (c-Myc), and caspase 1 (ICE) whereas upregulated the expression levels of CD95, p21, p53, and interleukin-13 (IL-13). Additionally, the protein expression levels of CD95 and Caspase 8 were significantly decreased after ILF2 overexpression while were significantly increased after ILF2 knock-down (P < 0.05). ILF2 knock-down may inhibit cell viability and promote cell apoptosis of hBVSMCs by regulating the expression levels of apoptosis-related genes and suppressing inflammatory response.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The dataset used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on a reasonable request.
References
Baudino TA et al (2002) c-Myc is essential for vasculogenesis and angiogenesis during development and tumor progression. Genes Dev 16:2530–2543. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1024602
Braddock M, Hanania NA, Sharafkhaneh A, Colice G, Carlsson M (2018) Potential risks related to modulating interleukin-13 and interleukin-4 signalling: a systematic review. Drug Saf 41:489–509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40264-017-0636-9
Chalouhi N et al (2012) Biology of intracranial aneurysms: role of inflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:1659–1676. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2012.84
Cheng S et al. (2016) Expression and critical role of interleukin enhancer binding factor 2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081373
Dang CV (2012) MYC on the path to cancer. Cell 149:22–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.003
Du H, Le Y, Sun F, Li K, Xu Y (2019) ILF2 directly binds and stabilizes CREB to stimulate malignant phenotypes of liver cancer cells. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 2019:1575031. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1575031
Eom YH, Kim HS, Lee A, Song BJ, Chae BJ (2016) BCL2 as a subtype-specific prognostic marker for breast cancer. J Breast Cancer 19:252–260. https://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2016.19.3.252
Fan XJ, Zhao HD, Yu G, Zhong XL, Yao H, Yang QD (2015) Role of inflammatory responses in the pathogenesis of human cerebral aneurysm. Genet Mol Res 14:9062–9070. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.August.7.15
Frosen J (2014) Smooth muscle cells and the formation, degeneration, and rupture of saccular intracranial aneurysm wall--a review of current pathophysiological knowledge. Transl Stroke Res 5:347–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-014-0340-3
Gartel AL (2009) p21(WAF1/CIP1) and cancer: a shifting paradigm? Biofactors 35:161–164. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.26
Huang Q et al (2014) Expression of NF45 correlates with malignant grade in gliomas and plays a pivotal role in tumor growth. Tumour Biol 35:10149–10157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2310-5
Ikedo T et al (2017) Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 inhibitor anagliptin prevents intracranial aneurysm growth by suppressing macrophage infiltration and activation. J Am Heart Assoc 6. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.116.004777
Jayaraman T et al (2005) Tumor necrosis factor alpha is a key modulator of inflammation in cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery 57:558–564; discussion 558-564. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000170439.89041.d6
Jin Z et al (2018) Interleukin enhancer binding factor 2 is a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer that also predicts neoadjuvant chemotherapy responses. Am J Transl Res 10:1677–1689
Krings T et al (2011) Intracranial aneurysms: from vessel wall pathology to therapeutic approach. Nat Rev Neurol 7:547–559. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2011.136
Lanzino G (2016) Modern management of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg Sci 60:21
Li MH et al (2013) Prevalence of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in Chinese adults aged 35 to 75 years: a cross-sectional study. Ann Intern Med 159:514–521. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-159-8-201310150-00004
Molchadsky A, Rivlin N, Brosh R, Rotter V, Sarig R (2010) p53 is balancing development, differentiation and de-differentiation to assure cancer prevention. Carcinogenesis 31:1501–1508. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgq101
Muller M et al (1998) p53 activates the CD95 (APO-1/Fas) gene in response to DNA damage by anticancer drugs. J Exp Med 188:2033–2045. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.188.11.2033
Naggara ON, Lecler A, Oppenheim C, Meder JF, Raymond J (2012) Endovascular treatment of intracranial unruptured aneurysms: a systematic review of the literature on safety with emphasis on subgroup analyses. Radiology 263:828–835. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12112114
Ni T et al (2015) Upregulated expression of ILF2 in non-small cell lung cancer is associated with tumor cell proliferation and poor prognosis. J Mol Histol 46:325–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-015-9624-5
Penn DL, Witte SR, Komotar RJ, Sander Connolly E Jr (2014) The role of vascular remodeling and inflammation in the pathogenesis of intracranial aneurysms. J Clin Neurosci 21:28–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2013.07.004
Peter ME, Hadji A, Murmann AE, Brockway S, Putzbach W, Pattanayak A, Ceppi P (2015) The role of CD95 and CD95 ligand in cancer. Cell Death Differ 22:885–886. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2015.25
Ruan C, Long H, Sun H, He M, Yang K, Zhang H, Mao B (2015) Endovascular coiling vs. surgical clipping for unruptured intracranial aneurysm: a meta-analysis. Br J Neurosurg 29:485–492. https://doi.org/10.3109/02688697.2015.1023771
Sahoo S et al (2016) MEF2C-MYOCD and Leiomodin1 suppression by miRNA-214 promotes smooth muscle cell phenotype switching in pulmonary arterial hypertension. PLoS One 11:e0153780. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0153780
Shamanna RA, Hoque M, Pe’ery T, Mathews MB (2013) Induction of p53, p21 and apoptosis by silencing the NF90/NF45 complex in human papilloma virus-transformed cervical carcinoma cells. Oncogene 32:5176–5185. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.533
Sikdar S, Mukherjee A, Khuda-Bukhsh AR (2015) Anti-lung cancer potential of pure esteric-glycoside condurangogenin A against nonsmall-cell lung cancer cells in vitro via p21/p53 mediated cell cycle modulation and DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Pharmacogn Mag 11:S73–S85. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1296.157698
Song C et al (2019) HOXA10 induces BCL2 expression, inhibits apoptosis, and promotes cell proliferation in gastric cancer. Cancer Med 8:5651–5661. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2440
Starke RM et al (2014) Vascular smooth muscle cells in cerebral aneurysm pathogenesis. Transl Stroke Res 5:338–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-013-0290-1
Strange F, Gruter BE, Fandino J, Marbacher S (2020) Preclinical intracranial aneurysm models: a systematic review. Brain Sci 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10030134
Sun C et al (2015) Down-regulation of c-Met and Bcl2 by microRNA-206, activates apoptosis, and inhibits tumor cell proliferation, migration and colony formation. Oncotarget 6:25533–25574. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4575
Sun L et al (2017) MiR-29b downregulation induces phenotypic modulation of vascular smooth muscle cells: implication for intracranial aneurysm formation and progression to rupture. Cell Physiol Biochem 41:510–518. https://doi.org/10.1159/000456887
Wang L et al (2016) Novel extracellular and nuclear caspase-1 and inflammasomes propagate inflammation and regulate gene expression: a comprehensive database mining study. J Hematol Oncol 9:122. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-016-0351-5
Wang Y et al (2020) TRIM28 and TRIM27 are required for expressions of PDGFRbeta and contractile phenotypic genes by vascular smooth muscle cells. FASEB J. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201902828RR
Wei L, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Yang C, Guan H, Chen Y, Sun Z (2018a) Identification of key genes, transcription factors and microRNAs involved in intracranial aneurysm. Mol Med Rep 17:891–897. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7940
Wei L, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Yang C, Guan H, Jiang J, Sun Z (2018b) Integrated analysis of microarray data to identify the genes critical for the rupture of intracranial aneurysm. Oncol Lett 15:4951–4957. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.7935
Xu G, Ao R, Zhi Z, Jia J, Yu B (2019) miR-21 and miR-19b delivered by hMSC-derived EVs regulate the apoptosis and differentiation of neurons in patients with spinal cord injury. J Cell Physiol 234:10205–10217. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27690
Yagi K, Tada Y, Kitazato KT, Tamura T, Satomi J, Nagahiro S (2010) Ibudilast inhibits cerebral aneurysms by down-regulating inflammation-related molecules in the vascular wall of rats. Neurosurgery 66:551–559; discussion 559. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000365771.89576.77
Yin ZH, Jiang XW, Shi WB, Gui QL, Yu DF (2017) Expression and clinical significance of ILF2 in gastric cancer. Dis Markers 2017:4387081. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4387081
Zhang HF, Zhao MG, Liang GB, Yu CY, He W, Li ZQ, Gao X (2016) Dysregulation of CD4(+) T cell subsets in intracranial aneurysm. DNA Cell Biol 35:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2015.3105
Zhao M et al (2019) ILF2 cooperates with E2F1 to maintain mitochondrial homeostasis and promote small cell lung cancer progression. Cancer Biol Med 16:771–783. https://doi.org/10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2019.0050
Zhou JD et al (2019) BCL2 overexpression: clinical implication and biological insights in acute myeloid leukemia. Diagn Pathol 14:68. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-019-0841-1
Zou Y, Huang Y, Ma X (2019) Phenylhexyl isothiocyanate suppresses cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis via repairing mutant P53 in human myeloid leukemia M2 cells. Oncol Lett 18:3358–3366. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10620
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Pudong new area science and technology development fund (No. PKJ2018-Y04) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 22120190215).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Chunlong Zhong, Zhiyang Sun, Cheng Yang, and Liang Wei; Methodology: Cheng Yang and Liang Wei; Formal analysis and investigation: Guangxue Wang, Keqin Li, Yanfei Zhang, and Hongxin Guan; Writing—original draft preparation: Liang Wei and Cheng Yang; Writing—review and editing: Chunlong Zhong and Zhiyang Sun; Supervision: Chunlong Zhong and Zhiyang Sun. All authors have read and approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Liang Wei and Cheng Yang are co-first authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, L., Yang, C., Wang, G. et al. Interleukin Enhancer Binding Factor 2 Regulates Cell Viability and Apoptosis of Human Brain Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. J Mol Neurosci 71, 225–233 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01638-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01638-0