Abstract
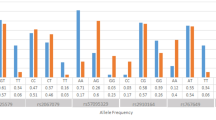
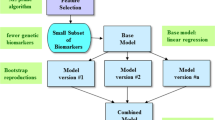
The artificial neural network (ANN) is a sort of machine learning method which has been used in determination of risk of human disorders. In the current investigation, we have created an ANN and trained it based on the genetic data of 401 multiple sclerosis (MS) patients and 390 healthy subjects. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within ANRIL (rs1333045, rs1333048, rs4977574 and rs10757278), EVI5 (rs6680578, rs10735781 and rs11810217), ACE (rs4359 and rs1799752), MALAT1 (rs619586 and rs3200401), GAS5 (rs2067079 and rs6790), H19 (rs2839698 and rs217727), NINJ2 (rs11833579 and rs3809263), GRM7 (rs6782011 and rs779867), VLA4 (rs1143676), CBLB (rs12487066) and VEGFA (rs3025039 and rs2071559) had been genotyped in all individuals. We used “Keras” package for generation and training the ANN model. The k-folds cross-validation strategy was applied to confirm model generalization and overfit prevention. The locally interpretable model-agnostic explanation (LIME) was applied to explain model predictions at the data sample level. The TT genotype of the GAS5 rs2067079 had the most protective effect against MS, while the DD genotype of the ACE rs1799752 was the most prominent risk genotype. The accuracy, sensitivity and specificity values of the model were 64.73%, 64.95% and 64.49% respectively. The ROC AUC value was 69.67%. The current study is a preliminary study to appraise the application of ANN for prediction of risk of MS based on genomic data.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cotsapas C, Mitrovic M (2018) Genome-wide association studies of multiple sclerosis. Clin Transl Immunol 7:e1018
Eftekhar B, Mohammad K, Ardebili HE, Ghodsi M, Ketabchi E (2005) Comparison of artificial neural network and logistic regression models for prediction of mortality in head trauma based on initial clinical data. BMC Med Inform Decis Making 5:1–8
Eftekharian MM, Noroozi R, Sayad A, Sarrafzadeh S, Toghi M, Azimi T, Komaki A, Mazdeh M, Inoko H, Taheri M, Mirfakhraie R (2016) RAR-related orphan receptor A (RORA): a new susceptibility gene for multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 369:259–262
Eftekharian MM, Noroozi R, Komaki A, Mazdeh M, Ghafouri-Fard S, Taheri M (2019) MALAT1 genomic variants and risk of multiple sclerosis. Immunol Investig 48(5):549–554
Garatachea N, Marin PJ, Lucia A (2013) The ACE DD genotype and D-allele are associated with exceptional longevity: a meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev 12:1079–1087
Garcia-Martin E, Pablo LE, Herrero R, Ara JR, Martin J, Larrosa JM, Polo V, Garcia-Feijoo J, Fernandez J (2013) Neural networks to identify multiple sclerosis with optical coherence tomography. Acta Ophthalmol 91:e628–e634
Grossi E, Veggo F, Narzisi A, Compare A, Muratori F (2016) Pregnancy risk factors in autism: a pilot study with artificial neural networks. Pediatr Res 79:339–347
Guo Z, Wang YH, Zhao Y, Jin Y, An L, Wu B, Liu ZQ, Chen XP, Zhou HH, Wang H, Zhang W (2017) Genetic polymorphisms of long non-coding RNA GAS5 predict platinum-based concurrent chemoradiotherapy response in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Oncotarget 8:62286–62297
Hoppenbrouwers IA, Aulchenko YS, Ebers GC, Ramagopalan SV, Oostra BA, VAN Duijn CM, Hintzen RQ (2008) EVI5 is a risk gene for multiple sclerosis. Genes Immun 9:334–337
Huang WJ, Chen WW, Zhang X (2017) Multiple sclerosis: pathology, diagnosis and treatments. Exp Ther Med 13:3163–3166
Iwai N, Ohmichi N, Nakamura Y, Kinoshita M (1994) DD genotype of the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene is a risk factor for left ventricular hypertrophy. Circulation 90:2622–2628
Khastavaneh H, Ebrahimpour-Komleh H (2017) Neural network-based learning kernel for automatic segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions on magnetic resonance images. J Biomed Phys Eng 7:155–162
Mahdi Eftekharian M, Norrozi R, Komaki A, Mazdeh M, Taheri M, Ghafouri-Fard S (2019) MALAT1 Genomic Variants and Risk of Multiple Sclerosis. Immunol Invest 48(5):549–554
Mazdeh M, Ghafouri-Fard S, Noroozi R, Sayad A, Khani M, Taheri M, Davood Omrani M (2017a) Ecotropic Viral Integration Site 5 (EVI5) variants are associated with multiple sclerosis in Iranian population. Mult Scler Relat Disord 18:15–19
Mazdeh M, Noroozi R, Gharesouran J, Sayad A, Komaki A, Eftekharian MM, Habibi M, Toghi M, Taheri M (2017b) The importance of VEGF-KDR signaling pathway genes should not be ignored when the risk of developing multiple sclerosis is taken into consideration. J Mol Neurosci 62:73–78
Mazdeh M, Noroozi R, Komaki A, Azari I, Ghafouri-Fard S, Taheri M (2019a) A single nucleotide polymorphism in the metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 gene is associated with multiple sclerosis in Iranian population. Mult Scler Relat Disord 28:189–192
Mazdeh M, Noroozi R, Komaki A, Taheri M, Ghafouri-Fard S (2019b) Single nucleotide polymorphisms of lncRNA H19 are not associated with risk of multiple sclerosis in Iranian population. Meta Gene 21:100592
Noroozi R, Azari I, Taheri M, Omrani MD, Ghafouri-Fard S (2019) A single nucleotide polymorphism within Ninjurin 2 is associated with risk of multiple sclerosis. Metab Brain Dis 34:1415–1419
Pontremoli R, Sofia A, Tirotta A, Ravera M, Nicolella C, Viazzi F, Bezante GP, Borgia L, Bobola N, Ravazzolo R, Sacchi G, Deferrari G (1996) The deletion polymorphism of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene is associated with target organ damage in essential hypertension. J Am Soc Nephrol 7:2550–2558
Rezazadeh M, Gharesouran J, Moradi M, Noroozi R, Omrani MD, Taheri M, Ghafouri-Fard S (2018) Association study of ANRIL genetic variants and multiple sclerosis. J Mol Neurosci 65:54–59
Ribeiro MT, Singh S, Guestrin C (2016) Why should i trust you? Explaining the predictions of any classifier. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 1135–1144. https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939778
Shi H-Y, Tsai J-T, Ho W-H, Wang S-C, Chen I-T, Lee K-T (2012a) Comparison of artificial neural network and logistic regression models for predicting in-hospital survival after hepatocellular carcinoma surgery. 2012 Proceedings of SICE Annual Conference (SICE). IEEE, Akita, pp 1262–1265
Shi H, Lu Y, Du J, Du W, Ye X, Yu X, Ma J, Cheng J, Gao Y, Cao Y, Zhou L, Li Q (2012b) Application of back propagation artificial neural network on genetic variants in adiponectin ADIPOQ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma, and retinoid X receptor-alpha genes and type 2 diabetes risk in a Chinese Han population. Diabetes Technol Ther 14:293–300
Taheri M, Noroozi R, Sayad A, Ghafouri-Fard S, Omrani MD (2018a) Association study of Casitas B-lineage lymphoma proto-oncogene B (CBLB) gene variant and multiple sclerosis. Acta Medica Mediterranea 34(1):87–90
Taheri M, Noroozi R, Sayad A, Ghafouri-Fard S, Omrani MD (2018b) Integrin subunit alpha 4 (ITGA4) variant is associated with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis in an Iranian population. Acta Medica Mediterranea 34(1):83–86
Taheri M, Noroozi R, Sadeghpour S, Omrnai MD, Ghafouri-Fard S (2020) The rs4759314 SNP within HOTAIR lncRNA is associated with risk of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord 40:101986
Tomida S, Hanai T, Koma N, Suzuki Y, Kobayashi T, Honda H (2002) Artificial neural network predictive model for allergic disease using single nucleotide polymorphisms data. J Biosci Bioeng 93:470–478
Tomita Y, Tomida S, Hasegawa Y, Suzuki Y, Shirakawa T, Kobayashi T, Honda H (2004) Artificial neural network approach for selection of susceptible single nucleotide polymorphisms and construction of prediction model on childhood allergic asthma. BMC Bioinforma 5
Valverde S, Cabezas M, Roura E, Gonzalez-Villa S, Pareto D, Vilanova JC, Ramio-Torrenta L, Rovira A, Oliver A, Llado X (2017) Improving automated multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation with a cascaded 3D convolutional neural network approach. Neuroimage 155:159–168
Yaeghmaie R, Ghafouri-Fard S, Noroozi R, Tavakoli F, Taheri M, Ayatollahi SA (2018) Polymorphisms in the angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) gene are associated with multiple sclerosis risk and response to interferon-beta treatment. Int Immunopharmacol 64:275–279
Zhou X, Han X, Wittfeldt A, Sun J, Liu C, Wang X, Gan L-M, Cao H, Liang Z (2016) Long non-coding RNA ANRIL regulates inflammatory responses as a novel component of NF-κB pathway. RNA Biol 13:98–108
Funding
The present article is financially supported by Research Department of the School of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MT designed and supervised the study. HMR and AD performed the data analyses. SGF and MDO wrote and revised the manuscript. All authors read the manuscript drafts, contributed edits and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Ethical approval was obtained from the ethical committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (IR.SBMU.MSP.REC.1397.1022).
Consent of Publication
Not applicable.
Availability of Data and Materials
The analysed data sets generated during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghafouri-Fard, S., Taheri, M., Omrani, M.D. et al. Application of Artificial Neural Network for Prediction of Risk of Multiple Sclerosis Based on Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Genotypes. J Mol Neurosci 70, 1081–1087 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01514-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01514-x