Abstract
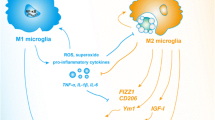
The purpose of the study was studying the influence of different NOD agonists on the morphological phenotype of primary murine microglia and to examine their influence on characteristic cytokines. Primary CD11b-positive cells were isolated from the brain of neonatal mice. The microglial phenotype of the cells was examined by ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule (Iba)1 staining. After14 days in culture, these cells were stimulated by iE-DAP, L18-MDP, or M-TriDAP as NOD1, NOD2, and NOD1/2 agonists, respectively. The cellular morphology was recorded and compared to the phenotype of cells cultured in medium alone or after LPS stimulation. The cells developed a specific phenotype only after treatment with the NOD2 agonist L18-MDP. These cells were characterized by straight extensions carrying tiny spikes and had a high ramification index. This was in sharp contrast to all other treatments, which always resulted in an amoeboid phenotype typically shown by activated microglia in vivo and by cultured microglia in vitro. The staining intensity of IL-6 and TNF-α did not reveal any clear difference independent of the NOD agonist treatment. In contrast, an increased staining intensity was observed for IL-10 after L18-MDP treatment. The NOD2 agonist L18-MDP induced a morphologically distinct phenotype characterized by microspike-decorated dendritiform extensions and a high degree of ramification in primary murine microglia. Increased ramification index and elevated staining intensity of anti-inflammatory IL-10 as hallmarks suggest that a M2-like phenotype of microglia was induced.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
abd-el-Basset E, Fedoroff S (1995) Effect of bacterial wall lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on morphology, motility, and cytoskeletal organization of microglia in cultures. J Neurosci Res 41(2):222–237. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.490410210
Aslanidis A, Karlstetter M, Scholz R, Fauser S, Neumann H, Fried C, Pietsch M, Langmann T (2015) Activated microglia/macrophage whey acidic protein (AMWAP) inhibits NF kappaB signaling and induces a neuroprotective phenotype in microglia. J Neuroinflammation 12:77. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-015-0296-6
Bauer D, Wasmuth S, Hermans P, Hennig M, Meller K, Meller D et al (2007) On the influence of neutrophils in corneas with necrotizing HSV-1 keratitis following amniotic membrane transplantation. Exp Eye Res 85(3):335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2007.05.009
Ben-Nun A, Yossefi S, Lehmann D (1993) Protection against autoimmune disease by bacterial agents. II. PPD and pertussis toxin as proteins active in protecting mice against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol 23(3):689–696. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.1830230318
Burm SM, Zuiderwijk-Sick EA, t jong AE, van der Putten C, Veth J, Kondova I et al (2015) Inflammasome-induced IL-1beta secretion in microglia is characterized by delayed kinetics and is only partially dependent on inflammatory caspases. J Neurosci 35(2):678–687. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2510-14.2015
Butovsky O, Jedrychowski MP, Moore CS, Cialic R, Lanser AJ, Gabriely G, Koeglsperger T, Dake B, Wu PM, Doykan CE, Fanek Z, Liu L, Chen Z, Rothstein JD, Ransohoff RM, Gygi SP, Antel JP, Weiner HL (2014) Identification of a unique TGF-beta-dependent molecular and functional signature in microglia. Nat Neurosci 17(1):131–143. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3599
Caldeira C, Oliveira AF, Cunha C, Vaz AR, Falcao AS, Fernandes A et al (2014) Microglia change from a reactive to an age-like phenotype with the time in culture. Front Cell Neurosci 8:152. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2014.00152
Caldeira C, Cunha C, Vaz AR, Falcao AS, Barateiro A, Seixas E et al (2017) Key aging-associated alterations in primary microglia response to Beta-amyloid stimulation. Front Aging Neurosci 9:277. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00277
Cardona AE, Huang D, Sasse ME, Ransohoff RM (2006) Isolation of murine microglial cells for RNA analysis or flow cytometry. Nat Protoc 1(4):1947–1951. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.327
Chamaillard M, Girardin SE, Viala J, Philpott DJ (2003) Nods, Nalps and Naip: intracellular regulators of bacterial-induced inflammation. Cell Microbiol 5(9):581–592. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1462-5822.2003.00304.x
Chen M, Zhao J, Luo C, Pandi SP, Penalva RG, Fitzgerald DC, Xu H (2012) Para-inflammation-mediated retinal recruitment of bone marrow-derived myeloid cells following whole-body irradiation is CCL2 dependent. Glia 60(5):833–842. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22315
Chhor V, Le Charpentier T, Lebon S, Ore MV, Celador IL, Josserand J et al (2013) Characterization of phenotype markers and neuronotoxic potential of polarised primary microglia in vitro. Brain Behav Immun 32:70–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2013.02.005
Chinnery HR, Naranjo Golborne C, Leong CM, Chen W, Forrester JV, McMenamin PG (2015) Retinal microglial activation following topical application of intracellular toll-like receptor ligands. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56(12):7377–7386. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.15-17587
Clausen BH, Lambertsen KL, Babcock AA, Holm TH, Dagnaes-Hansen F, Finsen B (2008) Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha are expressed by different subsets of microglia and macrophages after ischemic stroke in mice. J Neuroinflammation 5:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-5-46
Coffman RL, Sher A, Seder RA (2010) Vaccine adjuvants: putting innate immunity to work. Immunity 33(4):492–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2010.10.002
Coscas G, De Benedetto U, Coscas F, Li Calzi CI, Vismara S, Roudot-Thoraval F et al (2013) Hyperreflective dots: a new spectral-domain optical coherence tomography entity for follow-up and prognosis in exudative age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmologica 229(1):32–37. https://doi.org/10.1159/000342159
de Gracia P, Gallego BI, Rojas B, Ramirez AI, de Hoz R, Salazar JJ et al (2015) Automatic counting of microglial cells in healthy and glaucomatous mouse retinas. PLoS One 10(11):e0143278. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143278
Devarajan G, Chen M, Muckersie E, Xu H (2014) Culture and characterization of microglia from the adult murine retina. ScientificWorldJournal 2014:894368. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/894368
Ellouz F, Adam A, Ciorbaru R, Lederer E (1974) Minimal structural requirements for adjuvant activity of bacterial peptidoglycan derivatives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 59(4):1317–1325. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291x(74)90458-6
Frank MG, Baratta MV, Sprunger DB, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2007) Microglia serve as a neuroimmune substrate for stress-induced potentiation of CNS pro-inflammatory cytokine responses. Brain Behav Immun 21(1):47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2006.03.005
Ginhoux F, Prinz M (2015) Origin of microglia: current concepts and past controversies. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7(8):a020537. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a020537
Ginhoux F, Greter M, Leboeuf M, Nandi S, See P, Gokhan S, Mehler MF, Conway SJ, Ng LG, Stanley ER, Samokhvalov IM, Merad M (2010) Fate mapping analysis reveals that adult microglia derive from primitive macrophages. Science 330(6005):841–845. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1194637
Graeber MB, Streit WJ (2010) Microglia: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol 119(1):89–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0622-0
Grigsby JG, Cardona SM, Pouw CE, Muniz A, Mendiola AS, Tsin AT, Allen DM, Cardona AE (2014) The role of microglia in diabetic retinopathy. J Ophthalmol 2014:705783. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/705783
Hanisch UK, Kettenmann H (2007) Microglia: active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat Neurosci 10(11):1387–1394. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1997
Herber DL, Maloney JL, Roth LM, Freeman MJ, Morgan D, Gordon MN (2006) Diverse microglial responses after intrahippocampal administration of lipopolysaccharide. Glia 53(4):382–391. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.20272
Holt LM, Olsen ML (2016) Novel applications of magnetic cell sorting to analyze cell-type specific gene and protein expression in the central nervous system. PLoS One 11(2):e0150290. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150290
Huang H, Parlier R, Shen JK, Lutty GA, Vinores SA (2013) VEGF receptor blockade markedly reduces retinal microglia/macrophage infiltration into laser-induced CNV. PLoS One 8(8):e71808. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071808
Jin WN, Shi SX, Li Z, Li M, Wood K, Gonzales RJ, Liu Q (2017) Depletion of microglia exacerbates postischemic inflammation and brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 37(6):2224–2236. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X17694185
Jung DY, Lee H, Jung BY, Ock J, Lee MS, Lee WH et al (2005) TLR4, but not TLR2, signals autoregulatory apoptosis of cultured microglia: a critical role of IFN-beta as a decision maker. J Immunol 174(10):6467–6476. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.174.10.6467
Karlstetter M, Walczak Y, Weigelt K, Ebert S, Van den Brulle J, Schwer H et al (2010) The novel activated microglia/macrophage WAP domain protein, AMWAP, acts as a counter-regulator of proinflammatory response. J Immunol 185(6):3379–3390. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0903300
Kettenmann H, Hanisch UK, Noda M, Verkhratsky A (2011) Physiology of microglia. Physiol Rev 91(2):461–553. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00011.2010
Kierdorf K, Erny D, Goldmann T, Sander V, Schulz C, Perdiguero EG, Wieghofer P, Heinrich A, Riemke P, Hölscher C, Müller DN, Luckow B, Brocker T, Debowski K, Fritz G, Opdenakker G, Diefenbach A, Biber K, Heikenwalder M, Geissmann F, Rosenbauer F, Prinz M (2013) Microglia emerge from erythromyeloid precursors via Pu.1- and Irf8-dependent pathways. Nat Neurosci 16(3):273–280. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3318
Laffer B, Bauer D, Wasmuth S, Busch M, Jalilvand TV, Thanos S, Meyer Zu Hörste G, Loser K, Langmann T, Heiligenhaus A, Kasper M (2019) Loss of IL-10 promotes differentiation of microglia to a M1 phenotype. Front Cell Neurosci 13:430. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00430
Lai AY, Todd KG (2008) Differential regulation of trophic and proinflammatory microglial effectors is dependent on severity of neuronal injury. Glia 56(3):259–270. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.20610
Lee JE, Liang KJ, Fariss RN, Wong WT (2008) Ex vivo dynamic imaging of retinal microglia using time-lapse confocal microscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49(9):4169–4176
Lessard AJ, LeBel M, Egarnes B, Prefontaine P, Theriault P, Droit A et al (2017) Triggering of NOD2 receptor converts inflammatory Ly6C(high) into Ly6C(low) monocytes with patrolling properties. Cell Rep 20(8):1830–1843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.08.009
Liu X, Chauhan VS, Young AB, Marriott I (2010) NOD2 mediates inflammatory responses of primary murine glia to Streptococcus pneumoniae. Glia 58(7):839–847. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.20968
Luckoff A, Scholz R, Sennlaub F, Xu H, Langmann T (2017) Comprehensive analysis of mouse retinal mononuclear phagocytes. Nat Protoc 12(6):1136–1150. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2017.032
Macho Fernandez E, Valenti V, Rockel C, Hermann C, Pot B, Boneca IG, Grangette C (2011) Anti-inflammatory capacity of selected lactobacilli in experimental colitis is driven by NOD2-mediated recognition of a specific peptidoglycan-derived muropeptide. Gut 60(8):1050–1059. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2010.232918
Matsumoto K, Ogawa H, Nagase O, Kusama T, Azuma I (1981) Stimulation of nonspecific host resistance to infection induced by muramyldipeptides. Microbiol Immunol 25(10):1047–1058. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00111.x
Matsumoto K, Otani T, Une T, Osada Y, Ogawa H, Azuma I (1983) Stimulation of nonspecific resistance to infection induced by muramyl dipeptide analogs substituted in the gamma-carboxyl group and evaluation of N alpha-muramyl dipeptide-N epsilon-stearoyllysine. Infect Immun 39(3):1029–1040.PMCID: PMC348060
Mildner A, Huang H, Radke J, Stenzel W, Priller J (2017) P2Y12 receptor is expressed on human microglia under physiological conditions throughout development and is sensitive to neuroinflammatory diseases. Glia 65(2):375–387. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23097
Mizutani M, Pino PA, Saederup N, Charo IF, Ransohoff RM, Cardona AE (2012) The fractalkine receptor but not CCR2 is present on microglia from embryonic development throughout adulthood. J Immunol 188(1):29–36. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1100421
Philpott DJ, Sorbara MT, Robertson SJ, Croitoru K, Girardin SE (2014) NOD proteins: regulators of inflammation in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 14(1):9–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3565
Ransohoff RM, Perry VH (2009) Microglial physiology: unique stimuli, specialized responses. Annu Rev Immunol 27:119–145. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132528
Rao NA, Kimoto T, Zamir E, Giri R, Wang R, Ito S, Pararajasegaram G, Read RW, Wu GS (2003) Pathogenic role of retinal microglia in experimental uveoretinitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44(1):22–31. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.02-0199
Rosenzweig HL, Kawaguchi T, Martin TM, Planck SR, Davey MP, Rosenbaum JT (2009) Nucleotide oligomerization domain-2 (NOD2)-induced uveitis: dependence on IFN-gamma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50(4):1739–1745. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.08-2756
Rosenzweig HL, Galster K, Vance EE, Ensign-Lewis J, Nunez G, Davey MP, Rosenbaum JT (2011) NOD2 deficiency results in increased susceptibility to peptidoglycan-induced uveitis in mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52(7):4106–4112. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.10-6263
Ross RJ, Zhou M, Shen D, Fariss RN, Ding X, Bojanowski CM, Tuo J, Chan CC (2008) Immunological protein expression profile in Ccl2/Cx3cr1 deficient mice with lesions similar to age-related macular degeneration. Exp Eye Res 86(4):675–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2008.01.014
Sakai K, Hasebe R, Takahashi Y, Song CH, Suzuki A, Yamasaki T, Horiuchi M (2013) Absence of CD14 delays progression of prion diseases accompanied by increased microglial activation. J Virol 87(24):13433–13445. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02072-13
Shafique M, Wilschut J, de Haan A (2012) Induction of mucosal and systemic immunity against respiratory syncytial virus by inactivated virus supplemented with TLR9 and NOD2 ligands. Vaccine 30(3):597–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.11.054
Sterka D Jr, Marriott I (2006) Characterization of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD) protein expression in primary murine microglia. J Neuroimmunol 179(1–2):65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.06.009
Tadmouri A, Champagnat J, Morin-Surun MP (2014) Activation of microglia and astrocytes in the nucleus tractus solitarius during ventilatory acclimatization to 10% hypoxia in unanesthetized mice. J Neurosci Res 92(5):627–633. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23336
Wohl SG, Schmeer CW, Friese T, Witte OW, Isenmann S (2011) In situ dividing and phagocytosing retinal microglia express nestin, vimentin, and NG2 in vivo. PLoS One 6(8):e22408. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0022408
Wolf SA, Boddeke HW, Kettenmann H (2017) Microglia in physiology and disease. Annu Rev Physiol 79:619–643. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034406
Yanai A, Laver CR, Gregory-Evans CY, Liu RR, Gregory-Evans K (2015) Enhanced functional integration of human photoreceptor precursors into human and rodent retina in an ex vivo retinal explant model system. Tissue Eng Part A 21(11–12):1763–1771. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEA.2014.0669
Acknowledgements
Sincere thanks are extended to associate professor Gerd Meyer zu Hörste, Department of Neurology at University Clinic Münster. He kindly provided the access to the fluorescence microscope that was used for this study.
Funding
The study was supported by FOR 2240 (Lymph) angiogenesis and cellular immunity in inflammatory diseases of the eye.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Parts of the data were presented as a poster at the 115th German Ophthalmological Society (DOG) Congress 2017 (P-Fr07-10)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wasmuth, S., Jalilvand, T.V., Laffer, B. et al. Phenotypic Differences in Primary Murine Microglia Treated with NOD1, NOD2, and NOD1/2 Agonists. J Mol Neurosci 70, 600–609 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01466-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01466-x