Abstract
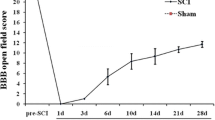
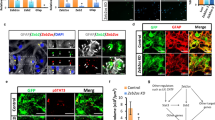
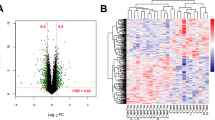
Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be lethal; however, the precise mechanisms underlying healing are unclear, limiting the development of effective therapies. In this study, the molecular mechanisms involved in SCI were investigated. Clinical peripheral blood samples from normal individuals and patients with incomplete SCI (ISCI) and complete SCI (CSCI) were analyzed by RNA-Seq. The expression levels of EPHA4, CDK16, BAD, MAP2 Normal 2, EGR, and RHOB differed significantly between the SCI group and normal individuals, and these results were verified by q-PCR. A gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis showed that differentially expressed genes were mostly enriched for the neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway. We verified the expression of neurotrophic factors and found that they were all expressed most highly in the SCI group. The results of this study demonstrate that neurotrophic factors are highly expressed after SCI and the neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway may be involved in the initiation of nerve system regeneration.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angerer IC, Hecker M, Koczan D, Roch L, Friess J, Ruge A, Fitzner B, Boxberger N, Schroder I, Flechtner K, Thiesen HJ, Winkelmann A, Meister S, Zettl UK (2018) Transcriptome profiling of peripheral blood immune cell populations in multiple sclerosis patients before and during treatment with a sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator. CNS Neurosci Ther. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12793
Blesch A, Tuszynski MH (2003) Cellular GDNF delivery promotes growth of motor and dorsal column sensory axons after partial and complete spinal cord transections and induces remyelination. J Comp Neurol 467:403–417. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.10934
Blesch A, Tuszynski MH (2007) Transient growth factor delivery sustains regenerated axons after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 27:10535–10545. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1903-07.2007
Cohen G, Ettinger K, Lecht S, Lelkes P, ILazarovici P (2014) Transcriptional down-regulation of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors by nerve growth factor (NGF) in PC12 cells. J Mol Neurosci 54:574–585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0388-2
Crown ED, Gwak YS, Ye Z, Johnson K, MHulsebosch CE (2008) Activation of p38 MAP kinase is involved in central neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 213:257–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.05.025
Devivo MJ (2012) Epidemiology of traumatic spinal cord injury: trends and future implications. Spinal Cord 50:365–372. https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2011.178
Dyjack N, Goleva E, Rios C, Kim BE, Bin L, Taylor P, Bronchick C, Hall CF, Richers BN, Seibold MA, Leung DY (2018) Minimally invasive skin tape strip RNA-seq identifies novel characteristics of type 2-high atopic dermatitis disease endotype. J Allergy Clin Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2017.10.046
Fang H, Liu C, Yang M, Li H, Zhang F, Zhang W, Zhang J (2017) Neurotrophic factor and Trk signaling mechanisms underlying the promotion of motor recovery after acute spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Ther Med 14:652–656. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4516
Freria CM, Hall JC, Wei P, Guan Z, Mctigue D, MPopovich PG (2017) Deletion of the fractalkine receptor, CX3CR1, improves endogenous repair, axon sprouting, and synaptogenesis after spinal cord injury in mice. J Neurosci 37:3568–3587. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2841-16.2017
Geissler SA, Sabin AL, Besser RR, Gooden OM, Shirk BD, Nguyen QM, Khaing ZZ, Schmidt CE (2018) Biomimetic hydrogels direct spinal progenitor cell differentiation and promote functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Neural Eng. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/aaa55c
Goldshmit Y, Spanevello MD, Tajouri S, Li L, Rogers F, Pearse M, Galea M, Bartlett PF, Boyd A, WTurnley AM (2011) EphA4 blockers promote axonal regeneration and functional recovery following spinal cord injury in mice. PLoS One 6:e24636. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0024636
Hu J, Selzer ME (2017) RhoA as a target to promote neuronal survival and axon regeneration. Neural Regen Res 12:525–528. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.205080
Huang Y, Ollikainen M, Sipila P, Mustelin L, Wang X, Su S, Huan T, Levy D, Wilson J, Snieder H, Kaprio J, Wang X (2018) Genetic and environmental effects on gene expression signatures of blood pressure: a transcriptome-wide twin study. Hypertension 71:457–464. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.117.10527
Jazayeri S, Beygi S, Shokraneh F, Hagen E, Rahimi-Movaghar V (2015) Incidence of traumatic spinal cord injury worldwide: a systematic review. Eur Spine J 24:905–918
Keefe KM, Sheikh I, SSmith GM (2017) Targeting neurotrophins to specific populations of neurons: NGF, BDNF, and NT-3 and their relevance for treatment of spinal cord injury. Int J Mol Sci 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030548
Kim D, Pertea G, Trapnell C, Pimentel H, Kelley R, Salzberg SL (2013) TopHat2: accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol 14:R36. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2013-14-4-r36
Lai Z, Lin Y (2013) Analysis of the global transcriptome of longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) embryogenic callus using Illumina paired-end sequencing. BMC Genomics 14:561. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-561
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL (2009) Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol 10:R25. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2009-10-3-r25
Li ZW, Li JJ, Wang L, Zhang JP, Wu JJ, Mao XQ, Shi GF, Wang Q, Wang F, Zou J (2014) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor ameliorates excessive astrogliosis and improves the regeneration microenvironment and functional recovery in adult rats following spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation 11:71. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-11-71
Li JA, Zan CF, Xia P, Zheng CJ, Qi ZP, Li CX, Liu ZG, Hou T, TYang XY (2016) Key genes expressed in different stages of spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res 11:1824–1829. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.194754
Li DTH, Hui ES, Chan Q, Yao N, Chua SE, Mcalonan GM, Pang SYY, Ho S, LMak HKF (2018) Quantitative susceptibility mapping as an indicator of subcortical and limbic iron abnormality in Parkinson’s disease with dementia. Neuroimage Clin 20:365–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2018.07.028
Liew CC, Ma J, Tang HC, Zheng R, Dempsey AA (2006) The peripheral blood transcriptome dynamically reflects system wide biology: a potential diagnostic tool. J Lab Clin Med 147:126–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lab.2005.10.005
Mao X, Cai T, Olyarchuk JG, Wei L (2005) Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 21:3787–3793. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti430
Maroilley T, Lemonnier G, Lecardonnel J, Esquerre D, Ramayo-Caldas Y, Mercat MJ, Rogel-Gaillard C, Estelle J (2017) Deciphering the genetic regulation of peripheral blood transcriptome in pigs through expression genome-wide association study and allele-specific expression analysis. BMC Genomics 18:967. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-4354-6
Martin L, Chaabo A, Lasne F (2015) Detection of tetracosactide in plasma by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Drug Test Anal 7:531–534. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.1705
Mcdonald J, Sadowsky C (2002) Spinal-cord injury. Lancet 359:417–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07603-1
Ogawa M (1993) Differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 81:2844–2853
Okuda S, Yamada T, Hamajima M, Itoh M, Katayama T, Bork P, Goto SKanehisa M (2008) KEGG atlas mapping for global analysis of metabolic pathways. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W423–W426. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn282
Oyinbo CA (2011) Secondary injury mechanisms in traumatic spinal cord injury: a nugget of this multiply cascade. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 71:281–299
Paquette AG, Shynlova O, Kibschull M, Price ND, Lye SJ (2018) Comparative analysis of gene expression in maternal peripheral blood and monocytes during spontaneous preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2017.12.234
Profyris C, Cheema SS, Zang D, Azari MF, Boyle K, Petratos S (2004) Degenerative and regenerative mechanisms governing spinal cord injury. Neurobiol Dis 15:415–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2003.11.015
Radhakrishna M, Makriyianni I, Marcoux JZhang X (2014) Effects of injury level and severity on direct costs of care for acute spinal cord injury. Int J Rehabil Res 37:349–353. https://doi.org/10.1097/MRR.0000000000000081
Rank MM, Murray KC, Stephens MJ, D’amico J, Gorassini MA, Bennett DJ (2011) Adrenergic receptors modulate motoneuron excitability, sensory synaptic transmission and muscle spasms after chronic spinal cord injury. J Neurophysiol 105:410–422. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00775.2010
Richardson MF, Sequeira F, Selechnik D, Carneiro M, Vallinoto M, Reid JG, West AJ, Crossland MR, Shine RRollins LA (2018) Improving amphibian genomic resources: a multitissue reference transcriptome of an iconic invader. Gigascience 7:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/gix114
Richner M, Ulrichsen M, Elmegaard SL, Dieu R, Pallesen L, TVaegter CB (2014) Peripheral nerve injury modulates neurotrophin signaling in the peripheral and central nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 50:945–970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8706-9
Shimizu K, Uematsu A, Imai YSawasaki T (2014) Pctaire1/Cdk16 promotes skeletal myogenesis by inducing myoblast migration and fusion. FEBS Lett 588:3030–3037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2014.05.060
Stevenson VL, Playford ED, Langdon DW, Thompson AJ (1996) Rehabilitation of incomplete spinal cord pathology: factors affecting prognosis and outcome. J Neurol 243:644–647
Sun Y, Zhang D, Sun G, Lv Y, Li Y, Li X, Song Y, Li J, Fan Z, Wang H (2017) RNA-sequencing study of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in sporadic Meniere’s disease patients: possible contribution of immunologic dysfunction to the development of this disorder. Clin Exp Immunol 192:33–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.13083
Takahashi S, Nakagawa K, Tomiyasu M, Nakashima A, Katayama K, Imura T, Herlambang B, Okubo F, Arihiro K, Kawahara Y, Yuge LSueda T (2018) Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy improves lower limb movement after spinal cord ischemia in rats. Ann Thorac Surg 105:1523–1530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2017.12.014
Toh H, Shirane K, Miura F, Kubo N, Ichiyanagi K, Hayashi K, Saitou M, Suyama M, Ito T, Sasaki H (2017) Software updates in the Illumina HiSeq platform affect whole-genome bisulfite sequencing. BMC Genomics 18:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-3392-9
Wang Y, Qin X, Guo T, Liu P, Wu P, Liu Z (2017) Up-regulation of CDK16 by multiple mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinoma promotes tumor progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36:97. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0569-2
Waters RL, Adkins RH, Yakura JS (1991) Definition of complete spinal cord injury. Paraplegia 29:573–581. https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1991.85
Wei Z, Yu D, Bi Y, Cao Y (2015) A disintegrin and metalloprotease 17 promotes microglial cell survival via epidermal growth factor receptor signalling following spinal cord injury. Mol Med Rep 12:63–70. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3395
Wen T, Hou J, Wang F, Zhang Y, Zhang T, Sun T (2016) Comparative analysis of molecular mechanism of spinal cord injury with time based on bioinformatics data. Spinal Cord 54:431–438. https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2015.171
Wu J, Sabirzhanov B, Stoica BA, Lipinski MM, Zhao Z, Zhao S, Ward N, Yang DFaden AI (2015) Ablation of the transcription factors E2F1-2 limits neuroinflammation and associated neurological deficits after contusive spinal cord injury. Cell Cycle 14:3698–3712. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2015.1104436
Xie J, Li Y, Jiang K, Hu K, Zhang S, Dong X, Dai X, Liu L, Zhang T, Yang K, Huang K, Chen J, Shi S, Zhang Y, Wu G, Xu S (2018) CDK16 phosphorylates and degrades p53 to promote radioresistance and predicts prognosis in lung Cancer. Theranostics 8:650–662. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.21963
Yanagi T, Matsuzawa S (2015) PCTAIRE1/PCTK1/CDK16: a new oncotarget? Cell Cycle 14:463–464. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2015.1006539
Yanagi T, Hata H, Mizuno E, Kitamura S, Imafuku K, Nakazato S, Wang L, Nishihara H, Tanaka S, Shimizu H (2017) PCTAIRE1/CDK16/PCTK1 is overexpressed in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and regulates p27 stability and cell cycle. J Dermatol Sci 86:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2017.02.281
Yang G, Tang WY (2017) Resistance of interleukin-6 to the extracellular inhibitory environment promotes axonal regeneration and functional recovery following spinal cord injury. Int J Mol Med 39:437–445. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2017.2848
Yoon C, Van Niekerk EA, Henry K, Ishikawa T, Orita S, Tuszynski M, HCampana WM (2013) Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1)-dependent cell signaling promotes axonal regeneration. J Biol Chem 288:26557–26568. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.478552
Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth G, KOshlack A (2010) Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol 11:R14. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-2-r14
Yu F, Sugawara T, Maier CM, Hsieh L, BChan PH (2005) Akt/Bad signaling and motor neuron survival after spinal cord injury. Neurobiol Dis 20:491–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2005.04.004
Zhou Q, Yu Y (2015) Upregulated CDK16 expression in serous epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Med Sci Monit 21:3409–3414. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.894990
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Guiyang Science and Technology Bureau fund (2018-1-88).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Lv, H., Li, Q. et al. RNA Sequencing of Peripheral Blood Revealed that the Neurotropic TRK Receptor Signaling Pathway Shows Apparent Correlation in Recovery Following Spinal Cord Injury at Small Cohort. J Mol Neurosci 68, 221–233 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01273-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01273-4