Abstract
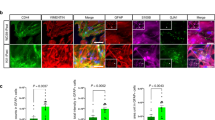
Focal cortical dysplasia type II (FCD II) and tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) are well-known causes of chronic refractory epilepsy in children. Canonical transient receptor potential channels (TRPCs) are non-selective cation channels that are commonly activated by phospholipase C (PLC) stimulation. Previous studies found that TRPC4 may participate in the process of epileptogenesis. This study aimed to examine the expression and distribution of TRPC4 in FCD II (n = 24) and TSC (n = 11) surgical specimens compared with that in age-matched autopsy control samples (n = 12). We found that the protein levels of TRPC4 and its upstream factor, PLC delta 1 (PLCD1), were elevated in FCD II and TSC samples compared to those of control samples. Immunohistochemistry assays revealed that TRPC4 staining was stronger in malformed cells, such as dysmorphic neurons, balloon cells and giant cells. Moderate-to-strong staining of the upstream factor PLCD1 was also identified in abnormal neurons. Moreover, double immunofluorescence staining revealed that TRPC4 was colocalised with glutamatergic and GABAergic neuron markers. Taken together, our results indicate that overexpression of TRPC4 protein may be involved in the epileptogenesis of FCD II and TSC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Andre VM, Wu N, Yamazaki I et al (2007) Cytomegalic interneurons: a new abnormal cell type in severe pediatric cortical dysplasia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:491–504
Balbuena P, Li W, Rzigalinski BA, Ehrich M (2012) Malathion/oxon and lead acetate increase gene expression and protein levels of transient receptor potential canonical channel subunits TRPC1 and TRPC4 in rat endothelial cells of the blood-brain barrier. Int J Toxicol 31:238–249
Blumcke I, Thom M, Aronica E et al (2011) The clinicopathologic spectrum of focal cortical dysplasias: a consensus classification proposed by an ad hoc task force of the ILAE diagnostic methods commission. Epilepsia 52:158–174
Cavalie A (2007) Ionic channels formed by TRPC4. Handbook of experimental pharmacology, 93-108.
Cepeda C, Andre VM, Wu N et al (2007) Immature neurons and GABA networks may contribute to epileptogenesis in pediatric cortical dysplasia. Epilepsia 48(Suppl 5):79–85
Cioffi DL (2011) Redox regulation of endothelial canonical transient receptor potential channels. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:1567–1582
Cooper D, Illig K, Varnell A, Ostertag E, Klipec W, and Cooper D (2011) TRPC4 ion channel protein is selectively expressed in a subpopulation of dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area. Nature Precedings.
Crino PB, Nathanson KL, Henske EP (2006) The tuberous sclerosis complex. N Engl J Med 355:1345–1356
Earley S, Brayden JE (2010) Transient receptor potential channels and vascular function. Clin Sci (Lond) 119:19–36
Engel J. (1987). Surgical treatment of the epilepsies: raven press.
Fowler MA, Sidiropoulou K, Ozkan ED, Phillips CW, Cooper DC (2007) Corticolimbic expression of TRPC4 and TRPC5 channels in the rodent brain. PLoS One 2:e573
Freichel M, Tsvilovskyy V, Camacho-Londono JE (2014) TRPC4- and TRPC4-containing channels. Handb Exp Pharmacol 222:85–128
Golovina VA (2005) Visualization of localized store-operated calcium entry in mouse astrocytes. Close proximity to the endoplasmic reticulum J Physiol 564:737–749
Guerrini R, Dobyns WB (2014) Malformations of cortical development: clinical features and genetic causes. The Lancet Neurology 13:710–726
Jeon JP, Hong C, Park EJ et al (2012) Selective Galphai subunits as novel direct activators of transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC)4 and TRPC5 channels. J Biol Chem 287:17029–17039
Jeon JP, Roh SE, Wie J et al (2013) Activation of TRPC4beta by Galphai subunit increases Ca2+ selectivity and controls neurite morphogenesis in cultured hippocampal neuron. Cell Calcium 54:307–319
Kim J, Kwak M, Jeon JP et al (2014) Isoform- and receptor-specific channel property of canonical transient receptor potential (TRPC)1/4 channels. Pflugers Archiv : European journal of physiology 466:491–504
Marin-Valencia I, Guerrini R, Gleeson JG (2014) Pathogenetic mechanisms of focal cortical dysplasia. Epilepsia 55:970–978
Munsch T, Freichel M, Flockerzi V, Pape HC (2003) Contribution of transient receptor potential channels to the control of GABA release from dendrites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:16065–16070
Phelan KD, Shwe UT, Abramowitz J et al (2013) Canonical transient receptor channel 5 (TRPC5) and TRPC1/4 contribute to seizure and excitotoxicity by distinct cellular mechanisms. Mol Pharmacol 83:429–438
Ramsey IS, Delling M, Clapham DE (2006) An introduction to TRP channels. Annu Rev Physiol 68:619–647
Seiffert E, Dreier JP, Ivens S et al (2004) Lasting blood-brain barrier disruption induces epileptic focus in the rat somatosensory cortex. J Neurosci 24:7829–7836
Song X, Zhao Y, Narcisse L et al (2005) Canonical transient receptor potential channel 4 (TRPC4) co-localizes with the scaffolding protein ZO-1 in human fetal astrocytes in culture. Glia 49:418–429
von Spiczak S, Muhle H, Helbig I et al (2010) Association study of TRPC4 as a candidate gene for generalized epilepsy with photosensitivity. NeuroMolecular Med 12:292–299
Thakur DP, Tian JB, Jeon J et al (2016) Critical roles of Gi/o proteins and phospholipase C-δ1 in the activation of receptor-operated TRPC4 channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, U.S.A.
Venkatachalam K, Montell C (2007) TRP channels. Annu Rev Biochem 76:387–417
van Vliet EA, da Costa AS, Redeker S, van Schaik R, Aronica E, Gorter JA (2007) Blood–brain barrier leakage may lead to progression of temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 130:521–534
van Vliet EA, Aronica E, Gorter JA (2015) Blood-brain barrier dysfunction, seizures and epilepsy. Semin Cell Dev Biol 38:26–34
Wang M, Bianchi R, Chuang SC, Zhao W, Wong RK (2007) Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent TRPC channel trafficking in hippocampal neurons. J Neurochem 101:411–421
Weick JP, Austin Johnson M, Zhang SC (2009) Developmental regulation of human embryonic stem cell-derived neurons by calcium entry via transient receptor potential channels. Stem Cells 27:2906–2916
Yang XL, Chen B, Zhang XQ et al (2017) Upregulations of CRH and CRHR1 in the epileptogenic tissues of patients with intractable infantile spasms. CNS neuroscience & therapeutics 23:57–68
Zechel S, Werner S, von Bohlen Und Halbach O (2007) Distribution of TRPC4 in developing and adult murine brain. Cell Tissue Res 328:651–656
Acknowledgments
The investigators would like to thank the technicians Jin Peng, Qian Chen and Wen-Qiang Cai (Central Laboratory of Xinqiao Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, China) for their excellent assistance with laser scanning confocal microscopy. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81471321, No. 81371424 and No. 81601142).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, LK., Chen, X., Zhang, CQ. et al. Elevated Expression of TRPC4 in Cortical Lesions of Focal Cortical Dysplasia II and Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. J Mol Neurosci 62, 222–231 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-0923-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-0923-z