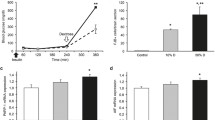
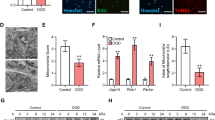
Abstract
Hypoxic–ischemic brain injury is an important cause of neonatal mortality and morbidity. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) has been reported to play a neuroprotective role in hypoxic–ischemic brain injury; however, the specific effects and mechanism of BDNF on hypoxic–hypoglycemic hippocampal neuron injury remains unknown. The current study investigated the action of BDNF in regulating cerebral hypoxic-ischemic injury by simulating hippocampal neuron ischemia and hypoxia. We found that BDNF, p-Trkb, and miR-134 expression levels decreased, and that exogenous BDNF increased survival and reduced apoptosis in hypoxic–hypoglycemic hippocampal neurons. The results also show that BDNF inhibits MiR-134 expression by activating the TrkB pathway. Transfection with TrkB siRNA and pre-miR-134 abrogated the neuroprotective role of BDNF in hypoxic–hypoglycemic hippocampal neurons. Our results suggest that exogenous BDNF alleviates hypoxic–ischemic brain injury through the Trkb/MiR-134 pathway. These findings may help to identify a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of hypoxic–ischemic brain injury.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boutilier J, Ceni C, Pagdala PC, Forgie A, Neet KE, Barker PA (2008) Proneurotrophins require endocytosis and intracellular proteolysis to induce TrkA activation. J Biol Chem 283:12709–12716
Chen A, Xiong LJ, Tong Y, Mao M (2013) The neuroprotective roles of BDNF in hypoxic ischemic brain injury, vol. 1. Biomed Rep 1(2):167–176
Chi W, Meng F, Li Y, Wang Q, Wang G, Han S, Wang P, Li J (2014) Downregulation of miRNA-134 protects neural cells against ischemic injury in N2A cells and mouse brain with ischemic stroke by targeting HSPA12B. Neuroscience 277:111–122
Doherty GH, Beccano-Kelly D, Du Yan S, Gunn-Moore FJ, Harvey J (2013) Leptin prevents hippocampal synaptic disruption and neuronal cell death induced by amyloid β. Neurobiol Aging 34:226–237
Frazzitta G, Maestri R, Ghilardi MF, Riboldazzi G, Perini M, Bertotti G, Boveri N, Buttini S, Lombino FL, Uccellini D et al (2014) Intensive rehabilitation increases BDNF serum levels in parkinsonian patients: a randomized study. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 28:163–168
Han BH, D’Costa A, Back SA, Parsadanian M, Patel S, Shah AR, Gidday JM, Srinivasan A, Deshmukh M, Holtzman DM (2000) BDNF blocks caspase-3 activation in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Neurobiol Dis 7:38–53
Huang W, Cao J, Liu X, Meng F, Li M, Chen B, Zhang J (2015a) AMPK plays a dual role in regulation of CREB/BDNF pathway in mouse primary hippocampal cells. J Mol Neurosci 56:782–788
Huang W, Liu X, Cao J, Meng F, Li M, Chen B, Zhang J (2015b) miR-134 regulates ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced neuronal cell death by regulating CREB signaling. J Mol Neurosci 55:821–829
Huang YN, Lin CI, Liao H, Liu CY, Chen YH, Chiu WC, Lin SH (2016) Cholesterol overload induces apoptosis in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells through the up regulation of flotillin-2 in the lipid raft and the activation of BDNF/Trkb signaling. Neuroscience 328:201–209
Johnston MV, Trescher WH, Ishida A, Nakajima W (2001) Neurobiology of hypoxic-ischemic injury in the developing brain. Pediatr Res 49:735–741
Konecna A, Heraud JE, Schoderboeck L, Raposo AA, Kiebler MA (2009) What are the roles of microRNAs at the mammalian synapse? Neurosci Lett 466:63–68
Liu C, Peng Z, Zhang N, Yu L, Han S, Li D, Li J (2012) Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs and their PKC-isoform specific gene network prediction during hypoxic pre-conditioning and focal cerebral ischemia of mice. J Neurochem 120:830–841
Luo L, Liu XL, Li J, Mu RH, Liu Q, Yi LT, Geng D (2015) Macranthol promotes hippocampal neuronal proliferation in mice via BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 762:357–363
Nguyen KQ, Rymar VV, Sadikot AF (2016) Impaired TrkB signaling underlies reduced BDNF-mediated trophic support of striatal neurons in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci 10:37
Numakawa T, Suzuki S, Kumamaru E, Adachi N, Richards M, Kunugi H (2010) BDNF function and intracellular signaling in neurons. Histol Histopathol 25:237–258
Pikula A, Beiser AS, Chen TC, Preis SR, Vorgias D, DeCarli C, Au R, Kelly-Hayes M, Kase CS, Wolf PA et al (2013) Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor and vascular endothelial growth factor levels are associated with risk of stroke and vascular brain injury: Framingham Study. Stroke 44:2768–2775
Qi D, Ouyang C, Wang Y, Zhang S, Ma X, Song Y, Yu H, Tang J, Fu W, Sheng L et al (2014) HO-1 attenuates hippocampal neurons injury via the activation of BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in stroke. Brain Res 19:69–76
Qiu J, Zhou XY, Zhou XG, Cheng R, Liu HY, Li Y (2013) Neuroprotective effects of microRNA-210 on hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Biomed Res Int 350419:9
Rosenblum S, Smith TN, Wang N, Chua JY, Westbroek E, Wang K, Guzman R (2015) BDNF pretreatment of human embryonic-derived neural stem cells improves cell survival and functional recovery after transplantation in hypoxic-ischemic stroke. Cell Transplant 24:2449–2461
Schmidt-Kastner R, Freund TF (1991) Selective vulnerability of the hippocampus in brain ischemia. Neuroscience 40:599–636
Schratt GM, Tuebing F, Nigh EA, Kane CG, Sabatini ME, Kiebler M, Greenberg ME (2006) A brain-specific microRNA regulates dendritic spine development. Nature 439:283–289
Silveira RC, Procianoy RS (2015) Hypothermia therapy for newborns with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. J Pediatr 91:4
Smith AL, Alexander M, Rosenkrantz TS, Sadek ML, Fitch RH (2014) Sex differences in behavioral outcome following neonatal hypoxia ischemia: insights from a clinical meta-analysis and a rodent model of induced hypoxic ischemic brain injury. Exp Neurol 254:54–67
Sun L, Guo C, Wang T, Li X, Li G, Luo Y, Xiao S (2014) LIMK1 is involved in the protective effects of bone morphogenetic protein 6 against amyloid-beta-induced neurotoxicity in rat hippocampal neurons. J Alzheimers Dis 42:543–554
Vannucci RC (2000) Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Am J Perinatol 17:113–120
Wang L, Kang F, Li J, Zhang J, Shan B (2013) Overexpression of p65 attenuates celecoxib-induced cell death in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell line. Cancer Cell Int 13:1
Xiang L, Ren Y, Cai H, Zhao W, Song Y (2015) MicroRNA-132 aggravates epileptiform discharges via suppression of BDNF/TrkB signaling in cultured hippocampal neurons. Brain Res 5:484–495
Xiong S, Zheng Y, Jiang P, Liu R, Liu X, Chu Y (2011) MicroRNA-7 inhibits the growth of human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells through targeting BCL-2. Int J Biol Sci 7:805–814
Yu H, Chen ZY (2011) The role of BDNF in depression on the basis of its location in the neural circuitry. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32:3–11
Yu Y, Zhang P, Yan J, Sun Y, Wu X, Xi S, Zhang L, Hu R, Jiang H (2016) Sevoflurane induces cognitive impairments via the MiR-27b/LIMK1-signaling pathway in developing rats. Inhal Toxicol 28:731–738
Acknowledgements
The project was supported by Natural Science Foundation Research Project of Shaanxi province (2016JM8073).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
1. H–H treatment decreased BDNF, p-Trkb, and miR-134 expression
2. Exogenous BDNF significantly increased p-Trkb expression
3. BDNF increased H–H-induced hippocampal neuron growth
4. BDNF inhibits miR-134 expression via activating TrkB
5. TrkB and miR-134 involved in the action of BDNF
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
Cocl2 treatment increased the expression of HIF-1α (marker of hypoxia) in hippocampal neurons. HIF-1α protein expression was measured by Western blot. Cells were treated by 300 μM Cocl2 for 3 and 9 h to simulate hypoxia in vitro. Data were repeated at least three times (n=3); *P<0.05 versus control group. (GIF 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, W., Meng, F., Cao, J. et al. Neuroprotective Role of Exogenous Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Hypoxia–Hypoglycemia-Induced Hippocampal Neuron Injury via Regulating Trkb/MiR134 Signaling. J Mol Neurosci 62, 35–42 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-0907-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-0907-z