Abstract
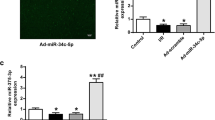
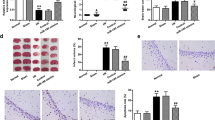
The p38α, also named Mapk14, is a pro-apoptotic protein, which is reported to be downregulated 2 h after cerebral ischemia. However, little is known what causes the downregulation of p38α protein level. Here, we studied the effect of cerebral ischemia on p38α mRNA expression and p38α protein level in brain of mice. We found that p38α protein level is reduced after middle cerebral artery occlusion. However, at the meantime, p38α mRNA expression has no detectable changes, suggesting that the possible posttranscription is regulated by ischemia. To reveal the mechanism for posttranscription of p38α protein, we tested the effect of miR-128-3p. Using luciferase reporter assay, we found that miR-128-3p could directly target p38α 3’UTR. We further tested the effect of miR-128-3p on the p38α protein level. We found that miR-128-3p strongly decreased the p38α protein level in SH-SY5Y cells after the cells were transfected with miR-128-3p using lentivirus vector containing precursor its RNA sequences. We further found that inhibition of miR-128-3p enhanced the infarct volume of brain in mice. Our study thus confirms that miR-128-3p can downregulate p38α protein level through posttranscription and increase of miR-128-3p level may contribute to neuronal survival in ischemia-induced brain injury.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adlakha YK, Saini N (2014) Brain microRNAs and insights into biological functions and therapeutic potential of brain enriched miRNA-128. Mol Cancer 13:33. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-13-33
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW, Bartel DP (2015) Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs eLife:4. doi:10.7554/eLife.05005
Bi XY, Wang TS, Zhang M, Liu QQ, Li WB, Zhang Y (2014) The up-regulation of p-p38 MAPK during the induction of brain ischemic tolerance induced by intermittent hypobaric hypoxia preconditioning in rats. Zhongguo ying yong sheng li xue za zhi = Zhongguo yingyong shenglixue zazhi = Chinese journal of applied physiology 30:97–100
Cao J, Semenova MM, Solovyan VT, Han J, Coffey ET, Courtney MJ (2004) Distinct requirements for p38α and c-Jun N-terminal kinase stress-activated protein kinases in different forms of apoptotic neuronal death. J Biol Chem 279:35903–35913. doi:10.1074/jbc.M402353200
Cernilogar FM, Di Giaimo R, Rehfeld F, Cappello S, Lie DC (2015) RNA interference machinery-mediated gene regulation in mouse adult neural stem cells. BMC Neurosci 16:60. doi:10.1186/s12868-015-0198-7
Chang JJ, Stanfill A, Pourmotabbed T (2016) The role of matrix metalloproteinase polymorphisms in ischemic stroke. Int J Mol Sci 17. doi:10.3390/ijms17081323
Chen KC, Chiou YL, Chang LS (2009) JNK1/c-Jun and p38 alpha MAPK/ATF-2 pathways are responsible for upregulation of Fas/FasL in human chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cells upon exposure to Taiwan cobra phospholipase A2. J Cell Biochem 108:612–620. doi:10.1002/jcb.22293
Cheng CY, Tang NY, Kao ST, Hsieh CL (2016) Ferulic acid administered at various time points protects against cerebral infarction by activating p38 MAPK/p90RSK/CREB/Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic signaling in the subacute phase of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. PLoS One 11:e0155748. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0155748
Cui JG, Zhao Y, Sethi P, Li YY, Mahta A, Culicchia F, Lukiw WJ (2010) Micro-RNA-128 (miRNA-128) down-regulation in glioblastoma targets ARP5 (ANGPTL6), Bmi-1 and E2F-3a, key regulators of brain cell proliferation. J Neuro-Oncol 98:297–304. doi:10.1007/s11060-009-0077-0
Evangelisti C et al. (2009) MiR-128 up-regulation inhibits Reelin and DCX expression and reduces neuroblastoma cell motility and invasiveness FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Exp Biol 23:4276–4287 doi:10.1096/fj.09-134965
Guven-Ozkan T, Busto GU, Schutte SS, Cervantes-Sandoval I, O’Dowd DK, Davis RL (2016) MiR-980 is a memory suppressor microRNA that regulates the autism-susceptibility gene A2bp1. Cell Rep 14:1698–1709. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2016.01.040
Han D, Scott EL, Dong Y, Raz L, Wang R, Zhang Q (2015) Attenuation of mitochondrial and nuclear p38alpha signaling: a novel mechanism of estrogen neuroprotection in cerebral ischemia. Mol Cell Endocrinol 400:21–31. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2014.11.010
Jiang Y, Chen C, Li Z, Guo W, Gegner JA, Lin S, Han J (1996) Characterization of the structure and function of a new mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38β). J Biol Chem 271:17920–17926
John B, Sander C, Marks DS (2006) Prediction of human microRNA targets. Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, NJ) 342:101–113. doi:10.1385/1-59745-123-1:101
Keasey MP, Scott HL, Bantounas I, Uney JB, Kelly S (2016) MiR-132 is upregulated by ischemic preconditioning of cultured hippocampal neurons and protects them from subsequent OGD toxicity. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience : MN 59:404–410. doi:10.1007/s12031-016-0740-9
Lawson SK, Dobrikova EY, Shveygert M, Gromeier M (2013) p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase depletion and repression of signal transduction to translation machinery by miR-124 and -128 in neurons. Mol Cell Biol 33:127–135. doi:10.1128/mcb.00695-12
Lee ST et al (2011) Altered microRNA regulation in Huntington’s disease models. Exp Neurol 227:172–179. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.10.012
Liu L et al (2008) FasL shedding is reduced by hypothermia in experimental stroke. J Neurochem 106:541–550. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05411.x
Liu Z, Li Y, Zhang RL, Cui Y, Chopp M (2011) Bone marrow stromal cells promote skilled motor recovery and enhance contralesional axonal connections after ischemic stroke in adult mice. Stroke; a Journal of Cerebral Circulation 42:740–744. doi:10.1161/strokeaha.110.607226
Liu XR et al (2012) Ischemic postconditioning diminishes matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression and attenuates loss of the extracellular matrix proteins in rats following middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics 18:855–863. doi:10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00366.x
Liu X et al (2013) MicroRNA-124-mediated regulation of inhibitory member of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 family in experimental stroke. Stroke; a Journal of Cerebral Circulation 44:1973–1980. doi:10.1161/strokeaha.111.000613
Lukiw WJ (2007) Micro-RNA speciation in fetal, adult and Alzheimer’s disease hippocampus. Neuroreport 18:297–300. doi:10.1097/WNR.0b013e3280148e8b
Nito C, Kamada H, Endo H, Narasimhan P, Lee YS, Chan PH (2012) Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in expression of the water channel protein aquaporin-4 after ischemia in rat cortical astrocytes. J Neurotrauma 29:2404–2412. doi:10.1089/neu.2012.2430
O’Keefe SJ et al (2007) Chemical genetics define the roles of p38alpha and p38beta in acute and chronic inflammation. J Biol Chem 282:34663–34671. doi:10.1074/jbc.M704236200
Piao CS, Kim JB, Han PL, Lee JK (2003) Administration of the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 affords brain protection with a wide therapeutic window against focal ischemic insult. J Neurosci Res 73:537–544. doi:10.1002/jnr.10671
Planells-Ferrer L et al (2016) Fas apoptosis inhibitory molecules: more than death-receptor antagonists in the nervous system. J Neurochem 139:11–21. doi:10.1111/jnc.13729
Roy Choudhury G et al (2014) Involvement of p38 MAPK in reactive astrogliosis induced by ischemic stroke. Brain Res 1551:45–58. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2014.01.013
Saba R, Goodman CD, Huzarewich RL, Robertson C, Booth SA (2008) A miRNA signature of prion induced neurodegeneration. PLoS One 3:e3652. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003652
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Sempere LF, Freemantle S, Pitha-Rowe I, Moss E, Dmitrovsky E, Ambros V (2004) Expression profiling of mammalian microRNAs uncovers a subset of brain-expressed microRNAs with possible roles in murine and human neuronal differentiation. Genome Biol 5:R13. doi:10.1186/gb-2004-5-3-r13
Shi ZM et al (2012) MiR-128 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting p70S6K1. PLoS One 7:e32709. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032709
Smirnova L, Grafe A, Seiler A, Schumacher S, Nitsch R, Wulczyn FG (2005) Regulation of miRNA expression during neural cell specification. Eur J Neurosci 21:1469–1477. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.03978.x
Tamura K, Sudo T, Senftleben U, Dadak AM, Johnson R, Karin M (2000) Requirement for p38α in erythropoietin expression: a role for stress kinases in erythropoiesis. Cell 102:221–231
Trouillas M et al (2008) Bcl2, a transcriptional target of p38α, is critical for neuronal commitment of mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Death Differ 15:1450–1459. doi:10.1038/cdd.2008.63
Wang XS et al (1997) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 272:23668–23674
Xiang L, Ren Y, Li X, Zhao W, Song Y (2016) MicroRNA-204 suppresses epileptiform discharges through regulating TrkB-ERK1/2-CREB signaling in cultured hippocampal neurons. Brain Res 1639:99–107. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2016.02.045
Xing B, Bachstetter AD, Van Eldik LJ (2015) Inhibition of neuronal p38α, but not p38β MAPK, provides neuroprotection against three different neurotoxic insults. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience : MN 55:509–518. doi:10.1007/s12031-014-0372-x
Zhang QG, Wang R, Khan M, Mahesh V, Brann DW (2008) Role of Dickkopf-1, an antagonist of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, in estrogen-induced neuroprotection and attenuation of tau phosphorylation. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 28:8430–8441. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.2752-08.2008
Zhang Y et al (2009) MicroRNA-128 inhibits glioma cells proliferation by targeting transcription factor E2F3a. Journal of Molecular Medicine (Berlin, Germany) 87:43–51. doi:10.1007/s00109-008-0403-6
Zhang, W et al. (2016) MiRNA-128 regulates the proliferation and neurogenesis of neural precursors by targeting PCM1 in the developing cortex. 5. doi:10.7554/eLife.11324
Zhen Y, Ding C, Sun J, Wang Y, Li S, Dong L (2016) Activation of the calcium-sensing receptor promotes apoptosis by modulating the JNK/p38 MAPK pathway in focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in mice. Am J Transl Res 8:911–921
Zhu P et al (2014) The roles of p38 MAPK/MSK1 signaling pathway in the neuroprotection of hypoxic postconditioning against transient global cerebral ischemia in adult rats. Mol Neurobiol 49:1338–1349. doi:10.1007/s12035-013-8611-7
Acknowledgments
We thank Xiaobing Zhang for helpful suggestions on the manuscript. Support is provided by the Shaanxi Science and Technology Research and Development Program (2012-KCT-16).
Author Contributions
GCM and GW performed statistical analysis, data interpretation and manuscript preparation. YLZ contributed to study concept, design and supervision. PYR and FY performed literature research and data extraction. YLZ and GW were responsible for quality control of data and accuracy. All authors wrote the manuscript and approved the final version of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, G., Ren, P., Wang, G. et al. MicroRNA-128-3p Protects Mouse Against Cerebral Ischemia Through Reducing p38α Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activity. J Mol Neurosci 61, 152–158 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0871-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0871-z