Abstract
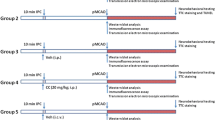
Remote ischemic perconditioning (RIPerC) and ischemic postconditioning (IPOC) are well-acknowledged neuroprotective procedures during ischemic injury. The present study established a combined RIPerC and IPOC (RIPerC + IPOC) model in rats and studied how it would regulate the autophagy process and affect HMGB1 levels in a rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). Rats with MCAO were treated with RIPerC by fastening and release of the left hind limb to achieve 4 cycles of 5 min remote ischemia reperfusion, 40 min prior to cerebral reperfusion, and then treated with IPOC by exposing the cerebral middle artery to 3 cycles of 30 s reperfusion/30 s occlusion at the onset of cerebral reperfusion. Infarction volumes, neurological deficits, and pathological changes were assessed 24 h after ischemia. The autophagy activator rapamycin (RAP) and the autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine (3-MA) were administrated for further mechanism. The expression and location of HMGB1 and the autophagy-related proteins like LC3, Beclin1, and P62 as well as plasma HMGB1 levels were measured. Our results suggested that RIPerC + IPOC attenuated plasma HMGB1 levels to intensify its neuroprotective effect against cerebral ischemic reperfusion injury via inhibiting the autophagy process.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- I/R:
-
Ischemia reperfusion
- IPOC:
-
Ischemic postconditioning
- RIPerC:
-
Remote ischemic perconditioning
- MCA:
-
Middle cerebral artery
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- HMGB1:
-
High-mobility group box 1
- RAP:
-
Rapamycin
- 3-MA:
-
3-Methyladenine
- MNSS:
-
Modified neurological severity scores
- TTC:
-
2,3,5
Triphenyltetrazolium chloride
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- FJC:
-
Fluoro-Jade C
- i.c.v.:
-
Intracerebral ventricle injection
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- IDV:
-
Integrated density value
References
Bellu AR, Kiel JA (2003) Selective degradation of peroxisomes in yeasts. Microsc Res Tech 61:161–170
Bowen ID, Mullarkey K, Margen SM (1996) Programmed cell death during meta-morphosis in the blow-fly Calliphora vormitoria. Microsc Res Tech 34:202–217
Chakrabarti L, Eng J, Ivanov N, et al. (2009) Autophagy activation and enhanced mitophagy characterize the Purkinje cells of pcd mice prior to neuronal death. Mol Brain 2:24
Cuervo AM (2004) Autophagy: in sickness and in health. Trends Cell Biol 14:70–77
Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, et al. (2008) Stroke. Lancet 371:1612–1623
Gao L, Jiang T, Guo J, et al. (2012) Inhibition of autophagy contributes to ischemic postconditioning-induced neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischemia in rats. PLoS ONE 7:e46092
Germano AF, Dixon CE, d’Avella D, et al. (1994) Behavioral deficits following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in the rat. J Neurotrauma 11:345–353
Goodwin GH, Sanders C, Johns EW (1973) A new group of chromatin associated proteins with a high content of acidic and basic amino acids. Eur J Biochem 38:14–19
Hess DC, Hoda MN, Bhatia K (2013) Remote limb perconditioning and postconditioning: will it translate into a promising treatment for acute stroke? Stroke 44:1191–1197
Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT, et al. (2011) The Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 18:571–580
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Nakamura T, Yamada S, Yoshioka T (2013) Brain hypothermic therapy dramatically decreases elevated blood concentrations of high mobility group box 1 in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Dis Markers 35:327–330
Puyal J, Clarke PG (2009) Targeting autophagy to prevent neonatal stroke damage. Autophagy 5:1060–1061
Rickenbacher A, Limani P, Ungethum U, et al. (2014) Fasting protects liver from ischemic injury through Sirt1-mediated downregulation of circulating HMGB1 in mice. J Hepatol 61:301–308
Rosen GD, Harry JD (1990) Brain volume estimation from serial section measurements: a comparison of methodologies. J Neurosci Meth. 35:115–124
Schmued LC, Stowers CC, Scallet AC, et al. (2005) Fluoro-Jade C results in ultra high resolution and contrast labeling of degenerating neurons. Brain Res 1035:24–31
Sheng R, Zhang LS, Han R, et al. (2010) Autophagy activation is associated with neuroprotection in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemic preconditioning. Autophagy 6:482–494
Thorburn J, Frankel AE, Thorburn A (2009) Regulation of HMGB1 release by autophagy. Autophagy 5:247–249
Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M (1999) HMGB-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science 285:248–251
Wang Q, Wang F, Li X, et al. (2012) Electroacupuncture pretreatment attenuates cerebral ischemic injury through α7 nicotinic acetylcholine. J Neuroinflamm. 9:24
Wang W, Kang J, Li H, et al. (2013) Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat cortex by p62/ZIP through the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway after transient focal cerebral ischaemia. Brain Inj 27:924–933
Wen YD, Zhang HL, Qin ZQ (2006) Inflammatory mechanism in ischemic neuronal injury. Neurosci Bull 22:171–182
Yan W, Zhang H, Bai X, et al. (2011) Autophagy activation is involved in neuroprotection induced by hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1402:109–121
Yang QW, Wang JZ, Li JC, et al. (2010) High-mobility group protein box-1 and its relevance to cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood F Met 30:243–254
Ying L, Huang Y, Chen H, et al. (2013) Downregulated MEG3 activates autophagy and increases cell proliferation in bladder cancer. Mol BioSyst 9:407–411
Zhao H. (2009) Ischemic postconditioning as a novel avenue to protect against brain injury after stroke. J Cerebr Blood F Met 29, 873–885.
Zhao Y, Guo Q, Chen J, et al. (2014) Role of long non-coding RNA HULC in cell proliferation, apoptosis and tumor metastasis of gastric cancer: a clinical and in vitro investigation. Oncol Rep 31:358–364
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by a grant from the Liaoning Province Science and Technology Project—Animal Scientific Research and Clinical Application for Major Disease of Liaoning Province (2012225021) and Science and Technology Projects of Liaoning Province (2009225010-2) to Dr. Feng.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Han, D., Sun, M. et al. A Combination of Remote Ischemic Perconditioning and Cerebral Ischemic Postconditioning Inhibits Autophagy to Attenuate Plasma HMGB1 and Induce Neuroprotection Against Stroke in Rat. J Mol Neurosci 58, 424–431 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0724-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0724-9