Abstract
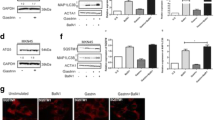
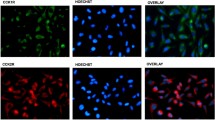
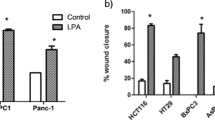
Cholecystokinin (CCK) receptors are G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) which are present on lung cancer cells. CCK-8 stimulates the proliferation of lung cancer cells, whereas the CCK2R receptor antagonist CI-988 inhibits proliferation. GPCR for some gastrointestinal hormones/neurotransmitters mediate lung cancer growth by causing epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) transactivation. Here, the role of CCK/gastrin and CI-988 on EGFR transactivation and lung cancer proliferation was investigated. Addition of CCK-8 or gastrin-17 (100 nM) to NCI-H727 human lung cancer cells increased EGFR Tyr1068 phosphorylation after 2 min. The ability of CCK-8 to cause EGFR tyrosine phosphorylation was blocked by CI-988, gefitinib (EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor), PP2 (Src inhibitor), GM6001 (matrix metalloprotease inhibitor), and tiron (superoxide scavenger). CCK-8 nonsulfated and gastrin-17 caused EGFR transactivation and bound with high affinity to NCI-H727 cells, suggesting that the CCK2R is present. CI-988 inhibited the ability of CCK-8 to cause ERK phosphorylation and elevate cytosolic Ca2+. CI-988 or gefitinib inhibited the basal growth of NCI-H727 cells or that stimulated by CCK-8. The results indicate that CCK/gastrin may increase lung cancer proliferation in an EGFR-dependent manner.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang AJ, Song DH, Wolfe MM (2006) Attenuation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) mediates gastrin-stimulated colorectal cancer cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 281:14700–14710
Clerc P, Dufresne M, Saillan C et al (1997) Differential expression of the CCK-A and CCK-B/gastrin receptor genes in human cancers of the esophagus, stomach and colon. Int J Cancer 72:931–936
Clerc P, Leung-Theung-Long S, Wang TC et al (2002) Expression of CCK2 receptors in the murine pancreas: proliferation, transdifferentiation of acinar cells and neoplasia. Gastroenterology 122:428–437
Colucci R, Blandizzi C, Tanini M et al (2005) Gastrin promotes human colon cancer cell growth via CCK-2 receptor-mediated cyclooxygenase-2 induction and prostaglandin E2 production. Br J Pharmacol 144:338–348
Coulson JM, Ocejo-Garcia M, Woll PJ (2003) Neuroendocrine phenotype of small cell lung cancer. Methods Mol Med 74:61–73
Crawley JN (1988) Modulation of mesolimbic dopaminergic behaviors by cholecystokinin. Ann N Y Acad Sci 547:380–396
Daulhac L, Kowalski-Chauvel A, Pradayrol L et al (1999) Src-family kinases in activation of ERK-1 and p85/p110-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by G/CCKB receptors. J Biol Chem 274:20657–20663
Dockray GJ, Moore A, Varro A, Pritchard DM (2012) Gastrin receptor pharmacology. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 14:453–459
Dufresne M, Seva C, Fourmy D (2006) Cholecystokinin and gastrin receptors. Physiol Rev 86:805–847
Ferrand A, Vatinel S, Kowalski-Chauvel A et al (2006) Mechanism for Src activation by the CCK2 receptor: Patho-physiological functions of this receptor in pancreas. World J Gastroenterol 12:4498–4503
George AJ, Hannan RD, Thomas WG (2013) Unravelling the molecular complexity of GPCR-mediated EGFR transactivation using functional genomics approaches. FEBS J 280:5258–5268
Gibbs J, Young RC, Smith GP (1973) Cholecystokinin elicits satiety in rats with open gastric fistulas. Nature 245:323–325
Gigoux V, Clerc P, Sanchez D et al (2008) Reg genes are CCK2 receptor targets in Elas CCK2 mice pancreas. Reg Peptides 146:88–98
Guo YS, Cheng JZ, Jin GF et al (2002) Gastrin stimulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression in intestinal epithelial cells through multiple signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 277:48755–48763
Hughes J, Boden P, Costall B et al (1990) Development of a class of selective cholecystokinin type B antagonists having potent anxiolytic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:6728–6732
Innes RB, Snyder SH (1980) Distinct cholecystokinin receptor in brain and pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 77:6917–6921
Jensen RT, Lemp GF, Gardner JD (1980) Interaction of cholecystokinin with specific membrane receptors on pancreatic acinar cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 77:2079–2083
Jensen RT, Wank SA, Rowley WH, Sato S, Gardner JD (1989) Interaction of CCK with pancreatic acinar cells. Trends Pharmacol Sci 10:418–423
Kaufman J, Horn L, Carbone D (2011) Molecular biology of lung cancer. In: DeVita V Jr, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA (eds) Cancer: principles and practice of oncology. Williams & Wilkins Philadelphia, Lippincott, pp 789–798
Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J (2010) Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 141:1117–1134
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R et al (2004) Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350:2129–2139
Moody TW, Jensen RT (2001) CI-988 inhibits the growth of small cell lung cancer cells. J Pharmacol Expt Ther 299:1154–1160
Moody TW, Berna MJ, Mantey S et al (2010) Neuromedin B receptors regulate EGF receptor tyrosine phosphorylation in lung cancer cells. Eur J Pharm 637:38–45
Moody TW, Osefo N, Nuche-Berenguer B, Ridnour L, Wink D, Jensen RT (2012) Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide causes tyrosine phosphorylation of the EGF receptor in lung cancer cells. J Pharm Exp Ther 341:873–881
Moody T, Chan D, Mantey S, Moreno P, Jensen RT (2014) SR48692 inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer growth in an EGFR-dependent manner. Life Sci 10:25–34
Mutt V, Jorpes E (1971) Hormonal polypeptides of the upper intestine. Biochem J 125:57P–58P
Ocejo-Garcia M, Ahmed SI, Coulson JM, Woll PJ (2001) Use of RT-PCR to detect co-expression of neuropeptides and their receptors in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 33:1–9
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC et al (2004) EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304:1497–1500
Paulssen RH, Fraeyman N, Florholmen J (2000) Activation of phospholipase C by cholecystokinin receptor subtypes with different G-protein-coupling specificities in hormone-secreting pancreatic cell lines. Biochem Pharmacol 60:865–875
Piiper A, Elez R, You SJ et al (2003) Cholecystokinin stimulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase through activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor, yes and protein kinase C. Signal amplification at the level of Raf by activation of protein kinase C epsilon. J Biol Chem 278:7065–7072
Rehfeld JF (2006) Gastrin and cancer. In: Kastin A (ed) Handbook of biologically active peptides. Academic, Philadelphia, pp 467–471
Reubi JC, Schaer JC, Waser B (1997) Cholecystokinin (CCK)-A and CCK-B/gastrin receptors in human tumors. Cancer Res 57:1377–1386
Sethi T, Rozengurt E (1991) Multiple neuropeptides stimulate clonal growth of small cell lung cancer: effects of bradykinin, vasopressin, cholecystokinin, galanin and neurotensin. Cancer Res 51:3621–3623
Sethi T, Herget T, Wu SV, Walsh JH, Rozengurt E (1993) CCKA and CCKB receptors are expressed in small cell lung cancer lines and mediate Ca2+ mobilization and clonal growth. Cancer Res 53:5208–5213
Seva C, Kowalski-Chauvel A, Daulhac L et al (1997) Wortmannin-sensitive activation of p70S6-kinase and MAP-kinase by the G protein-coupled receptor, G/CCKB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 238:202–206
Sinclair NF, Ai W, Raychowdhury R et al (2004) Gastrin regulates the heparin-binding epidermal-like growth factor promoter via a PKC/EGFR dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 286:G992–G999
Staley J, Fiskum G, Moody TW (1989) Cholecystokinin elevates cytosolic calcium in small cell lung cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163:605–610
Staley J, Jensen RT, Moody TW (1990) CCK antagonists interact with CCK-B receptors on human small cell lung cancer cells. Peptides 11:1033–1036
Stepan VM, Tatewaki M, Matsushima M et al (1999) Gastrin induces c-fos gene transcription via multiple signaling pathways. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 276:G415–G424
Tsutsui S, Shinomura Y, Higashiyama S et al (1997) Induction of heparin binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor and amphiregulin mRNAs by gastrin in rat stomach. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 235:520–523
Vatinel S, Ferrand A, Lopez F et al (2006) An ITIM-like motif within the CCK2 receptor sequence required for interaction with SHP-2 and the activation of the AKT pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763:1098–1107
Wang RY, Hu XT (1986) Does cholecystokinin potentiate dopamine action in the nucleus accumbens? Brain Res 380:363–367
Wank SA (1998) G protein-coupled receptors in gastrointestinal physiology. I. CCK receptors: an exemplary family. Am J Physiol 274:G607–G613
Whitmarsh AJ, Davies RJ (1996) Transcription factor AP-1 regulation by mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways. J Mol Med 74:589–607
Wroblewski LE, Pritchard DM, Carter S, Varro A (2002) Gastrin-stimulated gastric epithelial cells invasion: the role and mechanism of increased matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression. Biochem J 365:873–879
Yoder D, Moody TW (1987) Cholecystokinin binds with high affinity to small cell lung cancer cells. Peptides 8:103–107
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. J. Hughes for the CI-988 and Dr. D. Chan for the helpful discussions. This research is supported by the NIH intramural programs of NIDDK and NCI.
Conflict of Interest
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moody, T.W., Nuche-Berenguer, B., Moreno, P. et al. CI-988 Inhibits EGFR Transactivation and Proliferation Caused by Addition of CCK/Gastrin to Lung Cancer Cells. J Mol Neurosci 56, 663–672 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0533-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0533-6