Abstract
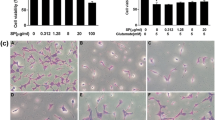
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress has been demonstrated to contribute to neurodegeneration in multiple nervous system diseases. Wogonin is a flavonoid isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis root and has multiple pharmacological effects, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer effects. It has a protective role in nervous system diseases; however, the pharmacological function of wogonin in the spinal cord is still with limited acquaintance. In the present study, rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons were pretreated with different concentrations of wogonin (0–100 μM) before inducing ER stress using tunicamycin (TUN) (0.75 μg/ml). Wogonin pretreatment at 75 and 100 μM had a cytoprotective effect on cells against TUN-induced toxicity. Wogonin also decreased the number of the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL)-positive DRG neurons and increased expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD), which was accompanied by decreased malondialdehyde (MDA) level. The induction of apoptosis was prevented with reduction in expression level of Bax and concomitant increase in B cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) level. Furthermore, wogonin downregulated expression level of ER stress genes coding for glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), active caspase 12, transcription factor 4 (ATF4), and phosphorylation of pancreatic ER stress kinase (PERK) and eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha (eIF2α). The current study indicated that wogonin modulated stress-responsive genes, helping DRG neurons prevent TUN-induced ER stress through the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badiola N, Penas C, Minano-Molina A, Barneda-Zahonero B, Fado R, Sanchez-Opazo G, Comella JX, Sabria J, Zhu C, Blomgren K, Casas C, Rodriguez-Alvarez J (2011) Induction of ER stress in response to oxygen-glucose deprivation of cortical cultures involves the activation of the PERK and IRE-1 pathways and of caspase-12. Cell Death Dis 2:e149
Chen CC, Hung TH, Wang YH, Lin CW, Wang PY, Lee CY, Chen SF (2012) Wogonin improves histological and functional outcomes, and reduces activation of TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling after experimental traumatic brain injury. PLoS One 7:e30294
Cho J, Lee HK (2004a) Wogonin inhibits excitotoxic and oxidative neuronal damage in primary cultured rat cortical cells. Eur J Pharmacol 485:105–110
Cho J, Lee HK (2004b) Wogonin inhibits ischemic brain injury in a rat model of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion. Biol Pharm Bull 27:1561–1564
Cribb AE, Peyrou M, Muruganandan S, Schneider L (2005) The endoplasmic reticulum in xenobiotic toxicity. Drug Metab Rev 37:405–442
Ding W, Yang L, Zhang M, Gu Y (2012) Reactive oxygen species-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to aldosterone-induced apoptosis in tubular epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 418:451–456
Eymin B, Dubrez L, Allouche M, Solary E (1997) Increased GADD153 messenger RNA level is associated with apoptosis in human leukemic cells treated with etoposide. Cancer Res 57:686–695
Friedman AD (1996) GADD153/CHOP, a DNA damage-inducible protein, reduced CAAT/enhancer binding protein activities and increased apoptosis in 32D c13 myeloid cells. Cancer Res 56:3250–3256
Gasiorowski K, Lamer-Zarawska E, Leszek J, Parvathaneni K, Yendluri BB, Blach-Olszewska Z, Aliev G (2011) Flavones from root of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi: drugs of the future in neurodegeneration? CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 10:184–191
Gawel S, Wardas M, Niedworok E, Wardas P (2004) Malondialdehyde (MDA) as a lipid peroxidation marker. Wiad Lek 57:453–455
Harding HP, Zhang Y, Bertolotti A, Zeng H, Ron D (2000) Perk is essential for translational regulation and cell survival during the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell 5:897–904
Hitomi J, Katayama T, Eguchi Y, Kudo T, Taniguchi M, Koyama Y, Manabe T, Yamagishi S, Bando Y, Imaizumi K, Tsujimoto Y, Tohyama M (2004) Involvement of caspase-4 in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and Abeta-induced cell death. J Cell Biol 165:347–356
Jana A, Hogan EL, Pahan K (2009) Ceramide and neurodegeneration: susceptibility of neurons and oligodendrocytes to cell damage and death. J Neurol Sci 278:5–15
Kim I, Xu W, Reed JC (2008) Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:1013–1030
Lai E, Teodoro T, Volchuk A (2007) Endoplasmic reticulum stress: signaling the unfolded protein response. Physiol (Bethesda) 22:193–201
Lee H, Kim YO, Kim H, Kim SY, Noh HS, Kang SS, Cho GJ, Choi WS, Suk K (2003a) Flavonoid wogonin from medicinal herb is neuroprotective by inhibiting inflammatory activation of microglia. FASEB J 17:1943–1944
Lin CC, Kuo CL, Lee MH, Lai KC, Lin JP, Yang JS, Yu CS, Lu CC, Chiang JH, Chueh FS, Chung JG (2011) Wogonin triggers apoptosis in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells through the endoplasmic reticulum stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and caspase-3-dependent signaling pathways. Int J Oncol 39:217–224
Lindholm D, Wootz H, Korhonen L (2006) ER stress and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Death Differ 13:385–392
Liu XD, Ko S, Xu Y, Fattah EA, Xiang Q, Jagannath C, Ishii T, Komatsu M, Eissa NT (2012) Transient aggregation of ubiquitinated proteins is a cytosolic unfolded protein response to inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem 287:19687–19698
Liu YM, Wang X, Nawaz A, Kong ZH, Hong Y, Wang CH, Zhang JJ (2011) Wogonin ameliorates lipotoxicity-induced apoptosis of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells via interfering with DAG-PKC pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32:1475–1482
Li-Weber M (2009) New therapeutic aspects of flavones: the anticancer properties of Scutellaria and its main active constituents wogonin, baicalein and baicalin. Cancer Treat Rev 35:57–68
McCullough KD, Martindale JL, Klotz LO, Aw TY, Holbrook NJ (2001) Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress by down-regulating Bcl2 and perturbing the cellular redox state. Mol Cell Biol 21:1249–1259
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, Yuan J (2000) Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta. Nat 403:98–103
Nakamura N, Hayasaka S, Zhang XY, Nagaki Y, Matsumoto M, Hayasaka Y, Terasawa K (2003) Effects of baicalin, baicalein, and wogonin on interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 expression, and nuclear factor-kappab binding activities induced by interleukin-1beta in human retinal pigment epithelial cell line. Exp Eye Res 77:195–202
Ohri SS, Hetman M, Whittemore SR (2013) Restoring endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Neurobiol Dis 58:29–37
Ohri SS, Maddie MA, Zhao Y, Qiu MS, Hetman M, Whittemore SR (2011) Attenuating the endoplasmic reticulum stress response improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Glia 59:1489–1502
Oyadomari S, Koizumi A, Takeda K, Gotoh T, Akira S, Araki E, Mori M (2002) Targeted disruption of the CHOP gene delays endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated diabetes. J Clin Invest 109:525–532
Penas C, Guzman MS, Verdu E, Fores J, Navarro X, Casas C (2007) Spinal cord injury induces endoplasmic reticulum stress with different cell-type dependent response. J Neurochem 102:1242–1255
Piao HZ, Jin SA, Chun HS, Lee JC, Kim WK (2004) Neuroprotective effect of wogonin: potential roles of inflammatory cytokines. Arch Pharm Res 27:930–936
Podratz JL, Windebank AJ (2005) NGF rescues DRG neurons in vitro from oxidative damage produced by hemodialyzers. Neurotoxicol 26:343–350
Puthalakath H, O’Reilly LA, Gunn P, Lee L, Kelly PN, Huntington ND, Hughes PD, Michalak EM, McKimm-Breschkin J, Motoyama N, Gotoh T, Akira S, Bouillet P, Strasser A (2007) ER stress triggers apoptosis by activating BH3-only protein Bim. Cell 129:1337–1349
Saleh M, Vaillancourt JP, Graham RK, Huyck M, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Steinberg MH, Nolan V, Baldwin CT, Hotchkiss RS, Buchman TG, Zehnbauer BA, Hayden MR, Farrer LA, Roy S, Nicholson DW (2004) Differential modulation of endotoxin responsiveness by human caspase-12 polymorphisms. Nat 429:75–79
Soboloff J, Berger SA (2002) Sustained ER Ca2+ depletion suppresses protein synthesis and induces activation-enhanced cell death in mast cells. J Biol Chem 277:13812–13820
Son D, Lee P, Lee J, Kim H, Kim SY (2004) Neuroprotective effect of wogonin in hippocampal slice culture exposed to oxygen and glucose deprivation. Eur J Pharmacol 493:99–102
Song X, Yao J, Wang F, Zhou M, Zhou Y, Wang H, Wei L, Zhao L, Li Z, Lu N, Guo Q (2013) Wogonin inhibits tumor angiogenesis via degradation of HIF-1alpha protein. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 271:144–155
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM, Samali A (2006) Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep 7:880–885
Tsai CF, Yeh WL, Huang SM, Tan TW, Lu DY (2012) Wogonin induces reactive oxygen species production and cell apoptosis in human glioma cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 13:9877–9892
Tsuchida M, Nakamachi T, Sugiyama K, Tsuchikawa D, Watanabe J, Hori M, Yoshikawa A, Imai N, Kagami N, Matkovits A, Atsumi T, Shioda S (2014) PACAP stimulates functional recovery after spinal cord injury through axonal regeneration. J Mol Neurosci
Wang F, Song X, Zhou M, Wei L, Dai Q, Li Z, Lu N, Guo Q (2013) Wogonin inhibits H2O2-induced vascular permeability through suppressing the phosphorylation of caveolin-1. Toxicol 305:10–19
Wang NS, Unkila MT, Reineks EZ, Distelhorst CW (2001) Transient expression of wild-type or mitochondrially targeted Bcl-2 induces apoptosis, whereas transient expression of endoplasmic reticulum-targeted Bcl-2 is protective against Bax-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 276:44117–44128
Wang XZ, Ron D (1996) Stress-induced phosphorylation and activation of the transcription factor CHOP (GADD153) by p38 MAP Kinase. Sci 272:1347–1349
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ (2001) Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Sci 292:727–730
Xu D, Zhao W, Pan G, Qian M, Zhu X, Liu W, Cai G, Cui Z (2014) Expression of Nemo-like kinase after spinal cord injury in rats. J Mol Neurosci 52:410–418
Xu M, Lu N, Zhang H, Dai Q, Wei L, Li Z, You Q, Guo Q (2013) Wogonin induced cytotoxicity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activation of unfolded protein response and inactivation of AKT. Hepatol Res: Off J Japan Soc Hepatol 43:890–905
Yang Y, Li XJ, Chen Z, Zhu XX, Wang J, Zhang LB, Qiang L, Ma YJ, Li ZY, Guo QL, You QD (2012) Wogonin induced calreticulin/annexin A1 exposure dictates the immunogenicity of cancer cells in a PERK/AKT dependent manner. PLoS One 7:e50811
Yu X, Wen H, Cao J, Sun B, Ding T, Li M, Wu H, Long L, Cheng X, Xu G, Zhang F (2013) Temporal and spatial expression of KIF3B after acute spinal cord injury in adult rats. J Mol Neurosci 49:387–394
Zha BS, Zhou H (2012) ER stress and lipid metabolism in adipocytes. Biochem Res Int 2012:312943
Zhang J, Li D, Shen A, Mao H, Jin H, Huang W, Xu D, Fan J, Chen J, Yang L, Cui Z (2013) Expression of RBMX after spinal cord injury in rats. J Mol Neurosci 49:417–429
Zhou J, Liu CY, Back SH, Clark RL, Peisach D, Xu Z, Kaufman RJ (2006) The crystal structure of human IRE1 luminal domain reveals a conserved dimerization interface required for activation of the unfolded protein response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:14343–14348
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Fangyi Chen and Rongbo Wu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, F., Wu, R., Zhu, Z. et al. Wogonin Protects Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons Against Tunicamycin-Induced ER Stress Through the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 Signaling Pathway. J Mol Neurosci 55, 995–1005 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0456-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0456-7