Abstract
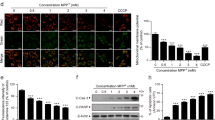
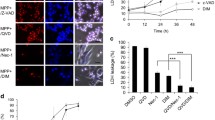
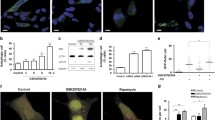
Neuronal cell cycle reentry maintained in a G2-like state before cell death, has been confirmed in dopaminergic neurons of patients with Parkinson's disease (PD). Caspase-3 is a final effector in apoptotic dopaminergic neurons in patients. The association of aberrant G2/M regulation with caspase-3 dependent apoptosis remains to be elucidated. Cell division cycle protein 2 (Cdc2) is a key player in G2/M transition in mitotic cells. Although the deregulation of Cdc2 correlated with the control of apoptosis in neurons, the molecular pathway by which Cdc2 involves in apoptosis is not clear. In a rotenone-based cell model of PD, we demonstrated that rotenone arrested cell cycle at G2/M phase and activated caspase-3 both in cytoplasm and nucleus. The decreased activity of Cdc2 by roscovitine or rotenone enhanced G2/M arrest. The increased cells in G2/M arrest by rotenone upregulated the expression of Cdc2. Suppression of Cdc2 expression downregulated cleaved caspase-3/9 and delayed cell apoptosis. Used together, the upregulation of Cdc2 contributes to rotenone-induced caspase-3/9-dependent apoptosis, which is associated with the enhancement of G2/M arrest. Our results suggest the deregulation of Cdc2 as a transition between cell cycle arrest and cell death.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Betarbet R, Anderson LR, Gearing M, Hodges TR, Fritz JJ, Lah JJ, Levey AI (2008) Fas-associated factor 1 and Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis 31:309–315
Buttitta LA, Katzaroff AJ, Edgar BA (2010) A robust cell cycle control mechanism limits E2F-induced proliferation of terminally differentiated cells in vivo. J Cell Biol 189:981–996
Cabeza-Arvelaiz Y, Schiestl RH (2012) Transcriptome analysis of a rotenone model of parkinsonism reveals complex I-tied and -untied toxicity mechanisms common to neurodegenerative diseases. PLoS One 7:e44700
Chadebech P, Truchet I, Brichese L, Valette A (2000) Up-regulation of cdc2 protein during paclitaxel-induced apoptosis. Int J Cancer 87:779–786
Cheung YT, Lau WK, Yu MS, Lai CS, Yeung SC, So KF, Chang RC (2009) Effects of all-trans-retinoic acid on human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma as in vitro model in neurotoxicity research. Neurotoxicology 30:127–135
Colell A, Green DR, Ricci JE (2009) Novel roles for GAPDH in cell death and carcinogenesis. Cell Death Differ 16:1573–1581
Currais A, Hortobágyi T, Soriano S (2009) The neuronal cell cycle as a mechanism of pathogenesis in Alzheimer's disease. Aging 1:363–371
Darzynkiewicz Z, Juan G, Bedner E (2001) Determining cell cycle stages by flow cytometry. Curr Protoc Cell Biol 8:8.4. doi: 10.1002/0471143030.cb0804s01
Demir O, Singh S, Klimaschewski L, Kurnaz IA (2009) From birth till death: neurogenesis, cell cycle, and neurodegeneration. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 292:1953–1961
El-Khodor BF, Oo TF, Kholodilov N, Burke RE (2003) Ectopic expression of cell cycle markers in models of induced programmed cell death in dopamine neurons of the rat substantia nigra pars compacta. Exp Neurol 179:17–27
Florentin A, Arama E (2012) Caspase levels and execution efficiencies determine the apoptotic potential of the cell. J Cell Biol 196:513–527
Folch J, Junyent F, Verdaguer E, Auladell C, Pizarro JG, Beas-Zarate C, Pallàs M, Camins A (2012) Role of cell cycle re-entry in neurons: a common apoptotic mechanism of neuronal cell death. Neurotox Res 22:195–207
Frade JM, López-Sánchez N (2010) A novel hypothesis for Alzheimer disease based on neuronal tetraploidy induced by p75 (NTR). Cell Cycle 9:1934–1941
Goodyear S, Sharma MC (2007) Roscovitine regulates invasive breast cancer cell (MDA-MB231) proliferation and survival through cell cycle regulatory protein cdk5. Exp Mol Pathol 82:25–32
Gu L, Zheng H, Murray SA, Ying H, Jim Xiao ZX (2003) Deregulation of Cdc2 kinase induces caspase-3 activation and apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 302:384–391
Hartmann A, Hunot S, Michel PP, Muriel MP, Vyas S, Faucheux BA, Mouatt-Prigent A, Turmel H, Srinivasan A, Ruberg M, Evan GI, Agid Y, Hirsch EC (2000) Caspase-3: a vulnerability factor and final effector in apoptotic death of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:2875–2880
Hilton GD, Stoica BA, Byrnes KR, Faden AI (2008) Roscovitine reduces neuronal loss, glial activation, and neurologic deficits after brain trauma. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:1845–1859
Höglinger GU, Breunig JJ, Depboylu C, Rouaux C, Michel PP, Alvarez-Fischer D, Boutillier AL, Degregori J, Oertel WH, Rakic P, Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2007) The pRb/E2F cell-cycle pathway mediates cell death in Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:3585–3590
Huang J, Xiong N, Chen C, Xiong J, Jia M, Zhang Z, Cao X, Liang Z, Sun S, Lin Z, Wang T (2011) Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: activity inhibition and protein overexpression in rotenone models for Parkinson's disease. Neuroscience 192:598–608
Kamada S, Kikkawa U, Tsujimoto Y, Hunter T (2005) Nuclear translocation of caspase-3 is dependent on its proteolytic activation and recognition of a substrate-like protein(s). J Biol Chem 280:857–860
Kuo PL, Hsu YL, Cho CY (2006) Plumbagin induces G2-M arrest and autophagy by inhibiting the AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 5:3209–3221
Larkins BA, Dilkes BP, Dante RA, Coelho CM, Woo YM, Liu Y (2001) Investigating the hows and whys of DNA endoreduplication. J Exp Bot 52:183–192
Li J, Spletter ML, Johnson DA, Wright LS, Svendsen CN, Johnson JA (2005) Rotenone-induced caspase 9/3-independent and -dependent cell death in undifferentiated and differentiated human neural stem cells. J Neurochem 92:462–466
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Lopes FM, Schröder R, da Frota ML, Zanotto-Filho A Jr, Müller CB, Pires AS, Meurer RT, Colpo GD, Gelain DP, Kapczinski F, Moreira JC, Fernandes Mda C, Klamt F (2010) Comparison between proliferative and neuron-like SH-SY5Y cells as an in vitro model for Parkinson disease studies. Brain Res 1337:85–94
Oo TF, Siman R, Burke RE (2002) Distinct nuclear and cytoplasmic localization of caspase cleavage products in two models of induced apoptoticdeath in dopamine neurons of the substantia nigra. Exp Neurol 175:1–9
Pompeiano M, Blaschke AJ, Flavell RA, Srinivasan A, Chun J (2000) Decreased apoptosis in proliferative and postmitotic regions of the caspase 3-deficient embryonic central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 423:1–12
Rigolio R, Miloso M, Nicolini G, Villa D, Scuteri A, Simone M, Tredici G (2005) Resveratrol interference with the cell cycle protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell from paclitaxel-induced apoptosis. Neurochem Int 46:205–211
Sherer TB, Kim JH, Betarbet R, Greenamyre JT (2003) Subcutaneous rotenone exposure causes highly selective dopaminergic degeneration and alpha-synuclein aggregation. Exp Neurol 179:9–16
Sundararaj KP, Wood RE, Ponnusamy S, Salas AM, Szulc Z, Bielawska A, Obeid LM, Hannun YA, Ogretmen B (2004) Rapid shortening of telomere length in response to ceramide involves the inhibition of telomere binding activity of nuclear glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 279:6152–6162
Taylor WR, Stark GR (2001) Regulation of the G2/M transition by p53. Oncogene 20:1803–1815
Vincent I, Jicha G, Rosado M, Dickson DW (1997) Aberrant expression of mitotic cdc2/cyclin B1 kinase in degenerating neurons of Alzheimer's disease brain. J Neurosci 17:3588–3598
Yam CH, Siu WY, Lau A, Poon RY (2000) Degradation of cyclin A does not require its phosphorylation by CDC2 and cyclin-dependent kinase 2. J Biol Chem 275:3158–3167
Yang Y, Mufson EJ, Herrup K (2003) Neuronal cell death is preceded by cell cycle events at all stages of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 23:2557–2563
Yap YW, Chen MJ, Peng ZF, Manikandan J, Ng JM, Llanos RM, La Fontaine S, Beart PM, Cheung NS (2013) Gene expression profiling of rotenone-mediated cortical neuronal death: evidence for inhibition of ubiquitin–proteasome system and autophagy–lysosomal pathway, and dysfunction of mitochondrial and calcium signaling. Neurochem Int 62:653–663
Zhu X, Siedlak SL, Wang Y, Perry G, Castellani RJ, Cohen ML, Smith MA (2008) Neuronal binucleation in Alzheimer disease hippocampus. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 34:457–465
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants (No. 81071021 and No. 31171211) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (to Tao Wang), grant (No. 81100958) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (to Zhentao Zhang), grant (No. 81200983) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (to Nian Xiong), grant (No. 2012B09) from the China Medical Foundation (to Nian Xiong).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hongcai Wang and Zhentao Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Zhang, Z., Huang, J. et al. The Contribution of Cdc2 in Rotenone-Induced G2/M Arrest and Caspase-3-Dependent Apoptosis. J Mol Neurosci 53, 31–40 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0185-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0185-3