Abstract
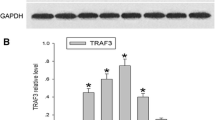
Some receptors that block axonal regeneration or promote cell death after spinal cord injury (SCI) are localized in membrane rafts. Flotillin-2 (Flot-2) is an essential protein associated with the formation of these domains and the clustering of membranal proteins, which may have signaling activities. Our hypothesis is that trauma will change Flot-2 expression and interference of this lipid raft marker will promote functional locomotor recovery after SCI. Analyses were conducted to determine the spatiotemporal profile of Flot-2 expression in adult rats after SCI, using the MASCIS impactor device. Immunoblots showed that SCI produced a significant decrease in the level of Flot-2 at 2 days post-injury (DPI) that increased until 28 DPI. Confocal microscopy revealed Flot-2 expression in neurons, reactive astrocytes and oligodendrocytes specifically associated to myelin structures near or close to the axons of the cord. In the open field test and grid walking assays, to monitor locomotor recovery of injured rats infused intrathecally with Flot-2 antisense oligonucleotides for 28 days showed significant behavioral improvement at 14, 21 and 28 DPI. These findings suggest that Flot-2 has a role in the nonpermissive environment that blocks locomotor recovery after SCI by clustering unfavorable proteins in membrane rafts.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn M, Kim H, Kim JT et al (2006) Gamma-ray irradiation stimulates the expression of caveolin-1 and GFAP in rat spinal cord: a study of immunoblot and immunohistochemistry. J Vet Sci 7:309–314
Asano A, Selvaraj V, Buttke DE et al (2009) Biochemical characterization of membrane fractions in murine sperm: identification of three distinct sub-types of membrane rafts. J Cell Physiol 218:537–548
Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC (1995) A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma 12:1–21
Benson MD, Romero MI, Lush ME, Lu QR, Henkemeyer M, Parada LF (2005) Ephrin-B3 is a myelin-based inhibitor of neurite outgrowth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 26:10694–10699
Bickel PE, Scherer PE, Scnitzer JE, Oh P, Lisanti MP, Lodish HF (1997) Flotillin and epidermal surface antigen define a new family of caveolae-associated integral membrane proteins. J Biol Chem 272:13793–13802
Boynapalli M, Kottis V, Lahoud O, Bamri-Ezzine S, Braun PE, Mikol DD (2005) Oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein is present in lipid rafts and caveolin-1-enriched membranes. Glia 52:219–227
Busch SA, Silver J (2007) The role of extracellular matrix in CNS regeneration. Curr Opin Neurobiol 17:120–127
Calvo AC, Moreno-Igoa M, Manzano R et al (2008) Determination of protein and RNA expression levels of common housekeeping genes in a mouse model of neurodegeneration. Proteomics 8:4338–4343
Cho YJ, Chema D, Moskow JJ et al (1995) Epidermal surface antigen (MS17S1) is highly conserved between mouse and human. Genomics 27:251–258
Cruz-Orengo L, Figueroa JD, Velazquez I et al (2006) Blocking EphA4 uregulation after spinal cord injury results in enhanced chronic pain. Exp Neurol 202:421–433
Davis AR, Lotocki G, Marciallo AE, Dietrich WD, Keane RW (2007) FasL, Fas and death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) proteins are recruited to membrane rafts after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 5:823–834
DeBruin LS, Haines JD, Bienzle D, Harauz G (2006) Partitioning of myelin basic protein into membrane microdomains in a spontaneously demyelinating mouse model for multiple sclerosis. Biochem Cell Biol 84:993–1005
Fawcett JW (2006) Overcoming inhibition in the damaged spinal cord. J Neurotrauma 23:371–383
Figueroa JD, Benton RL, Velazquez I et al (2006) Inhibition of EphA7 up-regulation after spinal cord injury reduces apoptosis and promotes locomotor recovery. J Neurosci Res 84:1438–1451
Fundytus ME, Yashpal K, Chabot JG et al (2001) Knockdown of spinal metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR(1)) alleviates pain and restores opioid efficacy after nerve injury in rats. Br J Pharmacol 132:354–367
Gajate C, Mollinedo F (2001) The antitumor ether lipid ET-18-OCH3 induces apoptosis through translocation and capping of Fas/CD95 into membrane rafts in human leukemic cells. Blood 98:3860–3863
Gajate C, Mollinedo F (2005) Cytoskeleton-mediated death receptor and ligand concentration in lipid rafts forms apoptosis-promoting clusters in cancer chemotherapy. J Biol Chem 280:11641–11647
Galbiati F, Volonte D, Gil O et al (1998) Expression of caveolin-1 and -2 in differentiating PC12 cells and dorsal root ganglion neurons: caveolin-2 is up-regulated in response to cell injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:10257–10262
Garcia-Alias G, Torres-Espin A, Vallejo C, Navarro X (2010) Functional involvement of the lumbar spinal cord after contusion to T8 spinal segment of the rat. Restor Neurol Neurosci 28:781–792
Gebreselassie D, Bowen WD (2004) Sigma-2 receptors are specifically localized to lipid rafts in rat liver membranes. Eur J Pharmacol 493:19–28
Hueber AO (2003) Role of membrane microdomain rafts in NFR-mediated signal transduction. Cell Death Differ 10:7–9
Hulsebosh CE (2005) From discovery to clinical trial: treatment trategies for central neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. Curr Pharm Des 11:1411–1420
Jacobowitz DM, Kallarakal AT (2004) Flotillin-1 in the substantia nigra of the Parkinson brain and a predominant localization in catecholaminergic nerves in the rat brain. Neurotox 6:245–257
Keane RW, Davis AR, Dietrich WD (2006) Inflammatory and apoptotic signaling after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 23:335–344
Kim H, Ahn M, Moon C, Matsumoto Y, Koh CS, Shin T (2006) Immunohistochemical study of flotillin-1 in the spinal cord of Lewis rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Res 1114:335–344
Klein R (2004) Eph/ephrin signaling in morphogenesis, neural development and plasticity. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16:580–589
Kokubo H, Lemere CA, Yamaguchi H (2000) Localization of flotillins in human brain and their accumulation with pregression of Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Neurosci Lett 290:93–96
Lai KO, Ip FC, Cheung J, Fu AK, Ip NY (2001) Expression of Eph receptors in skeletal muscle and their localization at the neuromuscular junction. Mol Cell Neurosci 17:1034–1047
Lang DM, Lommel S, Jung M et al (1998) Identification of Reggie-1 and Reggie-2 as plasmamembrane-associated proteins which cocluster with activated with activated GPI-anchored cell adhesion molecules in non-caveolar micropatches in neurons. J Neurobiol 37:502–523
Langhorst MF, Reuter A, Stuermer CA (2005) Scaffolding microdomains and beyond: the function of reggie/flotillin proteins. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:2228–2240
Liu BP, Cafferty WB, Budel SO, Strittmatter SM (2006) Extracellular regulators of axonal growth in the adult central nervous system. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 361:1593–1610
Lucero HA, Robbins PW (2004) Lipid rafts-protein association and the regulation of protein activity. Arch Biochem Biophys 426:208–224
Mairhofer M, Steiner M, Mosgoeller W, Prohaska R, Salzer U (2002) Stomatin is a major lipid-raft component of platelet alpha granules. Blood 100:897–904
Merkler D, Metz GAS, Raineteau O, Dietz V, Schwab ME, Fouad K (2001) Locomotor recovery in spinal cord-injured rats treated with an antibody neutralizing the myelin-associated neurite growth inhibitor Nogo-A. J Neurosci 21:3665–3673
Miranda JD, White LA, Marcillo AE, Willson CA, Jagid J, Whittemore SR (1999) Induction of Eph B3 after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 156:218–222
Mollinedo F, Gajate C (2010) Lipid rafts and clusters of apoptotic signaling molecule-enriched rafts in cancer therapy. Future Oncol 6:811–821
Munderloh M, Solis GP, Bodrikov V et al (2009) Reggies/flotillins regulate retinal axon regeneration in the zebrafish optic nerve and differentiation of hippocampal and N2a neurons. J Neurosci 20:6607–6615
Pasquale EB (2005) Eph receptor signalling casts a wide net on cell behavior. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:462–475
Pike LJ (2003) Lipid rafts: bringing order to chaos. J Lipid Res 44:655–667
Pike LJ (2004) Lipid rafts: heterogeneity on the high seas. Biochem J 378:281–292
Pike LJ (2006) Rafts defined: a report on the Keystone Symposium on Lipid Rafts and Cell Function. J Lipid Res 47:1597–1598
Rajendran L, Simons K (2005) Lipid rafts and membrane dynamics. J Cell Sci 118:1099–1102
Rouvinski A, Gahali-Sass I, Stav I, Metzer E, Atlan H, Taraboulos A (2003) Both raft- and non-raft proteins associate with CHAPS-insoluble complexes: some APP in large complexes. Biochem Biophysical Res Commun 308:750–758
Salgado IK, Serran M, Garcia JO, Martinez NA, Maldonado HM, Baez-Pagan CA, Lasalde-Dominicci JA, Silva WI (2012) SorLA in glia: shared subcellular distribution patterns with caveolin-1. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:409–421
Santamaria A, Castellanos E, Gomez V et al (2005) PTOV1 enables the nuclear translocation and mitegenic activity of Flotillin-1, a major protein of lipid rafts. Mol Cell Biol 25:1900–1911
Santiago JM, Rosas OR, Torrado AI, González MM, Kalyan-Masih PO, Miranda JD (2009) Molecular, anatomical, physiological and behavioral studies of rats treated with buprenorphine. J Neurotrauma 26:1783–1793
Schroeder WT, Stewart-Galetka S, Mandavilli S, Parryl DAD, Goldsmith L, Duvic M (1994) Cloning and characterization of a novel epidermal cell surface antigen (ESA). J Biol Chem 269:19983–19991
Schroeder RJ, Ahmed SN, Zhu Y, London E, Brown DA (1998) Cholesterol and sphingolipid enhance the Triton X-100 insolubility of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins by promoting the formation of detergent-insoluble ordered membrane domains. J Biol Chem 273:1150–1157
Schulte T, Paschke KA, Laessing U, Lottspeich F, Stuermer CA (1997) Reggie-1 and reggie-2, two cell surface proteins expressed by retinal ganglion cells during axon regeneration. Development 124:577–587
Shah MB, Sehgal PB (2007) Nondetergent isolation of rafts. Methods Mol Biol 398:21–28
Shin T (2007) Increases in the phosphorylated form of caveolin-1 in the spinal cord of rats with clip compression injury. Brain Res 1141:228–234
Silva WI, Maldonado HM, Lisanti MP et al (1999) Identification of caveolae and caveolin in C6 glioma cells. Int J Dev Neurosci 17:705–714
Silva WI, Maldonado HM, Velázquez G et al (2005) Caveolin isoform expression during differentiation of C6 glioma cells. Int J Dev Neurosci 7:599–612
Song KS, Li S, Okamoto T, Quilliam LA, Sargiacomo M, Lisanti MP (1996) Co-purification and direct interaction of Ras with Caveolin, an integral membrane protein of caveolae microdomains. J Biol Chem 271:9690–9697
Sugiyo S, Yonehara N, Appenteng K, Nokubi T, Shigenaga Y, Takemura M (2001) Effects of intrathecal c-fos antisense oligodeoxynucleotide on adjuvant-induced thermal hyperalgesia. Exp Brain Res 140:198–205
Vihanto MM, Vindis C, Djonov V, Cerreti DP, Huynh-Do U (2006) Caveolin-1 is required for signaling and membrane targeting of EphB1 receptor tyrosine kinase. J Cell Sci 119:2299–2309
White DM (2000) Neurotrophin-3 antisense oligonucleotide attenuates nerve injury-induced Abeta-fibre sprouting. Brain Res 885:79–86
Yaksh TL, Michener SR, Bailey JE et al (1988) Survey of distribution of substance P, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, cholecystokinin, neurotensin, Met-enkephalin, bombesin and PHI in the spinal cord of cat, dog, sloth and monkey. Peptides 9:357–372
Yu W, Guo W, Feng L (2004) Segregation of Nogo 66 receptors into lipid rafts in rat brain and inhibition of Nogo 66 signaling by cholesterol depletion. FEBS Lett 577:87–92
Yui G, He Z (2006) Glial inhibition of CNS axon regeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:617–627
Zhang H, Uchimura K, Kadomatsu K (2006) Brain keratan sulfate and glial scar formation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1086:81–90
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to the Experimental Surgery Facilities, the Animal Resource Center, the MBRS/SCORE Molecular Facilities and the RCMI Image Center at the UPR Medical Sciences Campus for the use of their facilities. This research project is in partial fulfillment of Mr. José M. Santiago’s doctoral dissertation. This work was supported by grants MBRS-RISE Program (R25-GM068138), MBRS/SCORE (S06-GM008224), NIH/NINDS (39405), M-RISP (532851), RCMI (G12RR03051) and the Associate Deanship of Biomedical Sciences and Graduate Studies of the UPR School of Medicine. Editorial support was provided by Dr. Mary Helen Mays, Puerto Rico Clinical and Translational Research Consortium, funded by the National Center for Research Resources (NCRR) (1U54RR026139-01A1), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official view of NCRR or NIH.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santiago, J.M., Torrado, A.I., Arocho, L.C. et al. Expression Profile of Flotillin-2 and Its Pathophysiological Role After Spinal Cord Injury. J Mol Neurosci 49, 347–359 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9873-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9873-7