Abstract
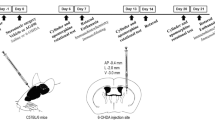
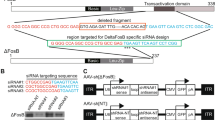
In this study, we investigated the protective role of silenced iNOS expression in neuron death in the nigrostriatal pathway in a 6-OHDA animal model of Parkinson’s disease (PD). The animal model was established by intrastriatal infusion of a single dose of 6-OHDA. Silencing of iNOS expression was established by intrastriatal infusion of adenovirus-carried iNOS-targeted small interfering RNA (siRNA). Apomorphine-induced rotation behavior was measured. Expression of iNOS, OX-42, and TH; levels of DA, DOPAC, and HVA in the striatum; and the levels of p53 phosphorylation, Bax, and cleaved caspase-3 (CC3) in the substantia nigra were measured. We demonstrated that co-infusion of 6-OHDA with adenovirus expressing siRNA of iNOS blocked the activation of microglia, iNOS transcription, and p53–Bax–CC3 apoptotic cascade as well as significantly blocking 6-OHDA-induced decreases in DA, DOPAC, HVA, and TH levels and effectively decreased rotation number. Our study highlighted the role of iNOS in the neurodegeneration of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons in the 6-OHDA animal model of PD and suggested that the microglial activation–iNOS–p53–Bax–CC3 apoptotic pathway plays a key role in the neurodegeneration in the 6-OHDA model.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athar M, Back JH, Kopelovich L, Bickers DR, Kim AL (2009) Multiple molecular targets of resveratrol: anti-carcinogenic mechanisms. Arch Biochem Biophys 486:95–102
Barthwal MK, Srivastava N, Dikshit M (2001) Role of nitric oxide in a progressive neurodegeneration model of Parkinson′s disease in the rat. Redox Rep 6:297–302
Ben-Shachar D, Youdim MB (1991) Intranigral iron injection induces behavioral and biochemical “parkinsonism” in rats. J Neurochem 57:2133–2135
Blandini F, Levandis G, Bazzini E, Nappi G, Armentero MT (2007) Time-course of nigrostriatal damage, basal ganglia metabolic changes and behavioural alterations following intrastriatal injection of 6-hydroxydopamine in the rat: new clues from an old model. Eur J Neurosci 25:397–405
Blandini F, Armentero MT, Martignoni E (2008) The 6-hydroxydopamine model: news from the past. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14:S124–129
Broom L, Marinova-Mutafchieva L, Sadeghian M, Davis JB, Medhurst AD, Dexter DT (2011) Neuroprotection by the selective iNOS inhibitor GW274150 in a model of Parkinson disease. Free Radic Biol Med 50:633–640
Chao OY, Huston JP, von Bothmer A, Pum ME (2011) Chronic progesterone treatment of male rats with unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesion of the dorsal striatum exasperates parkinsonian symptoms. Neuroscience 196:228–236
Coelln RV, Kugler S, Bahr M, Weller M, Dichgans J, Schulz JB (2001) Rescue from death but not from functional impairment: caspase inhibition protects dopaminergic cells against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis but not against the loss of their terminals. J Neurochem 77:263–273
Conti A, Miscusi M, Cardali S, Germanò A, Suzuki H, Cuzzocrea S, Tomasello F (2007) Nitric oxide in the injured spinal cord: synthases cross-talk, oxidative stress and inflammation. Brain Res Rev 54:205–218
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson′s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39:889–909
Dehmer T, Lindenau J, Haid S, Dichgans J, Schulz JB (2000) Deficiency of inducible nitric oxide synthase protects against MPTP toxicity in vivo. J Neurochem 74:2213–2216
Deumens R, Blokland A, Prickaerts J (2002) Modeling Parkinson′s disease in rats: an evaluation of 6-OHDA lesions of the nigrostriatal pathway. Exp Neurol 175:303–317
Hague S, Peuralinna T, Eerola J, Hellström O, Tienari PJ, Singleton AB (2004) Confirmation of the protective effect of iNOS in an independent cohort of Parkinson disease. Neurology 62:635–6
Hald A, Lotharius J (2005) Oxidative stress and inflammation in Parkinson′s disease: is there a causal link? Exp Neurol 193:279–290
Han BS, Hong HS, Choi WS, Markelonis GJ, Oh TH, Oh YJ (2003) Caspase-dependent and -independent cell death pathways in primary cultures of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons after neurotoxin treatment. J Neurosci 23:5069–5078
Hoang T, Choi DK, Nagai M, Wu DC, Nagata T, Prou D, Wilson GL, Vila M, Jackson-Lewis V, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Chesselet MF, Przedborski S (2009) Neuronal NOS and cyclooxygenase-2 contribute to DNA damage in a mouse model of Parkinson disease. Free Radic Biol Med 47:1049–1056
Holtz WA, Turetzky JM, Jong YJ, O’Malley KL (2006) Oxidative stress-triggered unfolded protein response is upstream of intrinsic cell death evoked by parkinsonian mimetics. J Neurochem 99:54–69
Holtz WA, O’Malley KL (2003) Parkinsonian mimetics induce aspects of unfolded protein response in death of dopaminergic neurons. J Biol Chem 278:19367–19377
Hunot S, Boissière F, Faucheux B, Brugg B, Mouatt-Prigent A, Agid Y, Hirsch EC (1996) Nitric oxide synthase and neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson′s disease. Neuroscience 72:355–363
Iravani MM, Kashefi K, Mander P, Rose S, Jenner P (2002) Involvement of inducible nitric oxide synthase in inflammation-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Neuroscience 110:49–58
Knott C, Stern G, Wilkin GP (2000) Inflammatory regulators in Parkinson′s disease: iNOS, lipocortin-1, and cyclooxygenases-1 and -2. Mol Cell Neurosci 16:724–739
Liberatore GT, Jackson-Lewis V, Vukosavic S, Mandir AS, Vila M, McAuliffe WG, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Przedborski S (1999) Inducible nitric oxide synthase stimulates dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP model of Parkinson disease. Nat Med 5:1403–1409
Liu B, Gao HM, Hong JS (2003) Parkinson′s disease and exposure to infectious agents and pesticides and the occurrence of brain injuries: role of neuroinflammation. Environ Health Perspect 111:1065–1073
Possel H, Noack H, Putzke J, Wolf G, Sies H (2000) Selective upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and cytokines in microglia: in vitro and in vivo studies. Glia 32:51–59
Okuno T, Nakatsuji Y, Kumanogoh A, Moriya M, Ichinose H, Sumi H, Fujimura H, Kikutani H, Sakoda S (2005) Loss of dopaminergic neurons by the induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 via CD 40: relevance to Parkinson′s disease. J Neurosci Res 81:874–882
O’Malley KL, Liu J, Lotharius J, Holtz W (2003) Targeted expression of BCL-2 attenuates MPP + but not 6-OHDA induced cell death in dopaminergic neurons. Neurobiol Dis 14:43–51
Rodrigues RW, Gomide VC, Chadi G (2001) Astroglial and microglial reaction after a partial nigrostriatal degeneration induced by the striatal injection of different doses of 6-hydroxydopamine. Int J Neurosci 109:91–126
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Academic, San Diego
Tieu K, Ischiropoulos H, Przedborski S (2003) Nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in Parkinson′s disease. IUBMB Life 55:329–335
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the China National High-tech project (grant No. 2007AA021809, 2007AA021803 to YC), the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (grant No. 30800518 to Chen Y), and the New Teachers of Doctor Fund Project of Ministry of Education (grant No. 200805331090 to Chen Y).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Dai, Fr., Du, Xp. et al. Neuroprotection by Silencing iNOS Expression in a 6-OHDA Model of Parkinson’s Disease. J Mol Neurosci 48, 225–233 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9814-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9814-5