Abstract
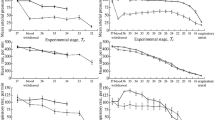
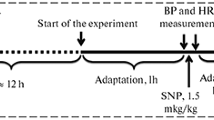
To investigate the effects of cold on blood pressure, serum endothelin-1 content, serum nitric oxide content, and morbidity of cerebral infarction, as well as assess the therapeutic effect of nimodipine. A total of 200 rats were initially assigned to a normal group (n = 10), sham group (n = 10), and carotid atherosclerosis group (n = 180), and subsequently the animals in the carotid atherosclerosis group were randomly assigned to three groups: non-cold (n = 59), cold treatment (n = 58), and nimodipine (n = 58). Rats in the cold and nimodipine groups experienced an artificial cold wave. The temperature was set at 22°C for 12 h (7:00 am to 7:00 pm) and then at 4°C for another 12 h (7:00 pm to 7:00 am), representing a cycle. The animals underwent three cycles of cold. Rats in the nimodipine group were treated with nimodipine and those in the cold group with given an equal volume of intragastric normal saline for 3 days. Hematoxylin and eosin staining showed features of carotid atherosclerosis in all animals. Blood pressure fluctuated with alteration of temperature. A temperature decrease was accompanied by an increase of blood pressure and elevation of serum levels of endothelium-1 and nitric oxide. In addition, although nimodipine could prevent the cold-induced increase of blood pressure and elevation of serum endothelium-1 and nitric oxide levels, it had no effect on blood pressure fluctuation or morbidity of cerebral infarction. The results suggest that dramatic variation in temperature is one of the main causes of cold-induced fluctuation of blood pressure.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adiarto S, Emoto N, Iwasa N, Yokoyama M (2007) Obesity-induced upregulation of myocardial endothelin-1 expression is mediated by leptin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 353:623–627
Boustany CM, Bharadwaj K, Daugherty A, Brown DR, Randall DC, Cassis LA (2004) Activation of the systemic and adipose renin–angiotensin system in rats with diet-induced obesity and hypertension. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 287:R943–R949
Chen TH, Tseng HP, Yang JY, Mao SJ (1998) Effect of antioxidant in endothelial cells exposed to oxidized low-density lipoproteins. Life Sci 62:PL277–PL282
Connor MD (2002) Does the weather influence stroke incidence? Stroke 33:1757–1758
Ebi KL, Exuzides KA, Lau E, Kelsh M, Barnston A (2004) Weather changes associated with hospitalizations for cardiovascular diseases and stroke in California, 1983–1998. Int J Biometeorol 49:48–58
Field ST, Hill DM (2002) Weather, Chinook, and stroke occurrence. Stroke 33:1751–1757
Furchgott RF, Zawadski JV (1980) The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature 288:373–376
Garcia JH, Wagner S, Liu KF, Hu XJ (1995) Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats: statistical validation. Stroke 26:627–634
Hirsch AT (2003) Vascular disease, hypertension and prevention: “from endothelium to clinical events”. J Am Coll Cardiol 42:377–379
Huang RX, Xiao XH, Li L (2001) Experimental study on the meteorological factors inducing the occurrence of stroke. Chin J Geriatr 20:366–368
Isezuo SA (2003) Seasonal variation in hospitalisation for hypertension-related morbidities in Sokoto, north-western Nigeria. Int J Circumpolar Health 62:397–409
Keatinge WR, Coleshaw SR, Cotter F, Mattock M, Murphy M, Chelliah R (1984) Increases in platelet and red cell counts, blood viscosity, and arterial pressure during mild surface cooling: factors in mortality from coronary and cerebral thrombosis in winter. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 289:1405–1408
Kyobutungi C, Grau A, Stieglbauer G, Becher H (2005) Absolute temperature, temperature changes and stroke risk: a case-crossover study. Eur J Epidemiol 20:693–698
Marasciulo FL, Montagnani M, Potenza MA (2006) Endothelin-1: the yin and yang on vascular function. Curr Med Chem 13:1655–1665
Martins MA, Catta-Preta M, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA et al (2010) High fat diets modulate nitric oxide biosynthesis and antioxidant defence in red blood cells from C57BL/6 mice. Arch Biochem Biophys 499:56–61
McArthur K, Dawson J, Walters M (2010) What is it with the weather and stroke? Expert Rev. Neurother 10:243–249
Morabito M, Crisci A, Vallorani R, Modesti PA, Gensini GF, Orlandini S (2011) Innovative approaches helpful to enhance knowledge on weather-related stroke events over a wide geographical area and a large population. Stroke 42:593–600
Neild PJ, Syndercombe-Court D, Keatinge WR, Donaldson GC, Mattock M, Caunce M (1994) Cold-induced increases in erythrocyte count, plasma cholesterol and plasma fibrinogen of elderly people without a comparable rise in protein C or factor X. Clin Sci (Lond) 86:43–48
Nomiya M, Sagawa K, Yazaki J et al (2012) Increased bladder activity is associated with elevated oxidative stress markers and proinflammatory cytokines in a rat model of atherosclerosis-induced chronic bladder ischemia. Neurourol Urodynam 31:185–189
Ozkan U, Aydin MD, Kemaloglu MS, Yilmaz F, Aydin IH (2004) Effect of nimodipine on histological alterations in basilar artery following the bilateral common carotid artery ligation (preliminary study). Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove) 47:7–12
Peltz A, Sherwani SI, Kotha SR et al (2009) Calcium and calmodulin regulate mercury-induced phospholipase D activation in vascular endothelial cells. Int J Toxicol 28:190–206
Petersson J, Andersson KE, Brandt L, Högestätt ED (1997) Modulation by the endothelium of the inhibitory effects of pinacidil and nimodipine on endothelin-induced contraction in cerebral arteries. Pharmacol Toxicol 80:30–37
Rahmouni K, Correia ML, Haynes WG, Mark AL (2005) Obesity-associated hypertension: new insights into mechanisms. Hypertension 45:9–14
Rosenthal T (2004) Seasonal variations in blood pressure. Am J Geriatr Cardiol 13:267–272
Rothwell PM, Howard SC, Dolan E et al (2010) Effects of beta blockers and calcium-channel blockers on within-individual variability in blood pressure and risk of stroke. Lancet Neurol 9:469–480
Sheu JR, Wu CH, Chen YC, Hsiao G, Lin CH (2001) Mechanisms in the inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia with triflavin in a rat model of balloon angioplasty. J Lab Clin Med 137:270–278
Sun Z, Wang X, Wood CE, Cade JR (2005) Genetic AT1A receptor deficiency attenuates cold-induced hypertension. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 288:R433–R439
Xu SY, Bian RL, Chen X (2001) Methodology of pharmacological experiments. People's Medical Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S et al (1988) A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature 332:411–415
You Y, Liu W, Li Y et al (2011) Joint preventive effects of swimming and Shenlian extract on rat atherosclerosis. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 47:187–198
Zhu D, Li R, Liu G, Hua W (1999) Nimodipine inhibits calcium-independent nitric oxide synthase activity in transient focal cerebral ischemia rats and cultured mouse astroglial cells. Life Sci 65:PL221–PL231
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, ZY., Zhu, QY., Xu, LJ. et al. Artificial Cold Wave-Induced Cerebral Infarction in Rats with Carotid Atherosclerosis. J Mol Neurosci 47, 278–285 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9735-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9735-3