Abstract
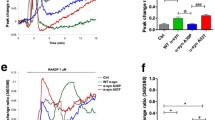
Duplication of alpha-synuclein gene (SNCA) is a recognized cause of Parkinson's disease (PD). However, the penetrance in families with SNCA duplication is as low as 30%, indicating that factors other than the SNCA gene dosage have an important role in neuronal death. In this study, using lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) derived from a parkinsonian kindred with SNCA duplication, we examined whether there is difference in (1) the level of SNCA mRNA and protein expression and cell viability and (2) the vulnerability to various insults relevant to PD between a patient, asymptomatic carrier, and unaffected control. Expression of SNCA mRNA and protein increased in the LCLs from subjects with SNCA gene duplication, irrespective of the disease status. In the absence of treatment, LCLs from the patient and carrier showed decreased viability compared with the LCL from the control. The LCL from the patient also showed decreased viability compared to the carrier. When susceptibility to various insults including lactacystin, dexamethasone, 3-methyladenine, H2O2, and rotenone was examined, surprisingly, the LCL from the patient was more resistant than the LCL from the control to all agents except for lactacystin. This study shows that both intrinsic and extrinsic factors and their interaction have important roles in cell death and in the development of PD and further indicates that the relationship between cell death and the level of alpha-synuclein may be more complicated than previously thought.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn TB, Kim S, Kim J, Park SS, Lee D, Min H et al (2008) α-Synuclein gene duplication is present in sporadic Parkinson disease. Neurology 70:43–49
Burbulla LF, Krüger R (2011) Converging environmental and genetic pathways in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci 306:1–8
Chartier-Harlin MC, Kachergus J, Roumier C, Mouroux V, Douay X, Lincoln S et al (2004) Alpha-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 364:1167–1169
Colapinto M, Mila S, Giraudo S, Stefanazzi P, Molteni M, Rossetti C et al (2006) Alpha-Synuclein protects SH-SY5Y cells from dopamine toxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 349:1294–1300
da Costa CA, Paitel E, Vincent B, Checler F (2002) α-synuclein lowers p53-dependent apoptotic response of neuronal cells. Abolishment by 6-hydroxydopamine and implication for Parkinson's disease. J Biol Chem 277:50980–50984
El-Agnaf O, Jakes R, Curran MD, Middleton D, Ingenito R, Bianchi E et al (1998) Aggregates from mutant and wild-type α-synuclein proteins and NAC peptide induce apoptotic cell death in human neuroblastoma cells by formation of β-sheet and amyloid-like filaments. FEBS Lett 440:71–75
Eriksen JL, Przedborski S, Petrucelli L (2005) Gene dosage and pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Trends Mol Med 11:91–96
Feany MB, Bender WW (2000) A Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease. Nature 404:394–398
Fuchs J, Tichopad A, Golub Y, Munz M, Schweitzer KJ, Wolf B et al (2008) Genetic variability in the SNCA gene influences α-synuclein levels in the blood and brain. FASEB J 22:1327–1334
Hashimoto M, Hsu LJ, Rockenstein E, Takenouchi T, Mallory M, Masliah E (2002) α-Synuclein protects against oxidative stress via inactivation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase stress-signaling pathway in neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 277:11465–11472
Ibanez P, Bonnet A, Debarges B, Lohmann E, Tison F, Pollak P et al (2004) Causal relation between α-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson's disease. Lancet 364:1169–1171
Ikeuchi T, Kakita A, Shiga A, Kasuga K, Kaneko H, Tan CF et al (2008) Patients homozygous and heterozygous for SNCA duplication in a family with parkinsonism and dementia. Arch Neurol 65:514–519
Kazantsev AG, Kolchinsky AM (2008) Central role of alpha-synuclein oligomers in neurodegeneration in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 65:1577–1581
Kim TD, Choi E, Rhim H, Paik SR, Yang CH (2004) α-Synuclein has structural and functional similarities to small heat shock proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 324:1352–1359
Lee JE, Nam HY, Shim SM, Bae GR, Han BG, Jeon JP (2010) Expression phenotype changes of EBV–transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines during long–term subculture and its clinical significance. Cell Prolif 43:378–384
Lee D, Paik SR, Choi KY (2004) β-Synuclein exhibits chaperone activity more efficiently than α-synuclein. FEBS Lett 576:256–260
Lee H, Zhu X, Takeda A, Perry G, Smith MA (2006) Emerging evidence for the neuroprotective role of α-synuclein. Exp Neurol 200:1–7
Manning-Boğ AB, McCormack AL, Purisai MG, Bolin LM, Di Monte DA (2003) α-Synuclein overexpression protects against paraquat-induced neurodegeneration. J Neurosci 23:3095–3099
Mata IF, Shi M, Agarwal P, Chung KA, Edwards KL, Factor SA et al (2010) SNCA variant associated with Parkinson disease and plasma α-synuclein level. Arch Neurol 67:1350–1356
Matsuoka Y, Vila M, Lincoln S, McCormack A, Picciano M, LaFrancois J et al (2001) Lack of nigral pathology in transgenic mice expressing human α-synuclein driven by the tyrosine hydroxylase promoter. Neurobiol Dis 8:535–539
Miller D, Hague S, Clarimon J, Baptista M, Gwinn-Hardy K, Cookson M et al (2004) α-Synuclein in blood and brain from familial Parkinson disease with SNCA locus triplication. Neurology 62:1835–1838
Mutez E, Leprêtre F, Le Rhun E, Larvor L, Duflot A, Mouroux V et al (2011) SNCA locus duplication carriers: from genetics to Parkinson disease phenotypes. Hum Mutat 32:E2079–2090
Nishioka K, Hayashi S, Farrer MJ, Singleton AB, Yoshino H, Imai H et al (2006) Clinical heterogeneity of α–synuclein gene duplication in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 59:298–309
Nishioka K, Ross OA, Ishii K, Kachergus JM, Ishiwata K, Kitagawa M et al (2009) Expanding the clinical phenotype of SNCA duplication carriers. Mov Disord 24:1811–1819
Quilty M, King A, Gai WP, Pountney D, West A, Vickers J et al (2006) Alpha-synuclein is upregulated in neurones in response to chronic oxidative stress and is associated with neuroprotection. Exp Neurol 199:249–256
Riebold M, Mankuta D, Lerer E, Israel S, Zhong S, Nemanov L et al (2011) All-trans retinoic acid upregulates reduced cd38 transcription in lymphoblastoid cell lines from autism spectrum disorder. Mol Med 17:799–806
Singleton A, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J et al (2003) Alpha-synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson's disease. Science 302:841
Sironi F, Trotta L, Antonini A, Zini M, Ciccone R, Della Mina E et al (2010) α-Synuclein multiplication analysis in Italian familial Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 16:228–231
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Virginia MYL, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840
Vekrellis K, Xilouri M, Emmanouilidou E, Rideout HJ, Stefanis L (2011) Pathological roles of α-synuclein in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol 10:1015–1025
Wu YR, Chen IC, Soong BW, Kao SH, Lee GC, Huang SY et al (2009) SCA8 repeat expansion: large CTA/CTG repeat alleles in neurological disorders and functional implications. Hum Genet 125:437–444
Xu J, Kao SY, Lee FJS, Song W, Jin LW, Yankner BA (2002) Dopamine-dependent neurotoxicity of α-synuclein: a mechanism for selective neurodegeneration in Parkinson disease. Nat Med 8:600–606
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HJ., Jeon, B.S., Yoon, MY. et al. Increased Expression of Alpha-Synuclein by SNCA Duplication is Associated with Resistance to Toxic Stimuli. J Mol Neurosci 47, 249–255 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9732-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9732-6