Abstract
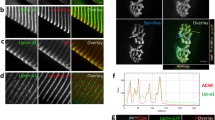
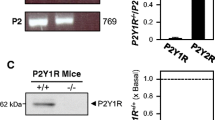
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is well known to process different molecular forms via the distinct interacting partners. Proline-rich membrane anchor (PRiMA)-linked tetrameric globular AChE (G4 AChE) is mainly found in the vertebrate brain; however, recent studies from our laboratory have suggested its existence at neuromuscular junctions (nmjs). Both muscle and motor neuron express AChE at the nmjs. In muscle, the expression of PRiMA-linked AChE is down-regulated during myogenic differentiation and by motor neuron innervation. As compared with muscle, spinal cord possessed higher total AChE activity and contained PRiMA-linked AChE forms. The spinal cord expression of this form increased during development. More importantly, PRiMA-linked G4 AChE identified as aggregates localized at nmjs. These findings suggest that the restricted localization of PRiMA-linked G4 AChE at the nmjs could be contributed by the pre-synaptic motor neuron and/or the post-synaptic muscle fiber.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anglister, L. (1991). Acetylcholinesterase from the motor nerve terminal accumulates on the synaptic basal lamina of the myofiber. Journal of Cell Biology, 115, 755–764.
Bacou, F. (1982). Acetylcholinesterase forms in fast and slow rabbit muscle. Nature, 296, 661–664.
Boudreau-Larivière, C., Chan, R. Y., Wu, J., & Jasmin, B. J. (2000). Molecular mechanisms underlying the activity-linked alterations in acetylcholinesterase mRNAs in developing versus adult rat skeletal muscles. Journal of Neurochemistry, 74, 2250–2258.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Choi, R. C. Y., Mok, M. K., Cheung, A. W., Siow, N. L., Xie, H. Q., & Tsim, K. W. K. (2008). Regulation of PRiMA-linked G4 AChE by a cAMP-dependent signaling pathway in cultured rat pheochromocyoma PC12 cells. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 175, 76–78.
De la Porte, S., Vallette, F. M., Grassi, J., Vigny, M., & Koenig, J. (1986). Presynaptic or postsynaptic origin of acetylcholinesterase in heterologous nerve-muscle cocultures. Developmental Biology, 116, 69–77.
Falasca, C., Perrier, N., Massoulié, J., & Bon, S. (2005). Determinants of the t peptide involved in folding, degradation and secretion of acetylcholinesterase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 878–886.
Jiang, J. X. S., Choi, R. C. Y., Siow, N. L., Lee, H. H. C., Wan, D. C. C., & Tsim, K. W. K. (2003). Muscle induces neuronal expression of acetylcholinesterase in neuron-muscle co-culture: Transcriptional regulation mediated by cAMP-dependent signaling. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 45435–45444.
Lee, H. H., Choi, R. C., Ting, A. K., Siow, N. L., Jiang, J. X., Massoulié, J., et al. (2004). Transcriptional regulation of acetylcholinesterase-associated collagen ColQ: Differential expression in fast and slow twitch muscle fibers is driven by distinct promoters. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 27098–27107.
Leung, K. W., Xie, H. Q., Chen, V. P., Mok, M. K. W., Chu, G. K. Y., Choi, R. C. Y., et al. (2009). Restricted localization of proline-rich membrane anchor (PRiMA) of globular form acetylcholinesterase at the neuromuscular junctions: Contribution and expression from motor neurons. FEBS J, 276, 3031–3042.
Loeb, J. A., & Fischbach, G. D. (1997). Neurotrophic factors increase neuregulin expression in embryonic ventral spinl cord neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 17, 1416–1424.
Lyles, J. M., Silman, I., & Barnard, E. A. (1979). Developmental changes in levels and forms of cholinesterases in muscles of normal and dystrophic chickens. Journal of Neurochemistry, 33, 727–738.
Massoulié, J. (1993). Molecular and cellular biology of cholinesterases. Progress in Neurobiology, 41, 31–91.
Massoulié, J. (2002). The origin of the molecular diversity and functional anchoring of cholinesterases. Neurosignals, 11, 130–143.
Massoulié, J., Bon, S., Perrier, N., & Falasca, C. (2005). The C-terminal peptides of acetylcholinesterase: Cellular trafficking, oligomerization and functional anchoring. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 157–158, 3–14.
McMahan, U. J., Sanes, J. R., & Marshall, L. M. (1987). Cholinesterase is associated with the asal lamina at the neuromuscular junction. Nature, 271, 172–174.
Perrier, A. L., Massoulié, J., & Krejci, E. (2002). PriMA: The membrane anchor of acetylcholinesterase in the brain. Neuron, 33, 275–285.
Perrier, N. A., Khérif, S., Perrier, A. L., Dumas, S., Mallet, J., & Massoulié, J. (2003). Expression of PRiMA in the mouse brain: Membrane anchoring and accumulation of ‘tailed’ acetylcholinesterase. European Journal of Neuroscience, 18, 1837–1847.
Tsim, K. W. K., Choi, R. C. Y., Dong, T. T. X., & Wan, D. C. C. (1997). A globular, not asymmetric, form of acetylcholinesterase is expressed in chick motor neurons: Down-regulation toward maturity and after denervation. Journal of Neurochemistry, 68, 479–487.
Wan, D. C., Ng, Y. P., Choi, R. C. Y., Cheung, P. W., Dong, T. T., & Tsim, K. W. K. (1997). Denervation decreases the ipsilateral expression of AChE in chick lumbric motor neurons. Neuroscience Letters, 232, 83–86.
Xie, H. Q., Choi, R. C. Y., Leung, K. W., Siow, N. L., Kong, L. W., Lau, F. T. C., et al. (2007). Regulation of a transcript encoding the proline-rich membrane anchor of globular muscle acatelycholinesterase. The suppressive roles of myogenesis and innervating nerves. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282, 11765–11775.
Xie, H. Q., Choi, R. C. Y., Leung, W. K. W., Chen, V. P., Chu, G. K. Y., & Tsim, K. W. K. (2009). Transcriptional regulation of proline-rich membrane anchor (PRiMA) of globular form acetylcholinesterase in neuron: An inductive effect of neuron differentiation. Brain Res, 1265, 13–23.
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by grants from Research Grants Council (HKUST6419/06M, 662407, 662608, and N_HKUST629/07) of the Hong Kong SAR to KWKT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Proceedings of the XIII International Symposium on Cholinergic Mechanisms
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsim, K.W.K., Leung, K.W., Mok, K.W. et al. Expression and Localization of PRiMA-Linked Globular Form Acetylcholinesterase in Vertebrate Neuromuscular Junctions. J Mol Neurosci 40, 40–46 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-009-9251-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-009-9251-2