Abstract
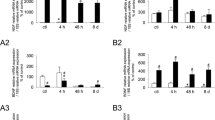
The expression of phosphorylated cAMP response element binding protein (p-CREB) in dorsal root ganglia (DRG) with and without cyclophosphamide (CYP)-induced cystitis (150 mg/kg, i.p; 48 h) was determined in VIP−/− and wild-type (WT) mice. p-CREB immunoreactivity (IR) was determined in bladder (Fast blue) afferent cells. Nerve growth factor (NGF) bladder content was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Basal expression of p-CREB-IR in DRG of VIP−/− mice was (p ≤ 0.01) greater in L1, L2, L5-S1 DRG compared to WT mice. CYP treatment in WT mice increased (p ≤ 0.05) p-CREB-IR in L1, L2, L5-S1 DRG. CYP treatment in VIP−/− mice (p ≤ 0.01) increased (p ≤ 0.01) p-CREB-IR in L6-S1 DRG compared to WT with CYP. In WT mice, bladder afferent cells (20–38%) in DRG expressed p-CREB-IR under basal conditions. With CYP, p-CREB-IR increased in bladder afferent cells (60–65%; L6-S1 DRG) in WT mice. In VIP−/− mice, bladder afferent cells (12–58%) expressed p-CREB-IR under basal conditions, and CYP increased p-CREB expression (78–84%) in L6-S1 DRG. Urinary bladder NGF expression in VIP−/− mice under basal conditions or after cystitis was significantly greater than WT. Detrusor smooth muscle thickness was significantly increased in VIP−/− mice. Bladder NGF expression may contribute to differences in p-CREB expression.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad, C., Martinez, C., Juarranz, M. G., et al. (2003). Therapeutic effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide in the trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid mice model of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology, 124, 961–971.
Amir, R., & Devor, M. (1996). Chemically mediated cross-excitation in rat dorsal root ganglia. Journal of Neuroscience, 16, 4733–4741.
Arthur, J. S., Fong, A. L., Dwyer, J. M., et al. (2004). Mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase 1 mediates cAMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation and activation by neurotrophins. Journal of Neuroscience, 24, 4324–4332.
Avelino, A., Cruz, C., & Cruz, F. (2002). Nerve growth factor regulates galanin and c-jun overexpression occurring in dorsal root ganglion cells after intravesical resiniferatoxin application. Brain Research, 951, 264–269.
Bancroft, J. D., & Stevens, A. (1990). Theory and practice of histological techniques. New York: Churchill Livingstone.
Bik, W., Wolinska-Witort, E., Chmielowska, M., Baranowska-Bik, A., Rusiecka-Kuczalek, E., & Baranowska, B. (2004). Vasoactive intestinal peptide can modulate immune and endocrine responses during lipopolysaccharide-induced acute inflammation. Neuroimmunomodulation, 11, 358–364.
Braas, K. M., May, V., Zvara, P., et al. (2006). Role for pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide in cystitis-induced plasticity of micturition reflexes. American Journal of Physiology. Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 290, R951–R962.
Chapple, C. R., Milner, P., Moss, H. E., & Burnstock, G. (1992). Loss of sensory neuropeptides in the obstructed human bladder. British Journal of Urology, 70, 373–381.
Chorny, A., Gonzalez-Rey, E., Varela, N., Robledo, G., & Delgado, M. (2006). Signaling mechanisms of vasoactive intestinal peptide in inflammatory conditions. Regulatory Peptide, 137, 67–74.
Colwell, C. S., Michel, S., Itri, J., Rodriguez, W., Tam, J., Lelievre, V., et al. (2003). Disrupted circadian rhythms in VIP- and PHI-deficient mice. American Journal of Physiology. Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 285, R939–949.
Cox, P. J. (1979). Cyclophosphamide cystitis—identification of acrolein as the causative agent. Biochemical Pharmacology, 28, 2045.
Delgado, M., Gomariz, R. P., Martinez, C., Abad, C., & Leceta, J. (2000). Anti-inflammatory properties of the type 1 and type 2 vasoactive intestinal peptide receptors: Role in lethal endotoxic shock. European Journal of Immunology, 30, 3236–3246.
Delgado, M., Munoz-Elias, E. J., Gomariz, R. P., & Ganea, D. (1999). Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide enhance IL-10 production by murine macrophages: In vitro and in vivo studies. Journal of Immunology, 162, 1707–1716.
Dickinson, T., Mitchell, R., Robberecht, P., & Fleetwood-Walker, S. M. (1999). The role of VIP/PACAP receptor subtypes in spinal somatosensory processing in rats with experimental peripheral mononeuropathy. Neuropharmacology, 38, 167–180.
Dmitrieva, N., Shelton, D., Rice, A. S. C., & McMahon, S. B. (1997). The role of nerve growth factor in a model of visceral inflammation. Neuroscience, 78, 449–459.
Donovan, M. K., Winternitz, S. R., & Wyss, J. M. (1983). An analysis of the sensory innervation of the urinary system of the rat. Brain Research Bulletin, 11, 321–324.
Driscoll, A., & Teichman, J. M. H. (2001). How do patients with interstitial cystitis present? Journal of Urology, 166, 2118–2120.
Erol, K., Ulak, G., Donmez, T., Cingi, M. I., Alpan, R. S., & Ozdemir, M. (1992). Effects of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide on isolated rat urinary bladder smooth muscle. Urology International, 49, 151–153.
Girard, B. A., Lelievre, V., Braas, K. M., et al. (2006). Noncompensation in peptide/receptor gene expression and distinct behavioral phenotypes in VIP- and PACAP-deficient mice. Journal of Neurochemistry, 99, 499–513.
Gold, B. G., Storm-Dickerson, T., & Austin, D. R. (1993). Regulation of the transcription factor c-JUN by nerve growth factor in adult sensory neurons. Neuroscience Letters, 154, 129–133.
Gonzalez-Rey, E., & Delgado, M. (2006). Therapeutic treatment of experimental colitis with regulatory dendritic cells generated with vasoactive intestinal peptide. Gastroenterology, 131, 1799–1811.
Harmar, A. J., Arimura, A., Gozes, I., et al. (1998). International Union of Pharmacology. XVIII. Nomenclature of receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide. Pharmacological Reviews, 50, 265–270.
Hawley, R. J., Scheibe, R. J., & Wagner, J. A. (1992). NGF induces the expression of the VGF gene through a cAMP response element. Journal of Neuroscience, 12, 2573–2581.
Hernandez, M., Barahona, M. V., Recio, P., et al. (2006). Neuronal and smooth muscle receptors involved in the PACAP- and VIP-induced relaxations of the pig urinary bladder neck. British Journal of Urology, 149, 100–109.
Ho, N., Koziol, J. A., & Parsons, C. L. (1997). Epidemiology of interstitial cystitis. In G. R. Sant (Ed.) Interstitial cystitis (pp. 9–16). Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven Publishers.
Hu, V. Y., Zvara, P., Dattilio, A., et al. (2005). Decrease in bladder overactivity with REN1820 in rats with cyclophosphamide induced cystitis. Journal of Urology, 173, 1016–1021.
Igawa, Y., Persson, K., Andersson, K. E., Uvelius, B., & Mattiasson, A. (1993). Facilitatory effect of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide on spinal and peripheral micturition reflex pathways in conscious rats with and without detrusor instability. Journal of Urology, 149, 884–889.
Ishihara, T., Shigemoto, R., Mori, K., Takahashi, K., & Nagata, S. (1992). Functional expression and tissue distribution of a novel receptor for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. Neuron, 8, 811–819.
Jaggar, S. I., Scott, H. C., & Rice, A. S. (1999). Inflammation of the rat urinary bladder is associated with a referred thermal hyperalgesia which is nerve growth factor dependent. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 83, 442–448.
Jennings, L. J., & Vizzard, M. A. (1999). Cyclophosphamide-induced inflammation of the urinary bladder alters electrical properties of small diameter afferent neurons from dorsal root ganglia. FASEB Journal, 13, A57.
Ji, R. R., & Rupp, F. (1997). Phosphorylation of transcription factor CREB in rat spinal cord after formalin-induced hyperalgesia: Relationship to c-fos induction. Journal of Neuroscience, 17, 1776–1785.
Johansson, S. L., Ogawa, K., & Fall, M. (1997). The pathology of interstitial cystitis. In G. R. Sant (Ed.) Interstitial cystitis (pp. 143–152). Lippincott-Raven Publishers: Philadelphia.
Juarranz, Y., Abad, C., Martinez, C., et al. (2005). Protective effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide on bone destruction in the collagen-induced arthritis model of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy, 7, R1034–R1045.
Karin, M., Liu, Z., & Zandi, E. (1997). AP-1 function and regulation. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 9, 240–246.
Keast, J. R., & de Groat, W. C. (1992). Segmental distribution and peptide content of primary afferent neurons innervating the urogenital organs and colon of male rats. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 319, 615–623.
Lantéri-Minet, M., Bon, K., de Pommery, J., Michiels, J. F., & Menétrey, D. (1995). Cyclophosphamide cystitis as a model of visceral pain in rats: Model elaboration and spinal structures involves as revealed by the expression of c-Fos and Krox-24 proteins. Experimental Brain Research, 105, 220–232.
Lasanen, L. T., Tammela, T. L., Liesi, P., Waris, T., & Polak, J. M. (1992). The effect of acute distension on vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), neuropeptide Y (NPY) and substance P (SP) immunoreactive nerves in the female rat urinary bladder. Urological Research, 20, 259–263.
Lelievre, V., Favrais, G., Abad, C., et al. (1997). Gastrointestinal dysfunction in mice with a targeted mutation in the gene encoding vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: A model for the study of intestinal ileus and Hirschsprung’s disease. Peptides, 28, 1688–1699.
Maggi, C. A., Lecci, A., Santiciolo, P., Del Biance, E., & Giuliani, S. (1992). Cyclophosphamide cystitis in rats: involvement of capsaicin-sensitive primary afferents. Journal of the Autonomic Nervous System, 38, 201–208.
Martinez, C., Juarranz, Y., Abad, C., et al. (2005). Analysis of the role of the PAC1 receptor in neutrophil recruitment, acute-phase response, and nitric oxide production in septic shock. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 77, 729–738.
Maruno, K., Absood, A., & Said, S. I. (1995). VIP inhibits basal and histamine-stimulated proliferation of human airway smooth muscle cells. American Journal of Physiology, 268, L1047–L1051.
Mayr, B., & Montminy, M. (2001). Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 2, 599–609.
Messersmith, D. J., Kim, D. J., & Iadarola, M. J. (1998). Transcription factor regulation of prodynorphin gene expression following rat hindpaw inflammation. Molecular Brain Research, 53, 259–269.
Morgan, C. W., Ohara, P. T., & Scott, D. E. (1999). Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in sacral primary sensory pathways in the cat. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 407, 381–394.
Murray, E., Malley, S. E., Qiao, L. Y., Hu, V. Y., & Vizzard, M. A. (2004). Cyclophosphamide induced cystitis alters neurotrophin and receptor tyrosine kinase expression in pelvic ganglia and bladder. Journal of Urology, 172, 2434–2439.
Nadelhaft, I., & Vera, P. L. (1995). Central nervous system neurons infected by pseudorabies virus injected into the rat urinary bladder following unilateral transection of the pelvic nerve. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 359, 443–456.
Newma, R., Cuan, N., Hampartzoumian, T., Connor, S. J., Lloyd, A. R., & Grimm, M. C. (2005). Vasoactive intestinal peptide impairs leucocyte migration but fails to modify experimental murine colitis. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 139, 411–420.
Petrone, R. L., Agha, A. H., Roy, J. B., & Hurst, R. E. (1995). Urodynamic findings in patients with interstitial cystitis. Journal of Urology, 153, 290A.
Qiao, L. Y., & Vizzard, M. A. (2002a). Cystitis-induced upregulation of tyrosine kinase (TrkA, TrkB) receptor expression and phosphorylation in rat micturition pathways. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 454, 200–211.
Qiao, L. Y., & Vizzard, M. A. (2002b). Up-regulation of tyrosine kinase (TrkA, TrkB) receptor expression and phosphorylation in lumbosacral dorsal root ganglia after chronic spinal cord (T8-T10) injury. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 449, 217–230.
Qiao, L. Y., & Vizzard, M. A. (2004). Up-regulation of phosphorylated CREB but not c-Jun in bladder afferent neurons in dorsal root ganglia after cystitis. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 469, 262–274.
Riccio, A., Ahn, S., Davenport, C. M., Blendy, J. A., & Ginty, D. D. (1999). Mediation by a CREB family transcription factor of NGF-dependent survival of sympathetic neurons. Science, 286, 2358–2361.
Said, S. I. (1991). Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in asthma. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 629, 305–318.
Sant, G., & Hanno, P. M. (2001). Interstitial cystitis: current issues and controversies in diagnosis. Urology, 57, 82.
Singh, S., Natarajan, K., & Aggarwal, B. B. (1996). Capsaicin (8-methyl-N-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) is a potent inhibitor of nuclear transcription factor-kappa B activation by diverse agents. Journal of Immunology, 157, 4412–4420.
Smet, P. J., Moore, K. H., & Jonavicius, J. (1997). Distribution and colocalization of calcitonin gene-related peptide, tachykinins, and vasoactive intestinal peptide in normal and idiopathic unstable human urinary bladder. Laboratory Investigation, 77, 37–49.
Steers, W. D., Creedon, D. J., & Tuttle, J. B. (1996). Immunity to nerve growth factor prevents afferent plasticity following urinary bladder hypertrophy. Journal of Urology, 155, 379–385.
Steers, W. D., & de Groat, W. C. (1988). Effect of bladder outlet obstruction on micturition reflex pathways in the rat. Journal of Urology, 140, 864–871.
Steers, W. D., Kolbeck, S., Creedon, D., & Tuttle, J. B. (1991). Nerve growth factor in the urinary bladder of the adult regulates neuronal form and function. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 88, 1709–1715.
Steers, W. D., & Tuttle, J. B. (2006). Mechanisms of Disease: the role of nerve growth factor in the pathophysiology of bladder disorders. Natural Clinical Practice in Urology, 3, 101–110.
Szema, A. M., Hamidi, S. A., Lyubsky, S., et al. (2006). Mice lacking the VIP gene show airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation, partially reversible by VIP. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 291, L880–886.
Tuttle, J. B., Steers, W. D., Albo, M., & Nataluk, E. (1994). Neural input regulates tissue NGF and growth of the adult rat urinary bladder. Journal of the Autonomic Nervous System, 49, 147–158.
Uckert, S., Stief, C. G., Lietz, B., Burmester, M., Jonas, U., & Machtens, S. A. (2002). Possible role of bioactive peptides in the regulation of human detrusor smooth muscle—Functional effects in vitro and immunohistochemical presence. World Journal of Urology, 20, 244–249.
Verge, V. M. K., Richardson, P. M., Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z., & Hokfelt, T. (1995). Differential influence of nerve growth factor on neuropeptide expression in vivo: a novel role in peptide suppression in adult sensory neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 15(3), 2081–2096.
Vizzard, M. A. (1997). Increased expression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in bladder afferent and spinal neurons following spinal cord injury. Developments in Neuroscience, 19, 232–246.
Vizzard, M. A. (2000a). Alterations in spinal cord Fos protein expression induced by bladder stimulation following cystitis. American Journal of Physiology. I Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 278, R1027–1039.
Vizzard, M. A. (2000b). Changes in urinary bladder neurotrophic factor mRNA and NGF protein following urinary bladder dysfunction. Experimental Neurology, 161, 273–284.
Vizzard, M. A. (2000c). Up-regulation of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide in urinary bladder pathways after chronic cystitis. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 420, 335–348.
Vizzard, M. A. (2001). Alterations in neuropeptide expression in lumbosacral bladder pathways following chronic cystitis. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy, 21, 125–138.
Vizzard, M. A., & Boyle, M. M. (1999). Increased expression of growth-associated protein (GAP-43) in lower urinary tract pathways following cyclophosphamide (CYP)-induced cystitis. Brain Research, 844, 174–187.
Vizzard, M. A., Braas, K. M., Studeny, S., et al. (2007a). Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide knockout (VIP−/−) mice exhibit altered bladder function and somatic sensitivity with cyclophosphamide (CYP)-induced cystitis. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 33, 311.
Vizzard, M. A., Malley, S., Braas, K. M., Waschek, J. A., & May, V. (2007b). Exaggerated cytokine and chemokine expression in vasoactive intestinal polypeptide knockout (VIP−/−) mice with cyclophosphamide (CYP)-induced cystitis. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 33, 338–339.
Voice, J. K., Dorsam, G., Chan, R. C., Grinninger, C., Kong, Y., & Goetzl, E. J. (2002). Immunoeffector and immunoregulatory activities of vasoactive intestinal peptide. Regulatory Peptide, 109, 199–208.
Wanigasekara, Y., Kepper, M. E., & Keast, J. R. (2003). Immunohistochemical characterisation of pelvic autonomic ganglia in male mice. Cell and Tissue Research, 311, 175–185.
Yoshimura, N., & de Groat, W. C. (1999). Increased excitability of afferent neurons innervating rat urinary bladder after chronic bladder inflammation. Journal of Neuroscience, 19, 4644–4653.
Zvara, P., & Vizzard, M. A. (2007). Exogenous overexpression of nerve growth factor in the urinary bladder produces bladder overactivity and altered micturition circuitry in the lumbosacral spinal cord. BMC Physiology, 7, 9.
Zvarova, K., & Vizzard, M. A. (2006). Changes in galanin-immunoreactivity in rat micturition reflex pathways after cyclophosphamide (CYP)-induced cystitis. Cell and Tissue Research, 324, 213–224.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the technical support of Susan E. Malley. This work was funded by NIH grants DK051369, DK060481, and DK065989. D.G. Jensen was supported by Drug Research Academy at Copenhagen University and Ferring Pharmaceutical, Copenhagen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jensen, D.G., Studeny, S., May, V. et al. Expression of Phosphorylated cAMP Response Element Binding Protein (p-CREB) in Bladder Afferent Pathways in VIP−/− Mice with Cyclophosphamide (CYP)-Induced Cystitis. J Mol Neurosci 36, 299–309 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9045-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9045-y