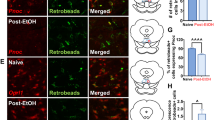
Abstract
Endogenous opioid systems have been suggested to play a key role in ethanol reinforcement mechanisms and alcohol-drinking behavior. Ethanol induces differential alterations in opioid peptide expression in brain areas of the reward circuits, which may be linked to the reinforcing effects of ethanol. In addition, ethanol-induced alterations in opioidergic nigrostriatal transmission could be involved in brain sensitivity to ethanol and play a role in addictive processes. The aim of this work was to study the effects of acute ethanol administration on proenkephalin (proenk) mRNA expression in the rat substantia nigra and caudate–putamen (CP) for up to 24 h post treatment. Male Wistar rats received ethanol (2.5 g/kg) or distilled water by intragastric administration, and proenk mRNA expression was studied by in situ hybridization and densitometry. Ethanol transiently increased proenk mRNA expression in the CP 1 h after drug administration. Proenk mRNA levels remained elevated 2 h post treatment in the anterior–medial and medial–posterior regions of the CP. In contrast, ethanol decreased proenk mRNA expression in the substantia nigra pars compacta and pars reticulata 2 h after drug exposure. Alterations in enkephalin expression in the substantia nigra and CP in response to ethanol exposure could be involved in the mechanisms underlying brain sensitivity to the drug.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asyyed, A., Storm, D., & Diamond, I. (2006). Ethanol activates cAMP response element-mediated gene expression in select regions of the mouse brain. Brain Research, 1106, 63–71.
Budygin, E. A., Mathews, T. A., Lapa, G. B., & Jones, S. R. (2005). Local effects of acute ethanol on dopamine neurotransmission in the ventral striatum in C57BL/6 mice. European Journal of Pharmacology, 523, 40–45.
Carlsson, A., Engel, J., & Svensson, T. H. (1972). Inhibition of ethanol induced excitation in mice and rats by alpha-methyl-p-tyrosine. Psychopharmacologia, 26, 307–312.
Chang, G. Q., Karatayev, O., Ahsan, R., Avena, N. M., Lee, C., Lewis, M. J., et al. (2007). Effect of ethanol on hypothalamic opioid peptides, enkephalin, and dynorphin: Relationship with circulating triglycerides. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 31, 249–259.
Chang, S. L., Patel, N. A., Romero, A. A., & Kening, V. (1994). Ethanol induces FOS immunoreactivity in the rat brain. Regulatory Peptides, 54, 51–52.
Crabbe, J. C., Feller, D. J., Terdal, E. S., & Merrill, C. D. (1990). Genetic components of ethanol responses. Alcohol, 7, 245–248.
de Gortari, P., Méndez, M., Rodríguez-Keller, I., Pérez-Martínez, L., & Joseph-Bravo, P. (2000). Acute ethanol administration induces changes in TRH and proenkephalin expression in hypothalamic and limbic regions of rat brain. Neurochemistry International, 37, 483–496.
Di Chiara, G., & Imperato, A. (1985). Ethanol preferentially stimulates dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of freely moving rats. European Journal of Pharmacology, 115, 131–132.
Duncan, P. M., & Baez, A. M. (1981). The effect of ethanol on wheel running in rats. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 15, 819–821.
Earleywine, M. (1994). Anticipated biphasic effects of ethanol’s psychomotor stimulant effect. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 18, 956–963.
Erwin, V. G., Korte, A., & Marty, M. (1987). Neurotensin selectively alters ethanol-induced anesthesia in LS/Ibg and SS/Ibg lines of mice. Brain Research, 400, 80–90.
Fadda, F., Argiolas, A., Melis, M. R., Serra, G., & Gessa, G. L. (1980). Differential effects of acute and chronic ethanol on dopamine metabolism in frontal cortex, caudate nucleus and substantia nigra. Life Sciences, 27, 979–986.
Froehlich, J. C. (1995). Genetic factors in alcohol self-administration. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 56(Suppl 7), 15–23.
Froehlich, J. C., Harts, J., Lumeng, L., & Li, T.-K. (1987). Naloxone attenuation of voluntary alcohol consumption. Alcohol and Alcoholism. Supplement, 1, 333–337.
Froehlich, J. C., & Wand, G. (1996). The neurobiology of ethanol/opioid interactions in ethanol reinforcement. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 20, 181–186.
Froehlich, J. C., Zweifel, M., Harts, J., Lumeng, L., & Li, T. -K. (1991). Importance of delta opioid receptors in maintaining high alcohol drinking. Psychopharmacology, 103, 467–472.
Gianoulakis, C., Krishnan, B., & Thavundayil, J. (1996). Enhanced sensitivity of pituitary beta-endorphin to ethanol in subjects at high risk of alcoholism. Archives of General Psychiatry, 53, 250–257.
Gingras, M. A., & Cools, A. R. (1996). Analysis of the biphasic locomotor response to ethanol in high and low responders to novelty: A study in Nijmegen wistar rats. Psychopharmacology, 125, 258–264.
Hernández-Vázquez, F., & Méndez, M. (2006). Stimulant and depressant behavioral actions of alcohol in non-selected Wistar rats. In F. J. Chen (Ed.), New trends in brain research (pp. 127–142). New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.
Howells, R. D., Kilpatrick, D. L., Bhatt, R., Monahan, J. J., Poonian, M., & Undenfriend, S. (1984). Molecular cloning and sequence determination of rat preproenkephalin cDNA: Sensitive probe for studying transcriptional changes in rat tissues. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 81, 7651–7655.
Hyman, S., Konradi, C., Kobierski, L., Cole, R., Senatus, P., & Green, D. (1990). Pharmacologic regulation of striatal proenkephalin gene expression via transcription factor CREB. Molecular Neurobiology, 20, 155–171.
Hyytiä, P., & Kiianmaa, K. (2001). Suppression of ethanol responding by centrally administered CTOP and naltrindole in AA and Wistar rats. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 25, 25–33.
Iwatsubo, K., & Clouet, D. H. (1977). Effects of morphine and haloperidol on electrical activity of rat nigro-striatal neurones. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 222, 182–189.
Jamensky, N. T., & Gianoulakis, C. (1999). Comparison of the proopiomelanocortin and proenkephalin opioid peptide systems in brain regions of the alcohol-preferring C57BL/6 and alcohol-avoiding DBA/2 mice. Alcohol, 18, 177–187.
Koob, G. F., Sanna, P. P., & Bloom, F. E. (1998). Neuroscience of addiction. Neuron, 21, 467–476.
Krishnan-Sarin, S., Jing, S. L., Kurtz, D. L., Zweifel, M., Portoghese, P. S., Li, T. -K., et al. (1995). The delta opioid receptor antagonist naltrindole attenuates both alcohol and saccharin intake in rats selectively bred for alcohol preference. Psychopharmacology, 120, 177–185.
Krishnan-Sarin, S., Wand, G. S., Li, X. -W., Li, T. -K., Portoghese, P. S., & Froehlich, J. C. (1998). Effect of mu opioid receptor blockade on alcohol intake in rats bred for high alcohol drinking. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 59, 627–635.
Li, X.-W., Li, T. -K., & Froehlich, J. C. (1992). The enkephalinergic system and alcohol preference. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 16, 359.
Marinelli, P. W., Bai, L., Quirion, R., & Gianoulakis, C. (2005). A microdialysis profile of Met-enkephalin release in the rat nucleus accumbens following alcohol administration. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 29, 1821–1828.
Marinelli, P. W., Kiianmaa, K., & Gianoulakis, C. (2000). Opioid propeptide mRNA content and receptor density in the brains of AA and ANA rats. Life Sciences, 66, 1915–1927.
Marinelli, P. W., Quirion, R., & Gianoulakis, C. (2003). A microdialysis profile of b-endorphin and catecholamines in the rat nucleus accumbens following alcohol administration. Psychopharmacology, 169, 60–67.
Martin, C. S., Earleywine, M., Musty, R. E., Perrine, M. W., & Swift, R. M. (1993). Development and validation of the biphasic alcohol effects scale. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 17, 140–146.
Méndez, M., Leriche, M., & Calva, J. C. (2001). Acute ethanol administration differentially modulates μ opioid receptors in the rat meso-accumbens and mesocortical pathways. Molecular Brain Research, 94, 148–156.
Méndez, M., Leriche, M., & Calva, J. C. (2003). Acute ethanol administration transiently decreases [3H]-DAMGO binding to mu opioid receptors in the rat substantia nigra pars reticulata but not in the caudate–putamen. Neuroscience Research, 47, 153–160.
Méndez, M., & Morales-Mulia, M. (2006). Ethanol exposure differentially alters pro-enkephalin mRNA expression in regions of the mesocorticolimbic system. Psychopharmacology, 189, 117–124.
Méndez, M., Morales-Mulia, M., & Leriche, M. (2004). [3H]DPDPE binding to δ opioid receptors in the rat mesocorticolimbic and nigrostriatal pathways is transiently increased by acute ethanol administration. Brain Research, 1028, 180–190.
Mereu, G., Fadda, F., & Gessa, G. L. (1984). Ethanol stimulates the firing rate of nigral dopaminergic neurons in unanesthetized rats. Brain Research, 292, 63–69.
Ng, G. Y. K., O’Dowd, B. F., & George, S. R. (1996). Genotypic differences in mesolimbic enkephalin gene expression in DBA/2J and C57BL/6J inbred mice. European Journal of Pharmacology, 311, 45–52.
Nylander, I., Hyytiä, P., Forsander, O., & Terenius, L. (1994). Differences between alcohol-preferring (AA) and alcohol-avoiding (ANA) rats in the prodynorphin and proenkephalin systems. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 18, 1272–1279.
Oliva, J. M., Ortiz, S., Pérez-Rial, S., & Manzanares, J. (2007). Time dependent alterations on tyrosine hydroxylase, opioid and cannabinoid CB1 receptor gene expressions after acute ethanol administration in the rat brain. European Neuropsychopharmacology, in press. DOI 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2007.09.001.
Olive, M. F., Koenig, H. N., Nannini, M. A., & Hodge, C. W. (2001). Stimulation of endorphin neurotransmission in the nucleus accumbens by ethanol, cocaine, and amphetamine. Journal of Neuroscience, 21, RC184 (1–5).
Ortiz, J., Fitzgerald, L. W., Charlton, M., Lane, S., Trevisan, L., Guitart, X., et al. (1995). Biochemical actions of chronic ethanol exposure in the mesolimbic system. Synapse, 21, 289–298.
Paxinos, G., & Watson, C. (1998). The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates (4th ed.). San Diego: Academic Press.
Pittius, C. W., Kley, N., Loeffler, J. P., & Höllt, V. (1985). Quantitation of proenkephalin A messenger RNA in bovine brain, pituitary and adrenal medulla: Correlation between mRNA and peptide levels. EMBO Journal, 4, 1257–1260.
Rasmussen, D. D., Bryant, C. A., Boldt, B. M., Colasurdo, E. A., Levin, N., & Wilkinson, C. W. (1998). Acute alcohol effects on opiomelanocortinergic regulation. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 22, 789–801.
Reid, L. D., & Hunter, G. A. (1984). Morphine and naloxone modulate intake of ethanol. Alcohol, 1, 33–37.
Robinson, D. L., Volz, T. J., Schenk, J. O., & Wightman, R. M. (2005). Acute ethanol decreases dopamine transporter velocity in rat striatum: In vivo and in vitro electrochemical measurements. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 29, 746–755.
Schuckit, M. A. (1994). Low level of response to alcohol as a predictor of future alcoholism. American Journal of Psychiatry, 151, 184–189.
Schulz, R., Wüster, M., Duka, T., & Herz, A. (1980). Acute and chronic ethanol treatment changes endorphin levels in brain and pituitary. Psychopharmacology, 68, 221–227.
Seizinger, B. R., Bovermann, K., Maysinger, D., Holt, V., & Herz, A. (1983). Differential effects of acute and chronic ethanol treatment on particular opioid systems in discrete regions of rat brain and pituitary. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 18, 361–369.
Sommer, W., Hyytïa, P., & Kiianmaa, K. (2006). The alcohol-preferring AA and alcohol-avoiding ANA rats: Neurobiology of the regulation of alcohol drinking. Addiction Biology, 11, 289–309.
Stuart, J. F., Dorow, J., & Feller, D. J. (1993). μ-opiate receptor binding and function in HOT and COLD selected lines of mice. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 46, 519–526.
Thibault, C., Lai, C., Wilke, N., Duong, B., Olive, M. F., Rahman, S., et al. (2000). Expression profiling of neural cells reveals specific patterns of ethanol-responsive gene expression. Molecular Pharmacology, 58, 1593–1600.
Thiriet, N., Aunis, D., & Zwiller, J. (2000). C-fos and egr-1 immediate-early gene induction by cocaine and cocaethylene in rat brain. Annals of New York Academy of Sciences, 914, 46–57.
Ulm, R. R., Volpicelli, J. R., & Volpicelli, L. A. (1995). Opiates and alcohol self-administration in animals. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 56(Suppl 7), 5–14.
Valles, S., Pitarch, J., Renau-Piqueras, J., & Guerri, C. (1997). Ethanol exposure affects glial fibrillary acidic protein gene expression and transcription during rat brain development. Journal of Neurochemistry, 69, 2484–2493.
Volpicelli, J. R., Ulm, R. R., & Hopson, N. (1991). Alcohol drinking in rats during and following morphine injections. Alcohol, 8, 289–292.
Walton, K. M., & Rehfuss, R. P. (1990). Molecular mechanisms of cAMP-regulated gene expression. Molecular Neurobiology, 4, 197–210.
Widdowson, P. S. (1987). The effect of neurotensin, TRH and the δ-opioid receptor antagonist ICI174864 on alcohol-induced narcosis in rats. Brain Research, 424, 281–289.
Widdowson, P. S., & Holman, R. B. (1992). Ethanol-induced increase in endogenous dopamine release may involve endogenous opiates. Journal of Neurochemistry, 59, 157–163.
Wild, K. D., & Reid, L. D. (1990). Modulation of ethanol intake by morphine: Evidence for a central site of action. Life Sciences, 47, PL49–PL54.
Wise, R. A., & Bozarth, M. A. (1982). Action of drugs of abuse on brain reward systems: An update with specific attention to opiates. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 17, 239–243.
Yanai, J., Bergman, A., Keltz, M., & Pick, C. G. (1988). Mechanisms of sensitivity and tolerance to ethanol and barbiturates. In J. Yanai, J. M. Rosenfeld, P. Eldar, & R. Bauml (Eds.), Alcohol dependence, the family and the community (pp. 143–158). London: Freund.
Yanai, J., Shaanani, R., & Pick, C. G. (1995). Altered brain sensitivity to ethanol in mice after MPTP treatment. Alcohol, 12, 127–130.
Yang, X., Horn, K., & Wand, G. S. (1998). Chronic ethanol exposure impairs phosphorylation of CREB and CRE-binding activity in rat striatum. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 22, 382–390.
Yoshikawa, K., Williams, C., & Sabol, S. L. (1984). Rat brain preproenkephalin mRNA. cDNA cloning, primary structure, and distribution in the central nervous system. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 259, 14301–14308.
Acknowledgments
We thank S.R. Mejía for the technical assistance. This work was supported by the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT 34359-N).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Méndez, M., Morales-Mulia, M. & Pérez-Luna, J.M. Ethanol-induced Changes in Proenkephalin mRNA Expression in the Rat Nigrostriatal Pathway. J Mol Neurosci 34, 225–234 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9039-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9039-9