Abstract
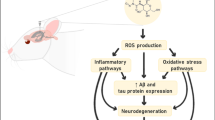
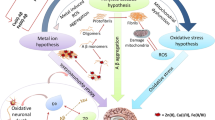
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia in the elderly. Without a treatment that significantly delays the progression of the disease over 14 million Americans are likely to be affected with AD by the middle of the 21st Century, presenting an enormous economic and social burden. Evidence gathered over the last two decades has implicated the abnormal accumulation of Aβ, in particular the longer more amyloidogenic form Aβ42, as a potential causative agent in the disease. To screen for compounds that reduce Aβ accumulation we have established several high throughput, cell based screens capable of the sensitive and selective detection of Aβ40 and Aβ42. Using these screens we have analyzed a proprietary library of natural product extracts for their ability to influence Aβ accumulation. Using this approach, we have identified several agents capable of influencing total Aβ concentration. In addition, we have identified one extract that selectively reduces Aβ42. Intracerebroventricular administration of this agent to mice results in a selective reduction in Aβ42 in the brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama H., Barger S., Barnum S., Bradt B., Bauer J., Cole G. M., et al. (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 21, 383–421.
Dovey H. F., John V., Anderson J. P., Chen L. Z., de Saint Andrieu P., Fang L. Y., et al. (2001) Functional gamma-secretase inhibitors reduce beta-amyloid peptide levels in brain. J. Neurochem. 76, 173–181.
Golde T. E., Eckman C. B., and Younkin S. G. (2000) Biochemical detection of Abeta isoforms: implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1502, 172–187.
Haugabook S. J., Le T., Yager D., Zenk B., Healy B. M., Eckman E. A., et al. (2001a) Reduction of Aβ accumulation in the Tg2576 animal model of Alzheimer’s disease after oral administration of the phosphatidylinositol kinase inhibitor wortmannin. FASEB J. 15, 16–18.
Haugabook S. J., Yager D. M., Eckman E. A., Golde T. E., Younkin S. G., and Eckman C. B. (2001b) High throughput screens for the identification of compounds that alter the accumulation of the Alzheimer’s amyloid β peptide (Aβ). J. Neurosci. Methods 108, 171–179.
Hsiao K., Chapman P., Nilsen S., Eckman C., Harigaya Y., Younkin S., Yang F., and Cole G. (1996) Correlative memory deficits, Abeta elevation, and amyloid plaques in transgenic mice. Science 274, 99–102.
Iversen L. L., Mortishire-Smith R. J., Pollack S. J., and Shearman M. S. (1995) The toxicity in vitro of beta-amyloid protein. Biochem. J. 311, 1–16.
Jarrett J. T. and Lansbury P. T. Jr. (1993) Seeding “one-dimensional crystallization” of amyloid: a pathogenic mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease and scrapie? Cell 73, 1055–1058.
Suzuki N., Cheung T. T., Cai X. D., Odaka A., Otvos L. Jr., Eckman C., et al. (1994) An increased percentage of long amyloid beta protein secreted by familial amyloid beta protein precursor (beta APP717) mutants. Science 264, 1336–1340.
Yankner B. A. (1996) Mechanisms of neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 16, 921–932.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yager, D., Watson, M., Healy, B. et al. Natural product extracts that reduce accumulation of the alzheimer’s amyloid β peptide. J Mol Neurosci 19, 129–133 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-002-0023-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-002-0023-5