Abstract
Introduction
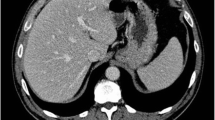
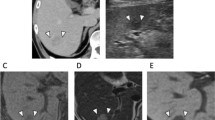
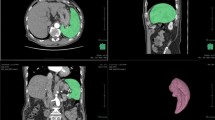
Oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy is commonly used in adjuvant treatment of colon cancer as well as in neoadjuvant setting in patients with liver metastases. However oxaliplatin can cause damage to non-tumor bearing liver which presents as sinusoidal obstructive syndrome (SOS). These changes are difficult to differentiate from metastasis clinic-radiologically and manifests as sinusoidal dilatation, peliosis and nodular regenerative hyperplasia.
Case
The present study reports the case of a patient with oxaliplatin-induced SOS which mimicked colo-rectal liver metastasis on follow up imaging studies after receiving neoadjuvant oxaliplatin based chemotherapy. After multidisciplinary discussion, patient was planned for simultaneous resection of rectal primary and right hepatectomy for metastasis. Final histopathology revealed no tumour in liver but the liver lesions seen radiologically were actually changes of oxaliplatin induced focal SOS and mimicked metastatic nodules.
Conclusion
In patients with colo-rectal cancer having received oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy, SOS may be considered as one of the causes of newly developed liver lesions, and should be subjected to additional radio-pathologic evaluation to prevent overtreatment and avoiding potentially morbid surgeries.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
André T, Boni C, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, Bonetti A, Clingan P, Bridgewater J, Rivera F, de Gramont A. Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or III colon cancer in the MOSAIC trial. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3109–16.
Haller DG, Tabernero J, Maroun J, de Braud F, Price T, Van Cutsem E, Hill M, Gilberg F, Rittweger K, Schmoll HJ. Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with fluorouracil and folinic acid as adjuvant therapy for stage III colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1465–71.
Rubbia-Brandt L, Audard V, Sartoretti P, et al. Severe hepatic sinusoidal obstruction associated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2004;15:460–6.
Aloia T, Sebagh M, Plasse M, et al. Liver histology and surgical outcomes after preoperative chemotherapy with fluorouracil plus oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer liver metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4983–90.
Ryan P, Nanji S, Pollett A, et al. Chemotherapy-induced liver injury in metastatic colorectal cancer: semiquantitative histologic analysis of 334 resected liver specimens shows that vascular injury but not steatohepatitis is associated with preoperative chemotherapy. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34:784–91.
Han NY, Park BJ, Sung DJ, Kim MJ, Cho SB, Lee CH, et al. Chemotherapy-induced focal hepatopathy in patients with gastrointestinal malignancy: gadoxetic acid–enhanced and diffusion-weighted MR imaging with clinical-pathologic correlation. Radiology. 2014;271:416–25.
Arakawa Y, Shimada M, Utsunomya T, Imura S, Morine Y, Ikemoto T, et al. Oxaliplatin-related sinusoidal obstruction syndrome mimicking metastatic liver tumors. Hepatol Res. 2013;43:685–9.
Yothers G, O’Connell MJ, Allegra CJ, Kuebler JP, Colangelo LH, Petrelli NJ, et al. Oxaliplatin as adjuvant therapy for colon cancer: updated results of NSABP C-07 trial, including survival and subset analyses. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(28):3768–74. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.36.4539.
Nordlinger B, Sorbye H, Glimelius B, Poston GJ, Schlag PM, Rougier P, et al. Perioperative chemotherapy with FOLFOX4 and surgery versus surgery alone for resectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer (EORTC Intergroup trial 40983): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2008;371:1007–16.
DeLeve LD, McCuskey RS, Wang X, Hu L, McCuskey MK, Epstein RB, et al. Characterization of a reproducible rat model of hepatic veno-occlusive disease. Hepatology. 1999;29:1779–91.
Zorzi D, Laurent A, Pawlik TM, Lauwers GY, Vauthey JN, Abdalla EK. Chemotherapy-associated hepatotoxicity and surgery for colorectal liver metastases. Br J Surg. 2007;94:274–86.
Deleve LD, Wang X, Tsai J, Kanel G, Strasberg S, Tokes ZA. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (veno-occlusive disease) in the rat is prevented by matrix metalloproteinase inhibition. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:882–90.
Kawai T, Yamazaki S, Iwama A, Higaki T, Sugitani M, Takayama T. Focal sinusoidal obstruction syndrome caused by oxaliplatin-induced chemotherapy: a case report. Hepat Mon. 2016;16(9): e37572.
Choi JH, Won YW, Kim HS, Oh YH, Lim S, Kim HJ. Oxaliplatin-induced sinusoidal obstruction syndrome mimicking metastatic colon cancer in the liver. Oncol Lett. 2016;11:2861–4.
Rojas Llimpe FL, Di Fabio F, Ercolani G, Giampalma E, Cappelli A, Serra C, Castellucci P, D'Errico A, Golfieri R, Pinna AD, Pinto C. Imaging in resectable colorectal liver metastasis patients with or without preoperative chemotherapy: results of the PROMETEO-01 study. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(4):667–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.351. Epub 2014 Jul 1. PMID: 24983362; PMCID: PMC4134499.
Tsili AC, Alexiou G, Naka C, Argyropoulou MI. Imaging of colorectal cancer liver metastases using contrast-enhanced US, multidetector CT, MRI, and FDG PET/CT: a meta-analysis. Acta Radiol. 2021;62(3):302–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185120925481. Epub 2020 Jun 6. PMID: 32506935.
Maffione AM, Lopci E, Bluemel C, Giammarile F, Herrmann K, Rubello D. Diagnostic accuracy and impact on management of (18)F-FDG PET and PET/CT in colorectal liver metastasis: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42(1):152–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-014-2930-4.
Li QW, Zheng RL, Ling YH, et al. Prediction of tumor response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer using (18)fluorine-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography and serum carcinoembryonic antigen: a prospective study. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2016;41(8):1448–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-016-0698-7.
Neofytou K, Giakoustidis A, Neves MC, et al. Increased carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) following neoadjuvant chemotherapy predicts poor prognosis in patients that undergo hepatectomy for liver-only colorectal metastases. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2017;402(4):599–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-016-1415-2.
Stremitzer S, Stift J, Graf A, Singh J, et al. CEA change after neoadjuvant chemotherapy including bevacizumab and clinical outcome in patients undergoing liver resection for colorectal liver metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;17.
Jones OM, Rees M, John TG, Bygrave S, Plant G. Biopsy of resectable colorectal liver metastases causes tumour dissemination and adversely affects survival after liver resection. Br J Surg. 2005;92(9):1165–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.4888.
Metcalfe MS, Bridgewater FH, Mullin EJ, Maddern GJ. Useless and dangerous–fine needle aspiration of hepatic colorectal metastases. BMJ. 2004;328(7438):507–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.328.7438.507.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Shraddha Patkar, Vipul Gupta and Amit Chopde. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Vipul Gupta and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The study is compliant with ethical standards. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for the surgery.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, V., Chopde, A., Patkar, S. et al. Oxaliplatin-Induced Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome Masquerading as Colorectal Liver Metastasis: A Case Report. J Gastrointest Canc 54, 682–686 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-022-00835-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-022-00835-x