Abstract
Background and Aim
Colon cancer ranks fourth and is responsible for causing 10% cancer-related mortality in western countries. Its incidence is rising in many countries due to widespread adoption of the Western diet and lifestyle. Carbamazepine (CBZ) is a FDA-approved antiepileptic drug and a histone deacetylase inhibitor. The aim of this study is to evaluate the cytotoxic potentials of CBZ in human colon cancer cells (HT-29 cells).
Methods
HT-29 cells were treated with 36 and 76 μg/ml of CBZ for 24 h. The cytotoxic effect was evaluated by MTT assay. The intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) expression was evaluated through dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate staining. Morphological changes related to apoptosis were evaluated by dual staining with acridine orange and ethidium bromide. Mitochondrial membrane potential was evaluated by rhodamine 123 staining. Immunofluorescence analysis of caspase 3 was done with confocal microscopy.
Results
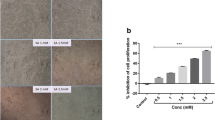
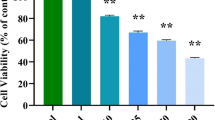
CBZ caused significant cytotoxicity in HT-29 cells and the effect was concentration dependent. CBZ treatments also caused significant expression of ROS in HT-29 cells. Dual staining showed early and late apoptotic cells and morphological alterations induced by the CBZ. Confocal microscopic studies confirmed the increased caspase 3 expression in CBZ-treated cells.
Conclusion
CBZ induced apoptosis in HT-29 cell through ROS generation and caspase 3 expression and these results pave the way for further in vivo studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gierbolini J, Giarratano M, Benbadis SR. Carbamazepine-related antiepileptic drugs for the treatment of epilepsy - a comparative review. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016;17:885–8.
Meador KJ, Seliger J, Boyd A, Razavi B, Falco-Walter J, Le S, et al. Comparative neuropsychological effects of carbamazepine and eslicarbazepine acetate. Epilepsy Behav. 2019;94:151–7.
Ceccacci E, Minucci S. Inhibition of histone deacetylases in cancer therapy: lessons from leukaemia. Br J Cancer. 2016;114:605–11.
Perri F, Longo F, Giuliano M, Sabbatino F, Favia G, Ionna F, et al. Epigenetic control of gene expression: potential implications for cancer treatment. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017;111:166–72.
Miller CP, Singh MM, Rivera-Del Valle N, Manton CA, Chandra J. Therapeutic strategies to enhance the anticancer efficacy of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011;2011:514261, 1, 17.
Eckschlager T, Plch J, Stiborova M, Hrabeta J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:E1414.
Beutler AS, Li S, Nicol R, Walsh MJ. Carbamazepine is an inhibitor of histone deacetylases. Life Sci. 2005;76:3107–15.
Salminen JK, Tammela TL, Auvinen A, Murtola TJ. Antiepileptic drugs with histone deacetylase inhibition activity and prostate cancer risk: a population-based case-control study. Cancer Causes Control. 2016;27:637–45.
Kuipers EJ, Grady WM, Lieberman D, Seufferlein T, Sung JJ, Boelens PG, et al. Colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1:15065.
Hatano Y, Fukuda S, Hisamatsu K, Hirata A, Hara A, Tomita H. Multifaceted interpretation of colon cancer stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:E1446.
Wei J, Ma L, Lai YH, Zhang R, Li H, Li C, et al. Bazedoxifene as a novel GP130 inhibitor for colon cancer therapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:63.
Akbarzadeh L, MoiniZanjani T, Sabetkasaei M. Comparison of anticancer effects of carbamazepine and valproic acid. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2016;18:e37230.
PonselviInduja M, Ezhilarasan D, Ashok Vardhan N. Evolvulus alsinoides methanolic extract triggers apoptosis in HepG2 cells. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2018;8:504–12.
Gheena S, Ezhilarasan D. Syringic acid triggers reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2019;38:694–702.
Gohel A, McCarthy MB, Gronowicz G. Estrogen prevents glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in osteoblasts in vivo and in vitro. Endocrinology. 1999;140:5339–47.
Fan J, Wang P, Wang X, Tang W, Liu C, Wang Y, et al. Induction of mitochondrial dependent apoptosis in human leukemia K562 cells by Meconopsis integrifolia: a species from traditional Tibetan medicine. Molecules. 2015;20:11981–93.
Abaza MS, Bahman AM, Al-Attiyah RJ. Valproic acid, an anti-epileptic drug and a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in combination with proteasome inhibitors exerts antiproliferative, pro-apoptotic and chemosensitizing effects in human colorectal cancer cells: underlying molecular mechanisms. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34:513–32.
Cornago M, Garcia-Alberich C, Blasco-Angulo N, Vall-Llaura N, Nager M, Herreros J, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors promote glioma cell death by G2 checkpoint abrogation leading to mitotic catastrophe. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1435.
Tseng JH, Chen CY, Chen PC, Hsiao SH, Fan CC, Liang YC, et al. Valproic acid inhibits glioblastoma multiforme cell growth via paraoxonase 2 expression. Oncotarget. 2017;8:14666–79.
Ezhilarasan D, Apoorva VS, Ashok Vardhan N. Syzygium cumini extract induced reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis in human oral squamous carcinoma cells. J Oral Pathol Med. 2019;48:115–21.
Liu K, Liu PC, Liu R, Wu X. Dual AO/EB staining to detect apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells compared with flow cytometry. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2015;21:15–20.
Grilo AL, Mantalaris A. Apoptosis: a mammalian cell bioprocessing perspective. Biotechnol Adv. 2019;37:459–75.
Zhang BB, Wang DG, Guo FF, Xuan C. Mitochondrial membrane potential and reactive oxygen species in cancer stem cells. Familial Cancer. 2015;14:19–23.
Gillissen B, Richter A, Richter A, Preissner R, Schulze-Osthoff K, Essmann F, et al. Bax/Bak-independent mitochondrial depolarization and reactive oxygen species induction by sorafenib overcome resistance to apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma. J Biol Chem. 2017;292:6478–92.
Arumugam A, Subramani R, Nandy S, Powell S, Velazquez M, Orozco A, et al. Desacetyl nimbinene inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis through reactive oxygen species mediated mechanisms. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:6527–37.
Yan J, Pang Y, Sheng J, Wang Y, Chen J, Hu J, et al. A novel synthetic compound exerts effective anti-tumour activity in vivo via the inhibition of tubulin polymerisation in A549 cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015;97:51–61.
McIlwain DR, Berger T, Mak TW. Caspase functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5:a008656.
Choudhary GS, Al-Harbi S, Almasan A. Caspase-3 activation is a critical determinant of genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1219:1–9.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. R. Parameshwari, Researcher, Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education and Research, Chennai, India for her scientific contribution to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS performed the research and written the manuscript; DE conceived the ideas, performed the research, and analyzed the data and corrected the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sohaib M, Ezhilarasan D Carbamazepine, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Induces Apoptosis in Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Cell Line HT-29. J Gastrointest Canc 51, 564–570 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-019-00286-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-019-00286-x