Abstract
Introduction
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), as a family of non-coding RNAs, have opened a new window in cancer biology and transcriptome. It has been revealed that miRNAs post-transcriptionally regulate the gene expression and involve in colorectal cancer (CRC) development and progression. Our aim was to examine the differential expression of miRNAs in a CRC and to correlate their expression levels with mRNA levels of CRC-related genes (K-ras, APC, p53).
Materials and Methods
Seventy-two colorectal tumor tissues from patients with newly diagnosed CRC and 72 matched normal adjacent tissues were analyzed. Relative expression of seven CRC-related miRNAs (miR-21, miR-31, miR-20a, miR-133b, and miR-145, miR-135b and let-7g) and three CRC-related genes (K-ras, APC, p53) was detected using the SYBR Green quantitative real-time PCR technique. The correlation between gene expression levels and clinicopathological features was evaluated.
Results
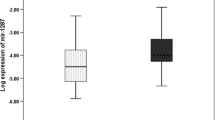
Our results showed a significant difference between the two groups for the expression level of miR-21, miR-31, miR-145, and miR-20a (P < 0.001). Also, a significant difference between the two groups for the expression level of K-ras was found (P < 0.001). Further analysis revealed an inverse significant correlation between miR-145 and K-ras (R2 = 0.662, P < 0.001), while a positive correlation was observed between miR-21 and K-ras (R2 = 0.732, P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Dysregulation of miRNAs and correlation with molecular signaling pathways designated a biological role for miRNAs in various cellular mechanisms underlying CRC. On the other hand, the pattern of miRNAs expression and its correlation with transcriptional status are helpful to discovery biomarkers and design therapeutics for CRC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agah S, Akbari A, Talebi A, Masoudi M, Sarveazad A, Mirzaei A, et al. Quantification of plasma cell-free circulating DNA at different stages of colorectal cancer. Cancer Investig. 2017;35(10):625–32.
Akbari A, Farahnejad Z, Akhtari J, Abastabar M, Mobini GR, Mehbod ASA. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B downregulates the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling transducers in human glioblastoma Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology 2016;5;9(5):e27297. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjm.27297.
Giancotti FG. Deregulation of cell signaling in cancer. FEBS Lett. 2014;588(16):2558–70.
Wang X, et al. The molecular landscape of synchronous colorectal cancer reveals genetic heterogeneity. Carcinogenesis. 2018;39(5):708–18.
Kheirelseid EA, et al. Clinical applications of gene expression in colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2013;4(2):144.
Inamura K. Colorectal cancers: an update on their molecular pathology. Cancers. 2018;10(1):26.
Mobini GR, Ghahremani MH, Amanpour S, Dehpour AR, Akbari A, Hoseiniharouni SM, et al. Transforming growth factor beta-induced factor 2-linked X (TGIF2LX) regulates two morphogenesis genes, Nir1 and Nir2 in human colorectal. Acta Med Iran. 2016;54(5):302–7.
Catalanotto C, Cogoni C, Zardo G. MicroRNA in control of gene expression: an overview of nuclear functions. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(10):1712.
Eslamizadeh S, Heidari M, Sh A, Faghihloo E, Ghazi H, Mirzaei A, et al. The role of microRNA signature as diagnostic biomarkers in different clinical stages of colorectal cancer. Cell J. 2018;20:220–30.
Zhou K, Liu M, Cao Y. New insight into microRNA functions in cancer: oncogene–microRNA–tumor suppressor gene network. Frontiers in molecular biosciences, vol. 4; 2017. p. 46.
Dong Y, Yu J, Ng SS. MicroRNA dysregulation as a prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2014;6:405.
Corsini LR, Bronte G, Terrasi M, Amodeo V, Fanale D, Fiorentino E, et al. The role of microRNAs in cancer: diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers and targets of therapies. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012;16(sup2):S103–9.
Oh M, Rhee S, Moon JH, Chae H, Lee S, Kang J, et al. Literature-based condition-specific miRNA-mRNA target prediction. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0174999.
Hashimoto Y, Akiyama Y, Yuasa Y. Multiple-to-multiple relationships between microRNAs and target genes in gastric cancer. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e62589.
Kandhavelu J, et al. Computational analysis of miRNA and their gene targets significantly involved in colorectal cancer progression. MicroRNA (Shariqah, United Arab Emirates). 2018.
Tariq K, Ghias K. Colorectal cancer carcinogenesis: a review of mechanisms. Cancer Biol Med. 2016;13(1):120–35.
Seo J, Jin D, Choi CH, Lee H. Integration of MicroRNA, mRNA, and protein expression data for the identification of cancer-related MicroRNAs. PLoS One. 2017;12(1):e0168412.
Wu X-m, Shao XQ, Meng XX, Zhang XN, Zhu L, Liu SX, et al. Genome-wide analysis of microRNA and mRNA expression signatures in hydroxycamptothecin-resistant gastric cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011;32(2):259–69.
Li M-h, Fu S-b, Xiao H-s. Genome-wide analysis of microRNA and mRNA expression signatures in cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015;36(10):1200–11.
Akbari A, Ghahremani MH, Mobini GR, Abastabar M, Akhtari J, Bolhassani M, et al. Down-regulation of miR-135b in colon adenocarcinoma induced by a TGF-β receptor I kinase inhibitor (SD-208). Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015;18(9):856–61.
Vlachos IS, Zagganas K, Paraskevopoulou MD, Georgakilas G, Karagkouni D, Vergoulis T, et al. DIANA-miRPath v3. 0: deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(W1):W460–6.
Cekaite L, et al. MicroRNAs as growth regulators, their function and biomarker status in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(6):6476.
Chen J, Wang W, Zhang Y, Hu T, Chen Y. The roles of miR-200c in colon cancer and associated molecular mechanisms. Tumor Biol. 2014;35(7):6475–83.
Yu Y, Nangia-Makker P, Farhana L, G. Rajendra S, Levi E, Majumdar APN. miR-21 and miR-145 cooperation in regulation of colon cancer stem cells. Mol Cancer. 2015;14(1):98.
Gao XH, et al. Differences of protein expression profiles, KRAS and BRAF mutation, and prognosis in right-sided colon, left-sided colon and rectal cancer. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):7882.
Boutin AT, Liao WT, Wang M, Hwang SS, Karpinets TV, Cheung H, et al. Oncogenic Kras drives invasion and maintains metastases in colorectal cancer. Genes Dev. 2017;31:370–82.
Nussinov R, Tsai C-J, Jang H. Independent and core pathways in oncogenic KRAS signaling. In: Independent and core pathways in oncogenic KRAS signaling: Taylor & Francis; 2016.
Chen Y, Gruidl M, Remily-Wood E, Liu RZ, Eschrich S, Lloyd M, et al. Quantification of β-catenin signaling components in colon cancer cell lines, tissue sections, and microdissected tumor cells using reaction monitoring mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res. 2010;9(8):4215–27.
Najdi R, Holcombe RF, Waterman ML. Wnt signaling and colon carcinogenesis: beyond APC. J Carcinog. 2011;10:5.
Novellasdemunt L, Antas P, Li VS. Targeting Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer. A review in the theme: cell signaling: proteins, pathways and mechanisms. Am J Phys Cell Phys. 2015;309(8):C511–21.
Ye J-J, Cao J. MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer as markers and targets: recent advances. World J Gastroenterol: WJG. 2014;20(15):4288.
Ferraro A, Kontos CK, Boni T, Bantounas I, Siakouli D, Kosmidou V, et al. Epigenetic regulation of miR-21 in colorectal cancer: ITGB4 as a novel miR-21 target and a three-gene network (miR-21-ITGΒ4-PDCD4) as predictor of metastatic tumor potential. Epigenetics. 2014;9(1):129–41.
Wu Y, Song Y, Xiong Y, Wang X, Xu K, Han B, et al. MicroRNA-21 (Mir-21) promotes cell growth and invasion by repressing tumor suppressor PTEN in colorectal cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(3):945–58.
Li T, et al. MicroRNA-21 as a potential colon and rectal cancer biomarker. World J Gastroenterol: WJG. 2013;19(34):5615.
Oliveto S, Mancino M, Manfrini N, Biffo S. Role of microRNAs in translation regulation and cancer. World J Biol Chem. 2017;8(1):45–56.
Aizer A, Shav-Tal Y. Intracellular trafficking and dynamics of P bodies. Prion. 2008;2(4):131–4.
Stalder L, Mühlemann O. Processing bodies are not required for mammalian nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Rna. 2009;15:1265–73.
Cantini L, et al. A review of computational approaches detecting microRNAs involved in cancer. Frontiers in Bioscience (Landmark edition). 2017;22:1774–91.
Serra RW, Fang M, Park SM, Hutchinson L, Green MR. A KRAS-directed transcriptional silencing pathway that mediates the CpG island methylator phenotype. Elife. 2014;3:e02313.
Valeri N, et al. MicroRNA-135b promotes cancer progression by acting as a downstream effector of oncogenic pathways in colon cancer. Cancer Cell. 2014;25(4):469–83.
Aslam MI, Hussein S, West K, Singh B, Jameson JS, Pringle JH. MicroRNAs associated with initiation and progression of colonic polyp: a feasibility study. Int J Surg. 2015;13:272–9.
Nagel R, le Sage C, Diosdado B, van der Waal M, Oude Vrielink JAF, Bolijn A, et al. Regulation of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene by the miR-135 family in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68(14):5795–802.
Chivukula RR, Shi G, Acharya A, Mills EW, Zeitels LR, Anandam JL, et al. An essential mesenchymal function for miR-143/145 in intestinal epithelial regeneration. Cell. 2014;157(5):1104–16.
Li S, Wu X, Xu Y, Wu S, Li Z, Chen R, et al. miR-145 suppresses colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting an ETS-related gene. Oncol Rep. 2016;36(4):1917–26.
Rokavec M, et al. The p53/microRNA connection in gastrointestinal cancer. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2014;7:395.
Vergoulis T, et al. TarBase 6.0: capturing the exponential growth of miRNA targets with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;40(D1):D222–9.
Zhang G, Yin S, Mao J, Liang F, Zhao C, Li P, et al. Integrated analysis of mRNA-seq and miRNA-seq in the liver of Pelteobagrus vachelli in response to hypoxia. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22907.
Guo L, et al. Integrative analysis of miRNA-mRNA and miRNA-miRNA interactions. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014.
Martinez-Pastor M, Lancaster WA, Tonner PD, Adams MWW, Schmid AK. A transcription network of interlocking positive feedback loops maintains intracellular iron balance in archaea. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(17):9990–10001.
Herranz H, Cohen SM. MicroRNAs and gene regulatory networks: managing the impact of noise in biological systems. Genes Dev. 2010;24(13):1339–44.
Lai X, Wolkenhauer O, Vera J. Understanding microRNA-mediated gene regulatory networks through mathematical modelling. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(13):6019–35.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the patients who participated in the study.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Deputy of Research, Iran University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. 26699).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PG and AA contributed to the study design and conception. FM and SM performed experiments. AA and AT assisted with the analysis of the data. AA prepared the manuscript which PG and AT significantly revised. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The project was approved by the Research Ethics Committee (Ethical code number: IR.IUMS.REC 94–26699.) All patients signed a free and informed consent form for enrollment in the study.
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moghadamnia, F., Ghoraeian, P., Minaeian, S. et al. MicroRNA Expression and Correlation with mRNA Levels of Colorectal Cancer-Related Genes. J Gastrointest Canc 51, 271–279 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-019-00249-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-019-00249-2