Abstract
Purpose
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the predominant types of esophageal cancer with poor prognosis which shows high prevalence in eastern countries. Studying microRNAs that were considered for their capabilities such as tissue-specific expression and involvement in different cell features may be informative in the field of diagnostic and prognostic tumor markers. The expression levels of miR-27a and miR-24-2 have been reported to be dysregulated in various cancers and contribute in tumorigenesis and progression; thus, evaluating their expressional behavior and its association with tumor states alteration in ESCC could potentially be helpful.
Methods
The study was conducted on 30 fresh specimens including tumor and normal counterparts’ tissues of ESCC. After the extraction of total RNA, complementary DNA synthesis was performed by the use of linear specific primers. Eventually, real-time polymerase chain reaction was carried out for the measurement of microRNAs expression level.
Results
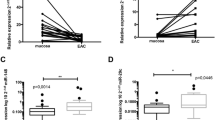
According to the obtained data, miR 27a and miR-24-2 were significantly upregulated (~2.5 fold, p < 0.05) in tumor specimens compared with their normal adjacent tissue; Moreover, upregulation of miR-27a and 24-2 showed cooperative relationship while analyzed. However, there was no correlation between clinicopathological features and microRNAs upregulation.
Conclusions
The results of this study show that miR-27a and miR-24-2 cooperatively upregulate in ESCC and suggest that these microRNAs can be introduced as a candidate for further study in the field of screening and prognostic biomarkers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 2013;381(9864):400–12.
Ludwig JA, Weinstein JN. Biomarkers in cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(11):845–56.
Iorio MV, Croce CM. MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med. 2012;4(3):143–59.
Farazi TA, Hoell JI, Morozov P, Tuschl T. MicroRNAs in human cancer. In: MicroRNA cancer regulation. Dordrecht: Springer; 2013. pp. 1–20.
Zhao B-S, Liu S-G, Wang T-Y, Ji Y-H, Qi B, Tao Y-P, et al. Screening of microRNA in patients with esophageal cancer at same tumor node metastasis stage with different prognoses. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(1):139–43.
He B, Yin B, Wang B, Xia Z, Chen C, Tang J. microRNAs in esophageal cancer (review). Mol Med Rep. 2012;6(3):459–65.
Chhabra R, Dubey R, Saini N (2010) Cooperative and individualistic functions of the microRNAs in the miR-23a~ 27a~ 24-2 cluster and its implication in human diseases. Mol Cancer 9 (1):232.ge
Salah Z, Arafeh R, Maximov V, Galasso M, Khawaled S, Abou-Sharieha S, et al. miR-27a and miR-27a* contribute to metastatic properties of osteosarcoma cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6(7):4920–35.
Huang D, Wang H, Liu R, Li H, Ge S, Bai M, et al. miRNA27a is a biomarker for predicting chemosensitivity and prognosis in metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(3):549–56.
Liu S-G, Qin X-G, Zhao B-S, Qi B, Yao WJ, Wang T-Y, et al. Differential expression of miRNAs in esophageal cancer tissue. Oncol Lett. 2013;5(5):1639–42.
Kimura S, Naganuma S, Susuki D, Hirono Y, Yamaguchi A, Fujieda S, et al. Expression of microRNAs in squamous cell carcinoma of human head and neck and the esophagus: miR-205 and miR-21 are specific markers for HNSCC and ESCC. Oncol Rep. 2010;23(6):1625–33.
Lee S-H, Chen T-Y, Dhar SS, Gu B, Chen K, Kim YZ, et al. A feedback loop comprising PRMT7 and miR-24-2 interplays with Oct4, Nanog, Klf4 and c-Myc to regulate stemness. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(22):10603–18.
Wang D, Si S, Wang Q, Luo G, Du Q, Liang Q, et al. MiR-27a promotes hemin-induced erythroid differentiation of K562 cells by targeting CDC25B. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(1):365–74.
Zhu L, Wang Z, Fan Q, Wang R, Sun. microRNA-27a functions as a tumor suppressor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting KRAS. Oncol Rep. 2014;30(1):280–6.
Dong W, Li B, Wang Z, et al. Clinical significance of microRNA-24 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasma. 2015;62(2):250–8.
Wang YL, Gong WG, Yuan QL. Effects of miR-27a upregulation on thyroid cancer cells migration, invasion, and angiogenesis. Genet Mol Res. 2016;4:15.
Zhang S, Ma C, Pang H, Zeng F, Cheng L, Fang B, et al. Arsenic trioxide suppresses cell growth and migration via inhibition of miR-27a in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;469(1):55–61.
Kerimis D, Kontos CK, Christodoulou S, Papadopoulos IN, Scorilas A. Elevated expression of miR-24-3p is a potentially adverse prognostic factor in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Clin Biochem. 2017;50(6):285–92.
Ba S, Xuan Y, Long Z-W, Chen H-Y, Zheng S-S. MicroRNA-27a promotes the proliferation and invasiveness of colon cancer cells by targeting SFRP1 through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(5):1920–33.
Cui S, Liao X, Ye C, Yin X, Liu M, Hong Y, et al. ING5 suppresses breast cancer progression and is regulated by miR-24. Mol Cancer. 2017;16(1):89.
Ye P, Ke X, Zang X, Sun H, Dong Z, Lin J, et al. Up-regulated MiR-27-3p promotes the G1-S phase transition by targeting inhibitor of growth family member 5 in osteosarcoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;101:219–27.
Lin S-C, Liu C-J, Lin J-A, Chiang W-F, Hung P-S, Chang K-W. miR-24 up-regulation in oral carcinoma: positive association from clinical and in vitro analysis. Oral Oncol. 2010;46(3):204–8.
Lu K, Wang J, Song Y, Zhao S, Liu H, Tang D, et al. miRNA-24-3p promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in human breast cancer by targeting p27Kip1. Oncol Rep. 2015;34(2):995–1002.
Zhang Z, Liu S, Shi R, Zhao G. miR-27 promotes human gastric cancer cell metastasis by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Genet. 2011;204(9):486–91.
Li X, Liu X, Xu W, Zhou P, Gao P, Jiang S, et al. C-MYC regulated miR-23a~ 24-2~ 27a cluster promotes mammary carcinoma cell invasion and hepatic metastasis by targeting Sprouty2. J Biol Chem. 2013;M113:478560.
Ma Y, Yu S, Zhao W, Lu Z, Chen J. miR-27a regulates the growth, colony formation and migration of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting Sprouty2. Cancer Lett. 2010;298(2):150–8.
Zhao J, Chi J, Gao M, Zhi J, Li Y, Zheng X. Loss of PTEN expression is associated with high MicroRNA 24 level and poor prognosis in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;75(7):1449. e1441–8.
Du WW, Fang L, Li M, Yang X, Liang Y, Peng C, et al. MicroRNA miR-24 enhances tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting PTPN9 and PTPRF to promote EGF signaling. J Cell Sci. 2013;126(6):1440–53.
Li Y, Li J, Sun X, Chen J, Sun X, Zheng J, et al. MicroRNA-27a functions as a tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma by targeting epidermal growth factor receptor. Oncol Lett. 2016;11(6):4217–23.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences. We are also grateful to the Golestan Research Center of Gastroenterology and Hepatology for their help in collecting the samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Standards
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki declaration of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent or substitute for it was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maghsudlu, M., Farashahi Yazd, E. & Amiriani, T. Increased Expression of MiR-27a and MiR-24-2 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J Gastrointest Canc 51, 227–233 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-019-00232-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-019-00232-x