Abstract
Background
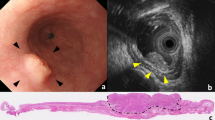
Accurate staging of esophageal carcinoma (EC) is important since it directs further management. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is the best tool available in the locoregional staging of EC; however, differentiating depth of tumor invasion (T) and nodal involvement (N) can be challenging. Accurate staging is particularly important to differentiate T1-2 N0 cancers, which can proceed directly to surgical resection versus TXN1 or T3N0/1 cancers, which benefit from induction chemoradiation prior to surgery. We report the accuracy of EUS staging for cT2N0 lesions.
Patients and Interventions
Six hundred six patients underwent EUS for staging of EC between October 2003 and February 2013 by a single interventional endoscopist specially trained in endoscopic ultrasound. Thirty-eight patients were diagnosed with T2N0 tumors and underwent surgical resection without preoperative chemoradiation. EUS staging was compared to surgical pathology to evaluate accuracy. Patient follow-up was obtained from a retrospective chart review.
Results
Thirty-eight patients (34 men, mean age 65.8 ± 10.5 years) with cT2N0 tumors by EUS underwent surgical resection of EC without chemoradiation after a mean of 22.4 ± 13.7 days post-EUS. When compared with final pathologic outcomes, 12 (32 %) were understaged by EUS and 18 (47 %) were overstaged. Understaging occurred due to tumor depth (T) in two patients (17 %), nodal disease (N) in six (50 %), and both in four (33 %). Overstaging occurred due to pathology consistent with pT1b tumors instead of T2 tumors in all 17 cases. Based on EUS, 74 % were referred for appropriate therapy.
Conclusion
While EUS is highly accurate in staging EC, it is less accurate in staging tumors which are not on either ends of the spectrum (mucosally based or clearly transmural). In this challenging group of patients, EUS understaged EC in 32 % of cases resulting in surgical resection when neoadjuvant chemoradiation may have been beneficial. We suspect that newer generation EUS systems, which provide better imaging, will result in improved accuracy in staging this group of patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300.
Rice TW, Blackstone EH, Rusch VW. 7th edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: esophagus and esophagogastric junction. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:1721–4.
Rice TW, Rusch VW, Ishwaran H, Blackstone EH. Worldwide Esophageal Cancer Collaboration. Cancer of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction: data-driven staging for the seventh edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer/International Union Against Cancer Cancer Staging Manuals. Cancer. 2010;116:3763–73.
Rice TW, Blackstone EH, Rusch VW. A cancer staging primer: esophagus and esophagogastric junction. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;139:527–9.
Byrne MF, Jowell PS. Gastrointestinal imaging: endoscopic ultrasound. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1631–48.
Vazquez-Sequeiros E, Norton ID, Clain JE, et al. Impact of EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration on lymph node staging in patients with esophageal carcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;53:751–7.
Lightdale CJ. Esophageal cancer. American College of Gastroenterology. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94:20–9.
Kelly S, Harris KM, Berry E, et al. A systematic review of the staging performance of endoscopic ultrasound in gastro-oesophageal carcinoma. Gut. 2001;49:534–9.
Hall JD, Kahaleh M, White GE, Talreja J, Northup PG, Shami VM. Presence of lymph node vasculature: a new EUS criterion for benign nodes? Dig Dis Sci. 2009;54:118–21.
Keller SM, Ryan LM, Coia LR, et al. High dose chemoradiotherapy followed by esophagectomy for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction: results of a phase II study of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Cancer. 1998;83:1908–16.
Rice TW, Mason DP, Murthy SC, et al. T2N0M0 esophageal cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;133:317–24.
Stiles BM, Mirza F, Coppolino A, et al. Clinical T2-T3N0M0 esophageal cancer: the risk of node positive disease. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;92:491–6. discussion 496-8.
May A, Gunter E, Roth F, et al. Accuracy of staging in early oesophageal cancer using high resolution endoscopy and high resolution endosonography: a comparative, prospective, and blinded trial. Gut. 2004;53:634–40.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The earlier data was presented in part at the annual meeting of the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, Digestive Diseases Week, May 1–May 5, 2010, New Orleans, LA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tekola, B.D., Sauer, B.G., Wang, A.Y. et al. Accuracy of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of T2N0 Esophageal Cancer. J Gastrointest Canc 45, 342–346 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-014-9616-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-014-9616-9