Abstract
Purpose
Three-dimensional computed tomography-based radiotherapy planning (3DCTP) is increasingly employed in the treatment of esophageal cancer. It is unknown whether a 3DCTP approach influences outcomes compared to two-dimensional planning (2DP). This study compares clinical outcomes for homogenously treated patient cohorts stratified by planning modality.
Methods and Materials
A retrospective chart review was conducted on patients with T3/4 and/or node-positive esophageal carcinoma treated at the Cleveland Clinic between July 1, 2003 and May 31, 2006 who were managed with an institutional regimen consisting of preoperative radiotherapy, whether 3DCTP or 2DP [30 Gy/20 fractions/1.5 Gy twice daily over 2 weeks], with concurrent cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil the first week. Following definitive resection, an identical postoperative course of concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CRT) was delivered.
Results
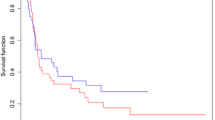
One hundred and forty-one patients completed preoperative CRT and were available for review. The median follow-up of living patients is 21.7 months. Fifty-five percent underwent 3DCTP and 45% had 2DP. The treatment groups were similar, with the exception of clinical stage group, with 2DP having more stage II and fewer stage III patients than 3DCTP (p = 0.02). 3DCTP plans had significantly smaller field sizes by area (p < 0.0001). Pathologic response, locoregional control, distant control, and overall survival were equivalent between the two planning modalities. Esophagitis was significantly less common with a 3D approach compared to 2D planning (49% vs. 71%, p = 0.0096), with other toxicities equivalent between the groups.
Conclusions
3DCTP reduces acute esophagitis in patients receiving multimodality therapy for esophageal cancer without compromising clinical outcomes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures 2006. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2006.
Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP, et al. Preoperative chemotherapy versus surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:11–20. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa055531.
Walsh TN, Noonan N, Hollywood D, Kelly A, et al. A comparison of multimodality therapy and surgery for esophageal adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:462–7. doi:10.1056/NEJM199608153350702.
MacDonald JS, Smalley SR, Benedetti J, et al. Chemoradiotherapy after surgery compared with surgery alone for adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:725–30. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa010187.
Herskovic A, Martz K, al-Sarraf M, et al. Combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy compared with radiotherapy alone in patients with cancer of the esophagus. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:1593–8.
Smith TJ, Ryan LM, Douglass HO, et al. Combined chemoradiotherapy vs. radiotherapy alone for early stage squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a study of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998;42:269–76. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(98)00232-6.
Kumar S, Dimri K, Khurana R, et al. A randomized trial of radiotherapy compared with cisplatin chemo-radiotherapy in patients with unresectable squamous cell cancer of the esophagus. Radiother Oncol. 2007;83:139–47. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2007.03.013.
Adelstein DJ, Rice TW, Rybicki LA, et al. A phase II trial of accelerated multimodality therapy for locoregionally advanced cancer of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction: the impact of clinical heterogeneity. Am J Clin Oncol. 2007;30:172–80. doi:10.1097/01.coc.0000251243.58048.12.
Nishioka T, Shirato H, Arimoto T, et al. Reduction of radiation-induced xerostomia in nasopharyngeal carcinoma using CT simulation with laser patient marking and three-field irradiation technique. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;38:705–12. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(97)00054-0.
Jabbari S, Kim HM, Eisbruch A, et al. Matched case-control study of quality of life and xerostomia after intensity-modulated radiotherapy or standard radiotherapy for head-and-neck cancer: initial report. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;63:725–31. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.02.045.
Graff P, Lapeyre M, Desandes E, et al. Impact of intensity-modulated radiotherapy on health-related quality of life for head and neck cancer patients: matched-pair comparison with conventional radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67:1309–17. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.11.012.
Vuong T, Kopek N, Ducruet T, et al. Conformal therapy improves the therapeutic index of patients with anal canal cancer treated with combined chemotherapy and external beam radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67:1394–400. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.11.038.
Chen MF, Tseng CJ, Tseng CC, et al. Clinical outcome in posthysterectomy cervical cancer patients treated with concurrent cisplatin and intensity-modulated pelvic radiotherapy: comparison with conventional radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67:1438–44. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.11.005.
Donovan E, Bleakley N, Denholm E, et al. Randomized trial of standard 2D radiotherapy (RT) versus intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) in patients prescribed breast radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2007;82:254–64. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2006.12.008.
Dearnaley DP, Khoo VS, Norman AR, et al. Comparison of radiation side-effects of conformal and conventional radiotherapy in prostate cancer: a randomized trial. Lancet. 1999;353:267–72. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(98)05180-0.
Koper PM, Stroom JC, van Putten WLJ, et al. Acute morbidity reduction using 3DCRT for prostate carcinoma: a randomized study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999;43:727–34. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(98)00406-4.
Guzel ZB, Childs JL, Nahum PJ, et al. A comparison of conventional and conformal radiotherapy of the oesophagus: work in progress. Br J Radiol. 1998;71:1076–82.
Ahmad M, Nath R. Three-dimensional radiotherapy of head and neck and esophageal carcinomas: a monoisocentric treatment technique to achieve improved dose distributions. Int J Cancer. 2001;96:55–65. doi:10.1002/1097-0215(20010220)96:1<55::AID-IJC6>3.0.CO;2-#.
Rosenman JG, Halle JS, Socinski MA, et al. High-dose conformal radiotherapy for treatment of stage IIIa/IIIb non-small-cell lung cancer: technical issues and results of a phase I/II trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;54:348–56. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(02)02958-9.
Bradley J, Deasy J, Bentzen S, et al. Dosimetric correlates for acute esophagitis in patients treated with radiation therapy for lung carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;58:1106–13. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.09.080.
Kim TH, Cho KH, Pyo HR, et al. Dose-volumetric parameters of acute esophageal toxicity in patients with lung cancer treated with three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;62:995–1002. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.12.025.
Fang LC, Komaki R, Allen P, et al. Comparison of outcomes for patients with medically inoperable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer treated with two-dimensional vs. three-dimensional radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66:108–16. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.04.015.
Sasso FS, Sasso G, Marsiglia HR, et al. Pharmacological and dietary prophylaxis and treatment of acute actinic esophagitis during mediastinal radiotherapy. Dig Dis Sci. 2001;46:746–9. doi:10.1023/A:1010735914163.
Antonadou D, Coliarakis N, Syndoinou M, et al. Randomized phase III trial of radiation treatment +/− amifostine in patients with advanced-stage lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;51:915–22. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(01)01713-8.
Antonadou D, Throuvalas N, Petridis A, et al. Effect of amifostine on toxicities associated with radiochemotherapy in patients with locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;57:402–8. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(03)00590-X.
Komaki R, Lee JS, Kaplan B, et al. Randomized phase III study of chemoradiation with or without amifostine for patients with favorable performance status inoperable stage II-III non-small cell lung cancer: preliminary results. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2002;12:46–9. doi:10.1053/srao.2002.31363.
Conflicts of Interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mackley, H.B., Adelstein, J.S., Reddy, C.A. et al. Choice of Radiotherapy Planning Modality Influences Toxicity in the Treatment of Locally Advanced Esophageal Cancer. J Gastrointest Canc 39, 130–137 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-009-9067-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-009-9067-x