Abstract
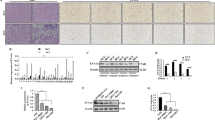
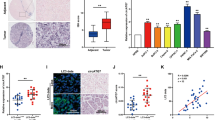
This study aims to investigate the role of circCBFB in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell proliferation and autophagy. qRT-PCR and Western blotting analyses quantified the expression levels of circCBFB, miR-424-5p, and ATG14 in HCC tissues and/or HCC cell lines. After transfection with pcDNA3.1-CircCBFB, sh-CircCBFB, miR-424-5p mimic, miR-424-5p inhibitor, pcDNA3.1-ATG14, sh-ATG14, sh-CircCBFB + miR-424-5p inhibitor, pcDNA3.1-CircCBFB + miR-424-5p mimic, sh-CircCBFB + pcDNA3.1-ATG14, or pcDNA3.1-CircCBFB + sh-ATG14, the proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of Huh-7 and HCCLM3 cells were detected, respectively, through MTT assay and flow cytometry. Western blotting measured the expression levels of ATG14 and autophagy-related proteins (LC3-ΙΙ/LC3-Ι, Beclin1, and p62). The interactions among circCBFB, miR-424-5p, and ATG14 were identified through RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization and RNA immunoprecipitation. In HCC tissues, circCBFB and ATG14 were highly expressed, and miR-424-5p expression was downregulated. Transfection of pcDNA3.1-CircCBFB, miR-424-5p inhibitor, or pcDNA3.1-ATG14 into HCC cells facilitated HCC cell proliferation and autophagy, while suppressing cell apoptosis, evidenced by elevated cell viability, increased protein levels of autophagosome markers (LC3-ΙΙ/LC3-Ι and Beclin1), repressed apoptosis rate, and suppressed protein level of autophagy receptor p62. miR-424-5p was a target gene of circCBFB, and miR-424-5p negatively mediated ATG14. CircCBFB inhibits miR-424-5p and upregulates ATG14, thus promoting HCC cell proliferation and autophagy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang W, Sui J, Ma Y, Simon TG, Chong D, Meyerhardt JA, et al. A prospective study of dairy product intake and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in U. S. men and women. Int J Cancer. 2020;146(5):1241–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.32423.
Chaudhary K, Poirion OB, Lu L, Garmire LX. Deep learning-based multi-omics integration robustly predicts survival in liver cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(6):1248–59. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0853.
Reynaert H, Colle I. Treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with somatostatin analogues: a review of the literature. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194811.
Ding H, Liu J, Zou R, Cheng P, Su Y. Long non-coding RNA TPTEP1 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by suppressing STAT3 phosphorylation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):189. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1193-0.
Zhou J, Zhang X, Tang H, Yu J, Zu X, Xie Z, et al. Nuclear factor erythroid 2 (NF-E2)-related factor 2 (Nrf2) in autophagy-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;506:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2020.02.028.
Kiruthiga C, Devi KP, Nabavi SM, Bishayee A. Autophagy: a potential therapeutic target of polyphenols in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(3). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12030562.
Niture S, Gyamfi MA, Lin M, Chimeh U, Dong X, Zheng W, et al. TNFAIP8 regulates autophagy, cell steatosis, and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(3):178. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2369-4.
Wang CZ, Yan GX, Dong DS, Xin H, Liu ZY. LncRNA-ATB promotes autophagy by activating yes-associated protein and inducing autophagy-related protein 5 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(35):5310–22. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i35.5310.
Xu WP, Liu JP, Feng JF, Zhu CP, Yang Y, Zhou WP, et al. miR-541 potentiates the response of human hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib treatment by inhibiting autophagy. Gut. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318830.
Huang KT, Kuo IY, Tsai MC, Wu CH, Hsu LW, Chen LY, et al. Factor VII-induced microRNA-135a inhibits autophagy and is associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017;9:274–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2017.10.002.
Qiu L, Huang Y, Li Z, Dong X, Chen G, Xu H, et al. Circular RNA profiling identifies circADAMTS13 as a miR-484 sponge which suppresses cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Oncol. 2019;13(2):441–55. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12424.
Wang S, Cui S, Zhao W, Qian Z, Liu H, Chen Y, et al. Screening and bioinformatics analysis of circular RNA expression profiles in hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2018;22(4):631–40. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-170910.
Qu S, Liu Z, Yang X, Zhou J, Yu H, Zhang R, et al. The emerging functions and roles of circular RNAs in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018;414:301–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.11.022.
Guan Z, Tan J, Gao W, Li X, Yang Y, Li X, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0016788 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis through miR-486/CDK4 pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2018;234(1):500–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26612.
Huang XY, Huang ZL, Xu YH, Zheng Q, Chen Z, Song W, et al. Comprehensive circular RNA profiling reveals the regulatory role of the circRNA-100338/miR-141-3p pathway in hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):5428. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05432-8.
Xia L, Wu L, Bao J, Li Q, Chen X, Xia H, et al. Circular RNA circ-CBFB promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia through regulating miR-607/FZD3/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(1):385–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.045.
Yue J, Zhu T, Yang J, Si Y, Xu X, Fang Y, et al. CircCBFB-mediated miR-28-5p facilitates abdominal aortic aneurysm via LYPD3 and GRIA4. Life Sci. 2020;253: 117533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117533.
Wang Z, Zhao Y, Sun R, Sun Y, Liu D, Lin M, et al. circ-CBFB upregulates p66Shc to perturb mitochondrial dynamics in APAP-induced liver injury. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(11):953. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03160-y.
Ding Z, Guo L, Deng Z, Li P. Circ-PRMT5 enhances the proliferation, migration and glycolysis of hepatoma cells by targeting miR-188-5p/HK2 axis. Ann Hepatol. 2020;19(3):269–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aohep.2020.01.002.
Pu J, Wang J, Li W, Lu Y, Wu X, Long X, et al. hsa_circ_0000092 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through up-regulating HN1 expression by binding to microRNA-338-3p. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15010.
Wei X, Zheng W, Tian P, He Y, Liu H, Peng M, et al. Oncogenic hsa_circ_0091581 promotes the malignancy of HCC cell through blocking miR-526b from degrading c-MYC mRNA. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(7):817–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2020.1731945.
Chen DP, Ning WR, Li XF, Wei Y, Lao XM, Wang JC, et al. Peritumoral monocytes induce cancer cell autophagy to facilitate the progression of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Autophagy. 2018;14(8):1335–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2018.1474994.
Xiong H, Ni Z, He J, Jiang S, Li X, He J, et al. LncRNA HULC triggers autophagy via stabilizing Sirt1 and attenuates the chemosensitivity of HCC cells. Oncogene. 2017;36(25):3528–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.521.
Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT, Tang D. The Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2011;18(4):571–80. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.191.
Shan Y, Li P. Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 665 regulates viability, apoptosis, and autophagy via the MiR-186-5p/MAP4K3 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Yonsei Med J. 2019;60(9):842–53. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.9.842.
Qiu DM, Wang GL, Chen L, Xu YY, He S, Cao XL, et al. The expression of beclin-1, an autophagic gene, in hepatocellular carcinoma associated with clinical pathological and prognostic significance. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:327. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-327.
Klionsky DJ, Baehrecke EH, Brumell JH, Chu CT, Codogno P, Cuervo AM et al. A comprehensive glossary of autophagy-related molecules and processes (2nd edition). Autophagy. 2011;7(11):1273–94. doi:https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.7.11.17661.
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495(7441):384–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11993.
Du H, Xu Q, Xiao S, Wu Z, Gong J, Liu C, et al. MicroRNA-424-5p acts as a potential biomarker and inhibits proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting TRIM29. Life Sci. 2019;224:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.03.028.
Zhang Y, Li T, Guo P, Kang J, Wei Q, Jia X, et al. MiR-424-5p reversed epithelial-mesenchymal transition of anchorage-independent HCC cells by directly targeting ICAT and suppressed HCC progression. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6248. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06248.
Li B, Wu X, Chen H, Zhuang C, Zhang Z, Yao S, et al. miR199a-5p inhibits hepatic insulin sensitivity via suppression of ATG14-mediated autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(3):405. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0439-7.
Yu F, Dong B, Dong P, He Y, Zheng J, Xu P. Hypoxia induces the activation of hepatic stellate cells through the PVT1-miR-152-ATG14 signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020;465(1–2):115–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03672-y.
Xiong X, Tao R, DePinho RA, Dong XC. The autophagy-related gene 14 (Atg14) is regulated by forkhead box O transcription factors and circadian rhythms and plays a critical role in hepatic autophagy and lipid metabolism. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(46):39107–14. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.412569.
Matsunaga K, Morita E, Saitoh T, Akira S, Ktistakis NT, Izumi T, et al. Autophagy requires endoplasmic reticulum targeting of the PI3-kinase complex via Atg14L. J Cell Biol. 2010;190(4):511–21. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200911141.
Fogel AI, Dlouhy BJ, Wang C, Ryu SW, Neutzner A, Hasson SA, et al. Role of membrane association and Atg14-dependent phosphorylation in beclin-1-mediated autophagy. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33(18):3675–88. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00079-13.
Wu FQ, Fang T, Yu LX, Lv GS, Lv HW, Liang D, et al. ADRB2 signaling promotes HCC progression and sorafenib resistance by inhibiting autophagic degradation of HIF1alpha. J Hepatol. 2016;65(2):314–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.04.019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Z., He, J. & Feng, C. CircCBFB is a mediator of hepatocellular carcinoma cell autophagy and proliferation through miR-424-5p/ATG14 axis. Immunol Res 70, 341–353 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-021-09255-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-021-09255-8