Abstract
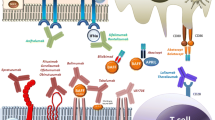
CD6 is a cell surface receptor expressed on the majority of T cells and a subset of B cells. When expressed, CD6 contributes to lymphocyte activation through its extracellular domain 1, while adhesion and cellular migration are related to the extracellular scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain (SRCR-D)-3 of CD6. Itolizumab, clone T1h, is a newly developed humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets CD6 SRCR-D1 and blocks immune activation. Itolizumab has been proposed to be effective in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren’s syndrome and multiple sclerosis. In Sjögren’s syndrome, the utilization of itolizumab as therapeutic option is reinforced by our recent observation that ALCAM, the CD6 ligand, is overexpressed and that CD6-positive T and B cells are detected within salivary glands from Sjögren’s syndrome patients. In this study, itolizumab-positive target cells were characterized within both peripheral blood and salivary glands in order to provide rational for anti-CD6 treatment in Sjögren’s syndrome.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tobon GJ, Pers JO, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Youinou P. Neurological Disorders in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome. Autoimmune Dis. 2012.
Roguedas AM, Pers JO, Lemasson G, Devauchelle V, Tobon GJ, Saraux A, Misery L, Youinou P. Memory B-cell aggregates in skin biopsy are diagnostic for primary Sjogren’s syndrome. J Autoimmun. 2010;35:241–7.
Youinou P, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Pers JO. Significance of B cells and B cell clonality in Sjogren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2605–10.
Agmon-Levin N, Kivity S, Tzioufas AG, Lopez Hoyos M, Rozman B, Efes I, Shapira Y, Shamis A, Amital H, Youinou P, Shoenfeld Y. Low levels of vitamin-D are associated with neuropathy and lymphoma among patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. J Autoimmun. 2012;39:234–9.
Brooks WH, Le Dantec C, Pers JO, Youinou P, Renaudineau Y. Epigenetics and autoimmunity. J Autoimmun. 2010;34:J207–19.
Cruz-Tapias P, Rojas-Villarraga A, Maier-Moore S, Anaya JM. HLA and Sjogren’s syndrome susceptibility. A meta-analysis of worldwide studies. Autoimmun Rev. 2012;11:281–7.
Le Dantec C, Varin MM, Brooks WH, Pers JO, Youinou P, Renaudineau Y. Epigenetics and Sjogren’s syndrome. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13:2046–53.
Pers JO, Devauchelle V, Daridon C, Bendaoud B, Le Berre R, Bordron A, Hutin P, Renaudineau Y, Dueymes M, Loisel S, Berthou C, Saraux A, Youinou P. BAFF-modulated repopulation of B lymphocytes in the blood and salivary glands of rituximab-treated patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1464–77.
Varin MM, Guerrier T, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Jamin C, Youinou P, Pers JO. In Sjogren’s syndrome, B lymphocytes induce epithelial cells of salivary glands into apoptosis through protein kinase C delta activation. Autoimmun Rev. 2012;11:252–8.
Christodoulou MI, Kapsogeorgou EK, Moutsopoulos HM. Characteristics of the minor salivary gland infiltrates in Sjogren’s syndrome. J Autoimmun. 2010;34:400–7.
Daridon C, Pers JO, Devauchelle V, Martins-Carvalho C, Hutin P, Pennec YL, Saraux A, Youinou P. Identification of transitional type II B cells in the salivary glands of patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2280–8.
Cornec D, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Tobon GJ, Pers JO, Jousse-Joulin S, Saraux A. B cells in Sjogren’s syndrome: from pathophysiology to diagnosis and treatment. J Autoimmun. 2012;39:161–7.
Alonso R, Buors C, Le Dantec C, Hillion S, Pers JO, Saraux A, Montero E, Marianowski R, Loisel S, Devauchelle V, Youinou P, Renaudineau Y. Aberrant expression of CD6 on B-cell subsets from patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. J Autoimmun. 2010;35:336–41.
Levesque MC, Heinly CS, Whichard LP, Patel DD. Cytokine-regulated expression of activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (CD166) on monocyte-lineage cells and in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41:2221–9.
Cayrol R, Wosik K, Berard JL, Dodelet-Devillers A, Ifergan I, Kebir H, Haqqani AS, Kreymborg K, Krug S, Moumdjian R, Bouthillier A, Becher B, Arbour N, David S, Stanimirovic D, Prat A. Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule promotes leukocyte trafficking into the central nervous system. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:137–45.
De Jager PL, Jia X, Wang J, de Bakker PI, Ottoboni L, Aggarwal NT, Piccio L, Raychaudhuri S, Tran D, Aubin C, Briskin R, Romano S, Baranzini SE, McCauley JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Haines JL, Gibson RA, Naeglin Y, Uitdehaag B, Matthews PM, Kappos L, Polman C, McArdle WL, Strachan DP, Evans D, Cross AH, Daly MJ, Compston A, Sawcer SJ, Weiner HL, Hauser SL, Hafler DA, Oksenberg JR. Meta-analysis of genome scans and replication identify CD6, IRF8 and TNFRSF1A as new multiple sclerosis susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 2009;41:776–82.
Kofler DM, Severson CA, Mousissian N, De Jager PL, Hafler DA. The CD6 multiple sclerosis susceptibility allele is associated with alterations in CD4 + T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 2011;187:3286–91.
Krintel SB, Essioux L, Wool A, Johansen JS, Schreiber E, Zekharya T, Akiva P, Ostergaard M, Hetland ML. CD6 and syntaxin binding protein 6 variants and response to tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors in Danish patients with rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e38539.
Oliveira MI, Goncalves CM, Pinto M, Fabre S, Santos AM, Lee SF, Castro MA, Nunes RJ, Barbosa RR, Parnes JR, Yu C, Davis SJ, Moreira A, Bismuth G, Carmo AM. CD6 attenuates early and late signaling events, setting thresholds for T-cell activation. Eur J Immunol. 2012;42:195–205.
Roque-Navarro L, Mateo C, Lombardero J, Mustelier G, Fernandez A, Sosa K, Morrison SL, Perez R. Humanization of predicted T-cell epitopes reduces the immunogenicity of chimeric antibodies: new evidence supporting a simple method. Hybrid Hybridomics. 2003;22:245–57.
Alonso R, Huerta V, de Leon J, Piedra P, Puchades Y, Guirola O, Chinea G, Montero E. Towards the definition of a chimpanzee and human conserved CD6 domain 1 epitope recognized by T1 monoclonal antibody. Hybridoma (Larchmt). 2008;27:291–301.
Alonso-Ramirez R, Loisel S, Buors C, Pers JO, Montero E, Youinou P, Renaudineau Y. Rationale for targeting CD6 as a treatment for autoimmune diseases. Arthritis. 2010;2010:130646.
Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R, Moutsopoulos HM, Alexander EL, Carsons SE, Daniels TE, Fox PC, Fox RI, Kassan SS, Pillemer SR, Talal N, Weisman MH. Classification criteria for Sjogren’s syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61:554–8.
Daniels TE. Labial salivary gland biopsy in Sjogren’s syndrome. Assessment as a diagnostic criterion in 362 suspected cases. Arthritis Rheum. 1984;27:147–56.
Guellec D, Cornec D, Jousse-Joulin S, Marhadour T, Marcorelles P, Pers JO, Saraux A, Devauchelle-Pensec V. Diagnostic value of labial minor salivary gland biopsy for Sjogren’s syndrome: a systematic review. Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12:416–20.
Braun M, Muller B, ter Meer D, Raffegerst S, Simm B, Wilde S, Spranger S, Ellwart J, Mosetter B, Umansky L, Lerchl T, Schendel DJ, Falk CS. The CD6 scavenger receptor is differentially expressed on a CD56 natural killer cell subpopulation and contributes to natural killer-derived cytokine and chemokine secretion. J Innate Immun. 2011;3:420–34.
Castro MA, Oliveira MI, Nunes RJ, Fabre S, Barbosa R, Peixoto A, Brown MH, Parnes JR, Bismuth G, Moreira A, Rocha B, Carmo AM. Extracellular isoforms of CD6 generated by alternative splicing regulate targeting of CD6 to the immunological synapse. J Immunol. 2007;178:4351–61.
Patel NC, Chinen J, Rosenblatt HM, Hanson IC, Brown BS, Paul ME, Abramson SL, Ritz J, Shearer WT. Long-term outcomes of nonconditioned patients with severe combined immunodeficiency transplanted with HLA-identical or haploidentical bone marrow depleted of T cells with anti-CD6 mAb. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122:1185–93.
Montero E, Falcon L, Morera Y, Delgado J, Amador JF, Perez R. CD6 molecule may be important in the pathological mechanisms of lymphocytes adhesion to human skin in psoriasis and ior t1 MAb a possible new approach to treat this disease. Autoimmunity. 1999;29:155–6.
Reichert JM. Antibody-based therapeutics to watch in 2011. MAbs. 2011;3:76–99.
Beck A, Wurch T, Reichert JM. 6th Annual European Antibody Congress 2010: November 29-December 1, 2010, Geneva, Switzerland. MAbs. 2011;3:111–32.
Rodriguez PC, Torres-Moya R, Reyes G, Molinero C, Prada D, Lopez AM, Hernandez IM, Hernandez MV, Martinez JP, Hernandez X, Casaco A, Ramos M, Avila Y, Barrese Y, Montero E, Hernandez P. A clinical exploratory study with itolizumab, an anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Results Immunol. 2012;2:204–11.
Le Pottier L, Devauchelle V, Fautrel A, Daridon C, Saraux A, Youinou P, Pers JO. Ectopic germinal centers are rare in Sjogren’s syndrome salivary glands and do not exclude autoreactive B cells. J Immunol. 2009;182:3540–7.
Devauchelle-Pensec V, Pennec Y, Morvan J, Pers JO, Daridon C, Jousse-Joulin S, Roudaut A, Jamin C, Renaudineau Y, Roue IQ, Cochener B, Youinou P, Saraux A. Improvement of Sjogren’s syndrome after two infusions of rituximab (anti-CD20). Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57:310–7.
Singh N, Cohen PL. The T cell in Sjogren’s syndrome: force majeure, not spectateur. J Autoimmun. 2012;39:229–33.
Mageed RA, Garaud S, Taher TE, Parikh K, Pers JO, Jamin C, Renaudineau Y, Youinou P. CD5 expression promotes multiple intracellular signaling pathways in B lymphocyte. Autoimmun Rev. 2012;11:795–8.
Singer NG, Fox DA, Haqqi TM, Beretta L, Endres JS, Prohaska S, Parnes JR, Bromberg J, Sramkoski RM. CD6: expression during development, apoptosis and selection of human and mouse thymocytes. Int Immunol. 2002;14:585–97.
Azzam HS, Grinberg A, Lui K, Shen H, Shores EW, Love PE. CD5 expression is developmentally regulated by T cell receptor (TCR) signals and TCR avidity. J Exp Med. 1998;188:2301–11.
Hippen KL, Tze LE, Behrens TW. CD5 maintains tolerance in anergic B cells. J Exp Med. 2000;191:883–90.
Renaudineau Y, Nedellec S, Berthou C, Lydyard PM, Youinou P, Pers JO. Role of B-cell antigen receptor-associated molecules and lipid rafts in CD5-induced apoptosis of B CLL cells. Leukemia. 2005;19:223–9.
Osorio LM, De Santiago A, Aguilar-Santelises M, Mellstedt H, Jondal M. CD6 ligation modulates the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and protects chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from apoptosis induced by anti-IgM. Blood. 1997;89:2833–41.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the “Association Française du Gougerot-Sjögren et des syndromes secs” and from the “Ligue contre le cancer” (Comités 22, 29 and 56). The authors are grateful to Simone Forest and Geneviève Michel for secretarial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le Dantec, C., Alonso, R., Fali, T. et al. Rationale for treating primary Sjögren’s syndrome patients with an anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody (Itolizumab). Immunol Res 56, 341–347 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-013-8423-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-013-8423-x