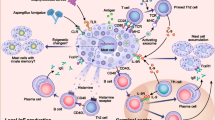
Abstract
Allergic diseases such as asthma are elicited by maladaptive activation of immune cells such as mast cells and lymphocytes by otherwise innocuous allergens. The numerous mediators secreted by such cells promote both acute inflammation and, in many instances, chronic tissue remodeling. Most of these compounds exert their effects on end-organ targets such as epithelial and endothelial cells and airway smooth muscle by activating G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which are by far the most abundant type of cell surface receptor. Since GPCRs are also the most common target of allergy therapeutics, a better understanding of their intracellular signaling mechanisms is vital to improve the efficacy of such drugs or to develop new targets. In this review, we focus on some of the new regulatory elements that control the duration and amplitude of GPCR signal transduction pathways in immune effector cells and end-organ structural cells affected by allergic inflammation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Premont RT, Gainetdinov RR. Physiological roles of G protein-coupled receptor kinases and arrestins. Annu Rev Physiol. 2007;69:511.
Pierce KL, Premont RT, Lefkowitz RJ. Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:639.
Gilman AG. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615.
Marinissen MJ, Gutkind JS. G-protein-coupled receptors and signaling networks: emerging paradigms. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001;22:368.
Gutkind JS. The pathways connecting G protein-coupled receptors to the nucleus through divergent mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1839.
Allen CD, Okada T, Cyster JG. Germinal-center organization and cellular dynamics. Immunity. 2007;27:190.
Allen CD, Ansel KM, Low C, Lesley R, Tamamura H, Fujii N, et al. Germinal center dark and light zone organization is mediated by CXCR4 and CXCR5. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:943.
Nurieva RI, Chung Y, Hwang D, Yang XO, Kang HS, Ma L, et al. Generation of T follicular helper cells is mediated by interleukin-21 but independent of T helper 1, 2, or 17 cell lineages. Immunity. 2008;29:138.
Vogelzang A, McGuire HM, Yu D, Sprent J, Mackay CR, King C. A fundamental role for interleukin-21 in the generation of T follicular helper cells. Immunity. 2008;29:127.
Matloubian M, Lo CG, Cinamon G, Lesneski MJ, Xu Y, Brinkmann V, et al. Lymphocyte egress from thymus and peripheral lymphoid organs is dependent on S1P receptor 1. Nature. 2004;427:355.
Schwab SR, Pereira JP, Matloubian M, Xu Y, Huang Y, Cyster JG. Lymphocyte sequestration through S1P lyase inhibition and disruption of S1P gradients. Science. 2005;309:1735.
Pappu R, Schwab SR, Cornelissen I, Pereira JP, Regard JB, Xu Y, et al. Promotion of lymphocyte egress into blood and lymph by distinct sources of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Science. 2007;316:295.
Gonzalo JA, Qiu Y, Lora JM, Al-Garawi A, Villeval JL, Boyce JA, et al. Coordinated involvement of mast cells and T cells in allergic mucosal inflammation: critical role of the CC chemokine ligand 1:CCR8 axis. J Immunol. 2007;179:1740.
Thomas SY, Banerji A, Medoff BD, Lilly CM, Luster AD. Multiple chemokine receptors, including CCR6 and CXCR3, regulate antigen-induced T cell homing to the human asthmatic airway. J Immunol. 2007;179:1901.
Palmqvist C, Wardlaw AJ, Bradding P. Chemokines and their receptors as potential targets for the treatment of asthma. Br J Pharmacol. 2007;151:725.
Penn RB, Benovic JL. Regulation of heterotrimeric G protein signaling in airway smooth muscle. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008;5:47.
Bansal G, Druey KM, Xie Z. R4 RGS proteins: regulation of G-protein signaling and beyond. Pharmacol Ther. 2007;116:473.
Willars GB. Mammalian RGS proteins: multifunctional regulators of cellular signalling. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2006;17:363.
De Vries L, Zheng B, Fischer T, Elenko E, Farquhar MG. The regulator of G protein signaling family. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2000;40:235.
Kim MS, Kuehn HS, Metcalfe DD, Gilfillan AM. Activation and function of the mTORC1 pathway in mast cells. J Immunol. 2008;180:4586.
Gilfillan AM, Tkaczyk C. Integrated signalling pathways for mast-cell activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:218.
Fukao T, Yamada T, Tanabe M, Terauchi Y, Ota T, Takayama T, et al. Selective loss of gastrointestinal mast cells and impaired immunity in PI3K-deficient mice. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:295.
Ali K, Bilancio A, Thomas M, Pearce W, Gilfillan AM, Tkaczyk C, et al. Essential role for the p110delta phosphoinositide 3-kinase in the allergic response. Nature. 2004;431:1007.
Kuehn HS, Gilfillan AM. G protein-coupled receptors and the modification of FcepsilonRI-mediated mast cell activation. Immunol Lett. 2007;113:59.
Laffargue M, Calvez R, Finan P, Trifilieff A, Barbier M, Altruda F, et al. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma is an essential amplifier of mast cell function. Immunity. 2002;16:441.
Bansal G, Xie Z, Rao S, Nocka KH, Druey KM. Suppression of immunoglobulin E-mediated allergic responses by regulator of G protein signaling 13. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:73.
Lenchner K, Grammer LC. A current review of idiopathic anaphylaxis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;3:305.
Peavy RD, Metcalfe DD. Understanding the mechanisms of anaphylaxis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;8:310.
de Paulis A, Annunziato F, Di Gioia L, Romagnani S, Carfora M, Beltrame C, et al. Expression of the chemokine receptor CCR3 on human mast cells. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001;124:146.
Juremalm M, Nilsson G. Chemokine receptor expression by mast cells. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2005;87:130.
Alam R, York J, Boyars M, Stafford S, Grant JA, Lee J, et al. Increased MCP-1, RANTES, and MIP-1alpha in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of allergic asthmatic patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;153:1398.
Humbles AA, Lu B, Friend DS, Okinaga S, Lora J, Al-Garawi A, et al. The murine CCR3 receptor regulates both the role of eosinophils and mast cells in allergen-induced airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:1479.
Grimbaldeston MA, Chen CC, Piliponsky AM, Tsai M, Tam SY, Galli SJ. Mast cell-deficient W-sash c-kit mutant Kit W-sh/W-sh mice as a model for investigating mast cell biology in vivo. Am J Pathol. 2005;167:835.
Shi GX, Harrison K, Wilson GL, Moratz C, Kehrl JH. RGS13 regulates germinal center B lymphocytes responsiveness to CXC chemokine ligand (CXCL)12 and CXCL13. J Immunol. 2002;169:2507.
Johnson EN, Druey KM. Functional characterization of the G protein regulator RGS13. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:16768.
Islam TC, Asplund AC, Lindvall JM, Nygren L, Liden J, Kimby E, et al. High level of cannabinoid receptor 1, absence of regulator of G protein signalling 13 and differential expression of Cyclin D1 in mantle cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 2003;17:1880.
Mayr B, Montminy M. Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:599.
Wolf I, Pevzner V, Kaiser E, Bernhardt G, Claudio E, Siebenlist U, et al. Downstream activation of a TATA-less promoter by Oct-2, Bob1, and NF-kappaB directs expression of the homing receptor BLR1 to mature B cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:28831.
Podojil JR, Kin NW, Sanders VM. CD86 and beta2-adrenergic receptor signaling pathways, respectively, increase Oct-2 and OCA-B Expression and binding to the 3’-IgH enhancer in B cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:23394.
Qin XF, Reichlin A, Luo Y, Roeder RG, Nussenzweig MC. OCA-B integrates B cell antigen receptor-, CD40L- and IL 4-mediated signals for the germinal center pathway of B cell development. EMBO J. 1998;17:5066.
Podojil JR, Sanders VM. Selective regulation of mature IgG1 transcription by CD86 and beta 2-adrenergic receptor stimulation. J Immunol. 2003;170:5143.
Ali H, Ahamed J, Hernandez-Munain C, Baron JL, Krangel MS, Patel DD. Chemokine production by G protein-coupled receptor activation in a human mast cell line: roles of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and NFAT. J Immunol. 2000;165:7215.
Cyster JG. Lymphoid organ development and cell migration. Immunol Rev. 2003;195:5.
Friedman RS, Jacobelli J, Krummel MF. Surface-bound chemokines capture and prime T cells for synapse formation. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:1101.
Luther SA, Cyster JG. Chemokines as regulators of T cell differentiation. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:102.
Molon B, Gri G, Bettella M, Gomez-Mouton C, Lanzavecchia A, Martinez AC, et al. T cell costimulation by chemokine receptors. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:465.
Galli SJ, Tsai M, Piliponsky AM. The development of allergic inflammation. Nature. 2008;454:445.
Medoff BD, Thomas SY, Luster AD. T cell trafficking in allergic asthma: the ins and outs. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:205.
Smit JJ, Lukacs NW. A closer look at chemokines and their role in asthmatic responses. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;533:277.
Shi G, Partida-Sanchez S, Misra RS, Tighe M, Borchers MT, Lee JJ, et al. Identification of an alternative G{alpha}q-dependent chemokine receptor signal transduction pathway in dendritic cells and granulocytes. J Exp Med. 2007;204:2705.
Neptune ER, Bourne HR. Receptors induce chemotaxis by releasing the betagamma subunit of Gi, not by activating Gq or Gs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:14489.
Kehrl JH. Chemoattractant receptor signaling and the control of lymphocyte migration. Immunol Res. 2006;34:211.
Hornquist CE, Lu X, Rogers-Fani PM, Rudolph U, Shappell S, Birnbaumer L, et al. G(alpha)i2-deficient mice with colitis exhibit a local increase in memory CD4+ T cells and proinflammatory Th1-type cytokines. J Immunol. 1997;158:1068.
Beadling C, Druey KM, Richter G, Kehrl JH, Smith KA. Regulators of G protein signaling exhibit distinct patterns of gene expression and target G protein specificity in human lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1999;162:2677.
Bowman EP, Campbell JJ, Druey KM, Scheschonka A, Kehrl JH, Butcher EC. Regulation of chemotactic and proadhesive responses to chemoattractant receptors by RGS (regulator of G-protein signaling) family members. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:28040.
Lippert E, Yowe DL, Gonzalo JA, Justice JP, Webster JM, Fedyk ER, et al. Role of regulator of G protein signaling 16 in inflammation-induced T lymphocyte migration and activation. J Immunol. 2003;171:1542.
Oliveira-Dos-Santos AJ, Matsumoto G, Snow BE, Bai D, Houston FP, Whishaw IQ, et al. Regulation of T cell activation, anxiety, and male aggression by RGS2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:12272.
Hsu HC, Yang P, Wang J, Wu Q, Myers R, Chen J, et al. Interleukin 17-producing T helper cells and interleukin 17 orchestrate autoreactive germinal center development in autoimmune BXD2 mice. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:166.
Estes JD, Thacker TC, Hampton DL, Kell SA, Keele BF, Palenske EA, et al. Follicular dendritic cell regulation of CXCR4-mediated germinal center CD4 T cell migration. J Immunol. 2004;173:6169.
Siddiqui S, Mistry V, Doe C, Roach K, Morgan A, Wardlaw A, et al. Airway hyperresponsiveness is dissociated from airway wall structural remodeling. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122:335.
Borchers MT, Biechele T, Justice JP, Ansay T, Cormier S, Mancino V, et al. Methacholine-induced airway hyperresponsiveness is dependent on Galphaq signaling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003;285:L114.
Moratz C, Hayman JR, Gu H, Kehrl JH. Abnormal B-cell responses to chemokines, disturbed plasma cell localization, and distorted immune tissue architecture in Rgs1-/- mice. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:5767.
Roy AA, Nunn C, Ming H, Zou MX, Penninger J, Kirshenbaum LA, et al. Up-regulation of endogenous RGS2 mediates cross-desensitization between Gs and Gq signaling in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:32684.
Chiba Y, Ueno A, Sakai H, Misawa M. Hyperresponsiveness of bronchial but not tracheal smooth muscle in a murine model of allergic bronchial asthma. Inflamm Res. 2004;53:636.
Chew AD, Hirota JA, Ellis R, Wattie J, Inman MD, Janssen LJ. Effects of allergen on airway narrowing dynamics as assessed by lung-slice technique. Eur Respir J. 2008;31:532.
Tliba O, Panettieri RA Jr. Regulation of inflammation by airway smooth muscle. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2008;8:262.
Tliba O, Amrani Y, Panettieri RA Jr. Is airway smooth muscle the “missing link” modulating airway inflammation in asthma? Chest. 2008;133:236.
Kong KC, Billington CK, Gandhi U, Panettieri RA Jr, Penn RB. Cooperative mitogenic signaling by G protein-coupled receptors and growth factors is dependent on G(q/11). FASEB J. 2006;20:1558.
Huang CD, Ammit AJ, Tliba O, Kuo HP, Penn RB, Panettieri RA Jr, et al. G-protein-coupled receptor agonists differentially regulate basal or tumor necrosis factor-alpha-stimulated activation of interleukin-6 and RANTES in human airway smooth muscle cells. J Biomed Sci. 2005;12:763.
Huang X, Fu Y, Charbeneau RA, Saunders TL, Taylor DK, Hankenson KD, et al. Pleiotropic phenotype of a genomic knock-in of an RGS-insensitive G184S Gnai2 allele. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:6870.
Roman DL, Talbot JN, Roof RA, Sunahara RK, Traynor JR, Neubig RR. Identification of small-molecule inhibitors of RGS4 using a high-throughput flow cytometry protein interaction assay. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;71:169.
Neubig RR, Siderovski DP. Regulators of G-protein signalling as new central nervous system drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002;1:187.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Dr. Zhihui Xie, our generous collaborators, and members of the Laboratory of Allergic Diseases for invaluable input and discussion. This work was supported by the Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Druey, K.M. Regulation of G-protein-coupled signaling pathways in allergic inflammation. Immunol Res 43, 62–76 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-008-8050-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-008-8050-0