Abstract
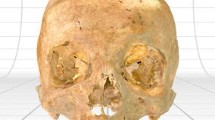
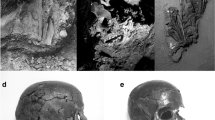
Facial reproduction validation uses the methodology typical of forensic anthropology to confirm the accuracy of three-dimensional reproductions of faces. Achieving high accuracy in virtual facial reproductions is still under study. In the present paper, the Tenchini collection, which contains wax reproductions of prisoners’ faces and their skulls, was used. By creating facial reproductions on skulls from this collection, the result was compared with the real face of the person to whom the skull belongs. The three-dimensional volume of each examined skull of Tenchini collection was acquired via CT scan and photogrammetry. Subsequently, the virtual reproduction of each skull was processed using three-dimensional graphics software (ZBrush, Pixologic®). The morphological comparison parameters used in the field of personal identification by forensic anthropology were used. The blind procedure required the operator to see the mask subsequent to the facial reproduction phase, so that the facial reproduction cannot exploit the information that knowledge of the mask would have produced. The parameters used in the study of facial reproductions have shown discrepancies between the characteristics of the masks and the facial reproductions, partly expected because due to the lack of soft tissue on the skull. However, a high degree of accuracy in the facial reproductions performed due to the applied methodology was documented. The present study allowed us to observe how these parameters can be useful to study the accuracy of facial reproduction and identify what difficulties are encountered in producing a result close to the real appearance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Greef S, Willems G. Three-dimensional cranio-facial reproduction in forensic identification: latest progress and new tendencies in the 21st century. J Forensic Sci. 2005;50(1):12–7. PMID: 15830991.
Garvin HM, Stock MK. The utility of advanced imaging in forensic anthropology. Acad Forensic Pathol. 2016;6(3):499–516. https://doi.org/10.23907/2016.050. Epub 2016 Sep 1. PMID: 31239924; PMCID: PMC6474549.
Donato L, Toni R, Porro A, Vitale M, Barbaro F, Cecchi R. The Tenchini’s collection: a forensic anthropometric legacy of 19th century Parma, Italy. Forensic Sci Res. 2019;4(1):82–7. PMID: 30915420; PMCID: PMC6427641.
Lusetti A, Dagoli S, Donato L, Cecchi R. Tenchini’s legacy as a starting point for the re-construction of the history of a criminal in the 19th century. Rassegna Italiana di Criminologia, 2022;XVI(1): 06–11. https://doi.org/10.7347/RIC-012022-p06.
Donato L, Cecchi R, Goldoni M, Ubelaker DH. Photogrammetry vs CT Scan: Evaluation of Accuracy of a Low-Cost Three-Dimensional Acquisition Method for Forensic Facial Approximation. J Forensic Sci. 2020;65(4):1260–1265. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.14319. Epub 2020 Mar 26. PMID: 32216148.
Gitto L, Donato L, Di Luca A, Bryant SM, Serinelli S. The application of Photogrammetry in the autopsy room: a Basic, practical Workflow. J Forensic Sci. 2020;65(6):2146–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.14493. Epub 2020 Jun 30. PMID: 32602938.
Wilkinson C. Forensic Facial Reproduction. Cambridge University Press; 2004.
Wilkinson C. Facial reproduction–anatomical art or artistic anatomy? J Anat. 2010;216(2):235–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01182.x. PMID: 20447245; PMCID: PMC2815945.
Wilkinson C. Computerized forensic facial reproduction: A review of current systems. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2005;1(3):173-7. https://doi.org/10.1385/FSMP:1:3:173PMID: 25870042.
Helmer R. Schädelidentifizierung durch elektronische Bildmischung. Heidelberg: Kriminalistik-; 1984.
Iscan MY, Steyn M. The human skeleton in forensic medicine. 3rd ed. Charles C Thomas Pub Ltd; 2013.
Baldasso RP, Moraes C, Gallardo E, Stumvoll MB, Crespo KC, Strapasson RAP, de Oliveira RN. 3D forensic facial approximation: Implementation protocol in a forensic activity. J Forensic Sci. 2021;66(1):383–388. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.14587. Epub 2020 Oct 7. PMID: 33027540.
Kaur P, Krishan K, Sharma SK, Kanchan T. Facial-recognition algorithms: a literature review. Med Sci Law. 2020;60(2):131–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/0025802419893168. Epub 2020 Jan 21. PMID: 31964224.
Phillips PJ, Yates AN, Hu Y, Hahn CA, Noyes E, Jackson K, Cavazos JG, Jeckeln G, Ranjan R, Sankaranarayanan S, Chen JC, Castillo CD, Chellappa R, White D, O’Toole AJ. Face recognition accuracy of forensic examiners, superrecognizers, and face recognition algorithms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(24):6171–6. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1721355115. Epub 2018 May 29. PMID: 29844174; PMCID: PMC6004481.
Kaur P, Krishan K, Sharma SK, Kanchan T. Integrating a Profile of Frontal Face With Its Mirror Image for Facial Reproduction. J Craniofac Surg. 2018;29(4):1026–1030. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000004627. PMID: 29771841.
Tome P, Fierrez J, Vera-Rodriguez R, Ramos D. Identification using face regions: application and assessment in forensic scenarios. Forensic Sci Int. 2013;233(1–3):75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2013.08.020. Epub 2013 Sep 3. PMID: 24314504.
Tome P, Fierrez J, Vera-Rodriguez R, Ortega-Garcia J. Combination of Face regions in forensic scenarios. J Forensic Sci. 2015;60(4):1046–51. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.12800. Epub 2015 Jul 17. PMID: 26189995.
De Donno A, Mele F, Angrisani C, Maselli R, Cozzolino M, Pedote P, Introna F, Santoro V. Facial approximation for identification purposes: soft tissue thickness in a caucasian population. Sex and age-related variations. J Forensic Odontostomatol. 2022;1(40):34–41. PMID: 35499535.
Rusia MK, Singh DK. A comprehensive survey on techniques to handle face identity threats: challenges and opportunities. Multimed Tools Appl 2022 Jun 10:1–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13248-6. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35702682; PMCID: PMC9183764.
Sáez Trigueros D, Meng L, Hartnett M. Generating photo-realistic training data to improve face recognition accuracy. Neural Netw. 2021;134:86–94. Epub 2020 Nov 27. PMID: 33291019.
Dietrichkeit Pereira JG, Guimarães MA, Alves da Silva RH. Applicability of forensic facial approximation in the recognition process of unclaimed victims. J Forensic Odontostomatol. 2021;3(39):30–40. PMID: 34999578.
Omari R, Hunt C, Coumbaros J, Chapman B. Virtual anthropology? Reliability of three-dimensional photogrammetry as a forensic anthropology measurement and documentation technique. Int J Legal Med. 2021;135(3):939–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-020-02473-z. Epub 2020 Nov 27. PMID: 33244707.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Donato, L., Ubelaker, D.H., Marsella, L.T. et al. Applications of forensic anthropology methodology: accuracy of virtual face reproductions performed on the Tenchini collection. Forensic Sci Med Pathol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-024-00839-y
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-024-00839-y