Abstract
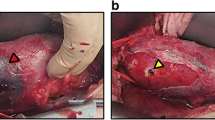
Page kidney is a condition where external compression of the renal artery and renal parenchyma leads to subsequent ischaemia and activation of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone axis. A 42-year-old female with hirsutism, hypertension and diabetes was diagnosed with a right adrenal mass and underwent laparoscopic adrenalectomy. Her hypertension worsened postoperatively and was managed medically. Subsequently she developed a right flank pain on the fifth postoperative day and died suddenly the next day. Autopsy revealed a pale body with cushingoid appearance. Surgical scars were healthy. Internal examination of the abdomen revealed a haemoperitoneum of 500 ml together with a large subcapsular haematoma measuring 1000 ml surrounding the right kidney, compressing the right renal artery. Kidneys were pale and the right kidney was soft and friable. Cortical surface of the right kidney demonstrated a possible surgical puncture site with an overlying thrombus together with a contused inferior vena cava. Other organs were pale but appeared otherwise normal. Histology revealed diffuse cortical necrosis of right kidney and features of adult respiratory distress syndrome in the lungs. Haemorrhagic shock following laparoscopic adrenalectomy for right adrenal tumor was declared as the cause of death, contributed by the development of the Page kidney. Trauma of several aetiologies including laparoscopic abdominal surgery may contribute to Page kidney. It presents with flank pain, hypertension and renal mass. Since postoperative blood loss usually manifests as hypotension, resulting hypertension may mislead the attending clinicians. Once diagnosed, it can be managed with surgical drainage and antihypertensives.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haydar A, Bakri RS, Prime M, Goldsmith DJ. Page kidney–a review of the literature. J Nephrol. 2003;16(3):329–33.
Page IH. The production of persistent arterial hypertension by cellophane perinephritis. JAMA. 1939;113(23):2046–48. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1939.02800480032008.
Engel WJ, Page IH. Hypertension due to renal compression resulting from subcapsular hematoma. J Urol. 1955;73(5):735–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)67466-4.
Dopson SJ, Jayakumar S, Velez JCQ. Page kidney as a rare cause of hypertension: case report and review of the literature. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;54(2):334–39.
McCune TR, Stone WJ, Breyer JA. Page kidney: case report and review of the literature. Am J Kidney Dis. 1991;18(5):593–99.
Chung J, Caumartin Y, Warren J, Luke PPW. Acute Page kidney following renal allograft biopsy: a complication requiring early recognition and treatment. Am J Transplant. 2008;8(6):1323–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02215.x.
Smyth A, Collins CS, Thorsteinsdottir B, Madsen BE, Oliveira GHM, Kane G, et al. Page kidney: etiology, renal function outcomes and risk for future hypertension. J Clin Hypertens. 2012;14(4):216–21.
Sokhal AK, Prakash G, Saini DK, Singh K, Sankhwar S, Singh BP. Page kidney: a rare but surgically treatable cause of hypertension. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplantation. 2018;29(1):193. https://doi.org/10.4103/1319-2442.225183.
McFadden JD, Hawksworth JS. Page kidney: an unusual complication of a renal transplant biopsy. Case Rep Urol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8768549.
Sri Lanka Medical Council. (2009) Instructions on serious professional misconduct to medical practitioners and dentists. https://slmc.gov.lk/images/PDF_Main_Site/serious%20professional%20misconduct2021-12.pdf.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design of the work; the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data work; drafting the work and reviewing it critically for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final of the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical statement
The presented autopsy case was conducted for medico-legal purposes and the findings are available in public domain. However, we used this information for academic purposes, including teaching and publication, according to the institutional guidelines with informed written consent of the next of kin and without divulging the identity of the individual.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumarasinghe, G., Sivasubramanium, M., Ekanayake, K.B. et al. A fatal misdiagnosis of page kidney – case report. Forensic Sci Med Pathol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-024-00807-6
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-024-00807-6