Abstract
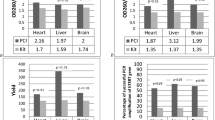
Tissue formalin fixation and paraffin embedding (FFPE) is a standard method for long-term preservation and morphological and molecular analysis. The aim of this study was to analyze the effect of storage time on the integrity of DNA isolated from three different healthy FFPE tissues. DNA was isolated from FFPE heart, liver and brain tissues obtained from autopsy and archived from 1988 to 2017 using two different methods of DNA isolation: phenol–chloroform-isoamyl alcohol (PCI) and PureLink Genomic DNA Kit. The quantification and purity of DNA was measured spectrophotometrically at 260 nm and 280 nm. The quality of isolated DNA was evaluated by PCR amplification of GPD1 (150 bp), ACTB (262 bp) and RPL4 (407 bp) genes. The histomorphological characteristics of FFPE tissues were not significantly changed during 30 years of storage. Higher yield (272.9 ± 10.3 µg) and purity (A260/280 = 2.05) of DNA was obtained using the PCI method for DNA isolation from FFPE liver tissue. The PCI extraction method showed reproducible and consistent results in PCR amplification of all of three examined genes. The GPD1 gene can be amplified up to 30 years, the ACTB gene in the same samples up to 26 years and the RPL4 gene up to 6 years of storage in FFPE blocks. Although the best yield and purity of isolated DNA (using both isolation methods) was obtained from FFPE liver tissue, the DNA with the most preserved integrity was obtained from brain tissue archived up to 30 years. This is the first report using long-term archived healthy FFPE tissues (up to 30 years) that shows that the DNA isolated from these tissues is of preserved integrity and can be used in molecular autopsy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sengüven B, Baris E, Oygur T, Berktas M. Comparison of methods for the extraction of DNA from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded archival tissues. Int J Med Sci. 2014;11:494–9.
Shibata D, Martin WJ, Arnheim N. Analysis of DNA sequences in forty-year-old paraffin-embedded thin-tissue sections: a bridge between molecular biology and classical histology. Cancer Res. 1988;48:4564–6.
Gouveia GR, Ferreira SC, Ferreira JE, Siqueira SA, Pereira J. Comparison of two methods of RNA extraction from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue specimens. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:151724.
Chu WS, Furusato B, Wong K, Sesterhenn IA, Mostofi FK, Wei MQ, et al. Ultrasound-accelerated formalin fixation of tissue improves morphology, antigen and mRNA preservation. Mod Pathol. 2005;18:850–63.
Budimlija Z, Lu C, Axler-DiPerte G, Seifarth J, Popiolek D, Fogt F, et al. Malignant tumors and forensics–dilemmas and proposals. Croat Med J. 2009;50:218–27.
Babol-Pokora K, Berent J. SNP-minisequencing as an excellent tool for analysing degraded DNA recovered from archival tissues. Acta Biochim Pol. 2008;55:815–9.
Reid KM, Maistry S, Ramesar R, Heathfield LJ. A review of the optimization of the use of formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue for molecular analysis in a forensic post-mortem setting. Forensic Sci Int. 2017;280:181–7.
Funabashi KS, Barcelos D, Visoná I, e Silva MS, e Sousa ML, de Franco MF, et al. DNA extraction and molecular analysis of non-tumoral liver spleen and brain from autopsy samples: the effect of formalin fixation and paraffin embedding. Pathol Res Pract. 2012;208:584–91.
Kokkat TJ, Patel MS, McGarvey D, LiVolsi VA, Baloch ZW. Archived formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) blocks: A valuable underexploited resource for extraction of DNA, RNA, and protein. Biopres Biobank. 2013;11:101–6.
Gilbert MT, Haselkorn T, Bunce M, Sanchez JJ, Lucas SB, Jewell LD, et al. The isolation of nucleic acids from fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues-which methods are useful when? PLoS ONE. 2007;2:e537.
Dietrich D, Uhl B, Sailer V, Holmes EE, Jung M, Meller S, et al. Improved PCR performance using template DNA from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues by overcoming PCR inhibition. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e77771.
Nam SK, Im J, Kwak Y, Han N, Nam KH, Seo AN, et al. Effects of fixation and storage of human tissue samples on nucleic Acid preservation. Korean J Pathol. 2014;48:36–42.
Gouvegia GR, Ferreira SC, Siqueira SAC, Pereira J. Nucleic acids extraction from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues. In: Larramendy ML, Soloneski S, editors. Nucleic acids-from basic aspects to laboratory tools. IntechOpen. London, UK. 2016. pp. 27–36.
Todorović D, Vitošević K, Todorović M, Slović Ž. Formalin fixation of human healthy autopsied tissues: The influence of type of tissue, temperature and incubation time on the quality of isolation DNA. Serbian J Experiment Clin Res. doi: https://doi.org/10.2478/sjecr-2019-0020
Rivero ER, Neves AC, Silva-Valenzuela MG, Sousa SO, Nunes FD. Simple salting-out method for DNA extraction from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Pathol Res Pract. 2006;202:523–9.
Chung JY, Yi JM, Xie R, Brown V, Lee O, Ahuja N, et al. A pressure cooking-based DNA extraction from archival formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue. Anal Biochem. 2012;425:128–34.
Okello JB, Zurek J, Devault AM, Kuch M, Okwi AL, Sewankambo NK, et al. Comparison of methods in the recovery of nucleic acids from archival formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded autopsy tissues. Anal Biochem. 2010;400:110–7.
Lu C, Budimlija Z, Popiolek D, Illei P, West B, Fogt F, et al. Multiplex STR and mitochondrial DNA testing for paraffin embedded specimen of healthy and malignant tissue: Interpretation issues. Int Congress Series. 2006;1288:648–50.
Duval K, Aubin RA, Elliott J, Gorn-Hondermann I, Birnboim HC, Jonker D, et al. Optimized manual and automated recovery of amplifiable DNA from tissues preserved in buffered formalin and alcohol-based fixative. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2010;4:80–8.
Gall K, Pavelić J, Jadro-Santel D, Poljak M, Pavelić K. DNA amplification by polymerase chain reaction from brain tissues embedded in paraffin. Int J Exp Pathol. 1993;74:333–7.
Vitošević K, Todorović M, Varljen T, Slović Ž, Matić S, Todorović D. Effect of formalin fixation on PCR amplification of DNA isolated from healthy autopsy tissues. Acta Histochem. 2018;120:780–8.
Turashvili G, Yang W, McKinney S, Kalloger S, Gale N, Ng Y, et al. Nucleic acid quantity and quality from paraffin blocks: defining optimal fixation, processing and DNA/RNA extraction techniques. Exp Mol Pathol. 2012;92:33–43.
Potluri K, Mahas A, Kent MN, Naik S, Markey M. Genomic DNA extraction methods using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Anal Biochem. 2015;486:17–23.
Ferguson AE, Cohn RJ, Ashton LJ. Use of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumor tissue as a DNA source in molecular epidemiological studies of pediatric CNS tumors. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2012;21:105–13.
Alvarez-Aldana A, Martínez JW, Sepúlveda-Arias JC. Comparison of five protocols to extract DNA from paraffin-embedded tissues for the detection of human papillomavirus. Pathol Res Pract. 2015;211:150–5.
Paireder S, Werner B, Bailer J, Werther W, Schmid E, Patzak B, et al. Comparison of protocols for DNA extraction from long-term preserved formalin fixed tissues. Anal Biochem. 2013;439:152–60.
Greer CE, Wheeler CM, Manos MM. Sample preparation and PCR amplification from paraffin-embedded tissues. PCR Methods Appl. 1994;3:S113–22.
Bass BP, Engel KB, Greytak SR, Moore HM. A review of preanalytical factors affecting molecular, protein, and morphological analysis of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue: how well do you know your FFPE specimen? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014;138:1520–30.
Ferrer I, Armstrong J, Capellari S, Parchi P, Arzberger T, Bell J, et al. Effects of formalin fixation, paraffin embedding, and time of storage on DNA preservation in brain tissue: a BrainNet Europe study. Brain Pathol. 2007;17:297–303.
Cao W, Hashibe M, Rao JY, Morgenstern H, Zhang ZF. Comparison of methods for DNA extraction from paraffin-embedded tissues and buccal cells. Cancer Detect Prev. 2003;27:397–404.
Kocjan BJ, Hošnjak L, Poljak M. Commercially available kits for manual and automatic extraction of nucleic acids from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2015;24:47–53.
Sam SS, Lebel KA, Bissaillon CL, Tafe LJ, Tsongalis GJ, Lefferts JA. Automation of genomic DNA isolation from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Pathol Res Pract. 2012;208:705–7.
Rabelo-Gonçalves E, Roesler B, Guardia AC, Milan A, Hara N, Escanhoela C, et al. Evaluation of five DNA extraction methods for detection of H pylori in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) liver tissue from patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 2014;210:142–6.
Ludyga N, Grünwald B, Azimzadeh O, Englert S, Höfler H, Tapio S, et al. Nucleic acids from long-term preserved FFPE tissues are suitable for downstream analyses. Virchows Arch. 2012;460:131–40.
Wang JH, Gouda-Vossos A, Dzamko N, Halliday G, Huang Y. DNA extraction from fresh-frozen and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human brain tissue. Neurosci Bull. 2013;29:649–54.
Lin J, Kennedy SH, Svarovsky T, Rogers J, Kemnitz JW, Xu A, et al. High-quality genomic DNA extraction from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded samples deparaffinized using mineral oil. Anal Biochem. 2009;395:265–7.
Carturan E, Tester DJ, Brost BC, Basso C, Thiene G, Ackerman MJ. Postmortem genetic testing for conventional autopsy-negative sudden unexplained death: an evaluation of different DNA extraction protocols and the feasibility of mutational analysis from archival paraffin-embedded heart tissue. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129:391–7.
Goelz SE, Hamilton SR, Vogelstein B. Purification of DNA from formaldehyde fixed and paraffin embedded human tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985;130:118–26.
Johansen IS, Thomsen VØ, Forsgren A, Hansen BF, Lundgren B. Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue specimens with necrotizing granulomatous inflammation by strand displacement amplification. J Mol Diagn. 2004;6:231–6.
Coombs NJ, Gough AC, Primrose JN. Optimisation of DNA and RNA extraction from archival formalin-fixed tissue. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27:e12.
Wang W, Kumar P, Schwarz M, Malone G, Haworth A, Kumar S. PCR amplification of 40-year-old paraffin-embedded tumor-tissues - comparison of 4 different DNA extraction and purification methods. Int J Oncol. 1994;5:453–7.
Niland EE, McGuire A, Cox MH, Sandusky GE. High quality DNA obtained with an automated DNA extraction method with 70+ year old formalin-fixed celloidin-embedded (FFCE) blocks from the Indiana medical history museum. Am J Transl Res. 2012;4:198–205.
Rich J, Dean DE, Powers RH. Forensic Medicine of the Lower Extremity. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2005.
Sato Y, Sugie R, Tsuchiya B, Kameya T, Natori M, Mukai K. Comparison of the DNA extraction methods for polymerase chain reaction amplification from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2001;10:265–71.
Farrugia A, Keyser C, Ludes B. Efficiency evaluation of a DNA extraction and purification protocol on archival formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue. Forensic Sci Int. 2010;194:e25–8.
Funding
This study was supported by grant of Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Kragujevac, Serbia (grand number JP: 05/13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Institutional ethical approval was obtained in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Authorization to use human biological samples for research was obtained. The Ethics Committee of the University of Kragujevac, Faculty of Medical Sciences, the Ethic Committee of Clinical Center of Kragujevac (no.01–2798), Appeal Public Prosecutor's Office from Kragujevac (A number 79/13) and Higher Court in Kragujevac (SU-VIII-110/13) agreed to these investigations.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vitošević, K., Todorović, M., Slović, Ž. et al. DNA isolated from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded healthy tissue after 30 years of storage can be used for forensic studies. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 17, 47–57 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-020-00327-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-020-00327-z