Abstract
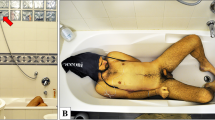
Suicide using a combination of a plastic bag over the head and inhalation of a non-irritating gas, such as helium, argon or nitrogen, has been reported in the literature. Here an unusual suicide method in a 17-year old man by suffocation from covering the face with household plastic wrap, combined with nitrous oxide inhalation, is presented. The case was reviewed based on police, autopsy and hospital reports. A PubMed search for scientific literature related to nitrous oxide abuse and suicide by suffocation was performed and our findings discussed in relation to the scientific literature found. The deceased was a 17-year old man who was found with the nose and mouth closed with a piece of kitchen plastic wrap. The plastic wrap had been removed prior to autopsy. Autopsy findings were suggestive of asphyxia, but were otherwise negative. Nitrous oxide was detected in the brain and lung tissue with headspace-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (headspace-GCMS). The cause of death was assumed to be suffocation caused by plastic wrap covering the face, combined with nitrous oxide inhalation. Suicide was suspected because of a history of depression for several months. Nitrous oxide, also known as laughing gas, has a euphoric effect and is used as a recreational inhalant drug that can be purchased legally. Deaths caused by recreational nitrous oxide abuse are rare but may occur if used in combination with a plastic bag over the head. This is the first report of suicide by suffocation by external obstruction combined with nitrous oxide inhalation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnung SK, Feddersen C. Suicide by inhaling helium inside a plastic bag. Ugeskr Laeger. 2004;166:3506–7.
Madentzoglou MS, Kastanaki AE, Nathena D, Kranioti EF, Michalodimitrakis M. Nitrogen-plastic bag suicide: a case report. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2013;34:311–4.
Ogden RD, Wooten RH. Asphyxial suicide with helium and a plastic bag. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2002;23:234–7.
Austin A, Winskog C, van den Heuvel C, Byard R. Recent trends in suicides utilizing helium. J Forensic Sci. 2011;56:649–51.
Gillman MA, Harker N, Lichtigfeld FJ. Combined cannabis/methaqualone withdrawal treated with psychotropic analgesic nitrous oxide. Int J Neurosci. 2006;116:859–69.
Gillman MA, Lichtigfeld FJ, Harker N. Psychotropic analgesic nitrous oxide for acute cocaine withdrawal in man. Int J Neurosci. 2006;116:847–57.
Gillman MA, Lichtigfeld FJ, Young TN. Psychotropic analgesic nitrous oxide for alcoholic withdrawal states. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;2:CD005190.
van Amsterdam J, Nabben T, van den Brink W. Recreational nitrous oxide use: prevalence and risks. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015;73:790–6.
Cheng HM, Park JH, Hernstadt D. Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord following recreational nitrous oxide use. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013
Garakani A, Welch AK, Jaffe RJ, Protin CA, McDowell DM. Psychosis and low cyanocobalamin in a patient abusing nitrous oxide and cannabis. Psychosomatics. 2014;55:715–9.
Schallner N, Goebel U. The perioperative use of nitrous oxide: renaissance of an old gas or funeral of an ancient relict? Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2013;26:354–60.
Moyes D, Cleaton-Jones P, Lelliot J. Evaluation of driving skills after brief exposure to nitrous oxide. S Afr Med J. 1979;56:1000–2.
LiPuma JP, Wellman J, Stern HP. Nitrous oxide abuse: a new cause of pneumomediastinum. Radiology. 1982;145:602.
Winek CL, Wahba WW, Rozin L. Accidental death by nitrous oxide inhalation. Forensic Sci Int. 1995;73:139–41.
Wagner SA, Clark MA, Wesche DL, Doedens DJ, Lloyd AW. Asphyxial deaths from the recreational use of nitrous oxide. J Forensic Sci. 1992;37:1008–15.
Kunkel DB. Nitrous-oxide - not a laughing matter anymore. Emerg Med. 1987;19:79–84.
Gillman MA. Nitrous oxide abuse in perspective. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1992;15:297–306.
Herbst J, Stanley W, Byard RW. Autopsy reenactment--a useful technique in the evaluation of adhesive tape asphyxia. J Forensic Sci. 2014;59:841–3.
Turillazzi E, D'Errico S, Neri M, Fineschi V. An unusual mechanical asphyxia in a homicide-suicide case by smothering and strangulation. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2006;27:166–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leth, P.M., Astrup, B.S. Suffocation caused by plastic wrap covering the face combined with nitrous oxide inhalation. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 13, 372–374 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-017-9887-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-017-9887-0