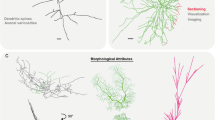
Abstract
Neuroanatomical analysis, such as classification of cell types, depends on reliable reconstruction of large numbers of complete 3D dendrite and axon morphologies. At present, the majority of neuron reconstructions are obtained from preparations in a single tissue slice in vitro, thus suffering from cut off dendrites and, more dramatically, cut off axons. In general, axons can innervate volumes of several cubic millimeters and may reach path lengths of tens of centimeters. Thus, their complete reconstruction requires in vivo labeling, histological sectioning and imaging of large fields of view. Unfortunately, anisotropic background conditions across such large tissue volumes, as well as faintly labeled thin neurites, result in incomplete or erroneous automated tracings and even lead experts to make annotation errors during manual reconstructions. Consequently, tracing reliability renders the major bottleneck for reconstructing complete 3D neuron morphologies. Here, we present a novel set of tools, integrated into a software environment named ‘Filament Editor’, for creating reliable neuron tracings from sparsely labeled in vivo datasets. The Filament Editor allows for simultaneous visualization of complex neuronal tracings and image data in a 3D viewer, proof-editing of neuronal tracings, alignment and interconnection across sections, and morphometric analysis in relation to 3D anatomical reference structures. We illustrate the functionality of the Filament Editor on the example of in vivo labeled axons and demonstrate that for the exemplary dataset the final tracing results after proof-editing are independent of the expertise of the human operator.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ascoli, G. A. (2006). Mobilizing the base of neuroscience data: the case of neuronal morphologies. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 7(4), 318–324.
Ascoli, G. A., Donohue, D. E., & Halavi, M. (2007). NeuroMorpho. Org: a central resource for neuronal morphologies. J Neurosci, 27(35), 9247–9251. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2055-07.2007.
Binzegger, T., Douglas, R. J., & Martin, K. A. (2004). A quantitative map of the circuit of cat primary visual cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 24(39), 8441–8453.
Broser, P. J., Schulte, R., Lang, S., Roth, A., Helmchen, F., Waters, J., et al. (2004). Nonlinear anisotropic diffusion filtering of three-dimensional image data from two-photon microscopy. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 9(6), 1253–1264. doi:10.1117/1.1806832.
Broser, P. J., Grinevich, V., Osten, P., Sakmann, B., & Wallace, D. J. (2008). Critical period plasticity of axonal arbors of layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons in rat somatosensory cortex: layer-specific reduction of projections into deprived cortical columns. Cerebral Cortex, 18(7), 1588–1603.
Cannon, R. C., Turner, D. A., Pyapali, G. K., & Wheal, H. V. (1998). An on-line archive of reconstructed hippocampal neurons. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 84(1–2), 49–54.
Carnevale, N. T., & Hines, M. L. (2006). The NEURON Book: University Press.
Crook, S., Gleeson, P., Howell, F., Svitak, J., & Silver, R. A. (2007). MorphML: level 1 of the NeuroML standards for neuronal morphology data and model specification. Neuroinformatics, 5(2), 96–104.
Dercksen, V. J., Weber, B., Guenther, D., Oberlaender, M., Prohaska, S., & Hege, H. C. (2009). Automatic alignment of stacks of filament data. IEEE Int. Symp. on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro (ISBI), 971–974.
Dodt, H. U., Leischner, U., Schierloh, A., Jahrling, N., Mauch, C. P., Deininger, K., et al. (2007). Ultramicroscopy: three-dimensional visualization of neuronal networks in the whole mouse brain. Nature Methods, 4(4), 331–336. doi:10.1038/nmeth1036.
Donohue, D. E., & Ascoli, G. A. (2011). Automated reconstruction of neuronal morphology: an overview. Brain Research Reviews, 67(1–2), 94–102. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.11.003.
Erturk, A., Mauch, C. P., Hellal, F., Forstner, F., Keck, T., Becker, K., et al. (2012). Three-dimensional imaging of the unsectioned adult spinal cord to assess axon regeneration and glial responses after injury. Nature Medicine, 18(1), 166–171. doi:10.1038/nm.2600.
FEI-VisualizationSciencesGroup (2013a). Amira 5.5. www.vsg3d.com/amira/overview
FEI-VisualizationSciencesGroup (2013b). Amira 5.5 Reference Guide. www.vsg3d.com/sites/default/files/Amira_Reference_Guide.pdf
Feldmeyer, D., & Sakmann, B. (2000). Synaptic efficacy and reliability of excitatory connections between the principal neurones of the input (layer 4) and output layer (layer 5) of the neocortex. Journal of Physiology, 525(Pt 1), 31–39.
Frick, A., Feldmeyer, D., Helmstaedter, M., & Sakmann, B. (2007). Monosynaptic Connections between Pairs of L5A Pyramidal Neurons in Columns of Juvenile Rat Somatosensory Cortex. Cereb Cortex 18(2), 397-406.
Fuchs, H., Kedem, Z. M., & Uselton, S. P. (1977). Optimal Surface Reconstruction from Planar Contours (Vol. 20, Communications of the ACM, 20(10), 693-702).
Gillette, T. A., Brown, K. M., & Ascoli, G. A. (2011). The DIADEM metric: comparing multiple reconstructions of the same neuron. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 233–245. doi:10.1007/s12021-011-9117-y.
Groh, A., Meyer, H. S., Schmidt, E. F., Heintz, N., Sakmann, B., & Krieger, P. (2010). Cell-type specific properties of pyramidal neurons in neocortex underlying a layout that is modifiable depending on the cortical area. Cerebral Cortex, 20(4), 826–836.
Halavi, M., Hamilton, K. A., Parekh, R., & Ascoli, G. A. (2012). Digital reconstructions of neuronal morphology: three decades of research trends. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 6, 49. doi:10.3389/fnins.2012.00049.
Helmstaedter, M., Briggman, K. L., & Denk, W. (2011). High-accuracy neurite reconstruction for high-throughput neuroanatomy. Nature Neuroscience, 14(8), 1081–1088. doi:10.1038/nn.2868.
Hill, S. L., Wang, Y., Riachi, I., Schurmann, F., & Markram, H. (2012). Statistical connectivity provides a sufficient foundation for specific functional connectivity in neocortical neural microcircuits. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(42), E2885–E2894. doi:10.1073/pnas.1202128109.
Horikawa, K., & Armstrong, W. E. (1988). A versatile means of intracellular labeling: injection of biocytin and its detection with avidin conjugates. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 25(1), 1–11.
Jungblut, D., Vlachos, A., Schuldt, G., Zahn, N., Deller, T., & Wittum, G. (2012). SpineLab: tool for three-dimensional reconstruction of neuronal cell morphology. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 17(7), 076007. doi:10.1117/1.JBO.17.7.076007.
Kleinfeld, D., Bharioke, A., Blinder, P., Bock, D. D., Briggman, K. L., Chklovskii, D. B., et al. (2011). Large-scale automated histology in the pursuit of connectomes. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(45), 16125–16138. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4077-11.2011.
Lang, S., Dercksen, V. J., Sakmann, B., & Oberlaender, M. (2011). Simulation of signal flow in 3D reconstructions of an anatomically realistic neural network in rat vibrissal cortex. Neural Networks, 24(9), 998–1011. doi:10.1016/j.neunet.2011.06.013.
Liang, Y. D., Barsky, B. A., & M., S. (1992). Some Improvements to a Parametric Line Clipping Algorithm. Tech. Rep. UCB/CSD-92-688. EECS Department, University of California, Berkley.
Luisi, J., Narayanaswamy, A., Galbreath, Z., & Roysam, B. (2011). The FARSIGHT trace editor: an open source tool for 3-D inspection and efficient pattern analysis aided editing of automated neuronal reconstructions. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 305–315. doi:10.1007/s12021-011-9115-0.
Margrie, T. W., Brecht, M., & Sakmann, B. (2002). In vivo, low-resistance, whole-cell recordings from neurons in the anaesthetized and awake mammalian brain. Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology, 444(4), 491–498.
Markram, H. (2006). The blue brain project. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 7(2), 153–160.
Mayerich, D., Bjornsson, C., Taylor, J., & Roysam, B. (2011). Metrics for Comparing Explicit Representations of Interconnected Biological Networks. In IEEE Symposium on Biological Data Visualization, Providence RI, (pp. 79–86).
McGuffin, M. J., & Jurisica, I. (2009). Interaction techniques for selecting and manipulating subgraphs in network visualizations. In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 15(6), 937–944.
Meijering, E. (2010). Neuron tracing in perspective. Cytometry. Part A, 77(7), 693–704. doi:10.1002/cyto.a.20895.
Meyer, H. S., Wimmer, V. C., Hemberger, M., Bruno, R. M., de Kock, C. P., Frick, A., et al. (2010). Cell type-specific thalamic innervation in a column of rat vibrissal cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 20(10), 2287–2303.
Myatt, D. R., Hadlington, T., Ascoli, G. A., & Nasuto, S. J. (2012). Neuromantic - from semi-manual to semi-automatic reconstruction of neuron morphology. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 6, 4. doi:10.3389/fninf.2012.00004.
Nielsen, J., & Mack, R. L. (1994). Usability Inspection Methods: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Oberlaender, M., Bruno, R. M., Sakmann, B., & Broser, P. J. (2007). Transmitted light brightfield mosaic microscopy for three-dimensional tracing of single neuron morphology. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 12(6), 064029. doi:10.1117/1.2815693.
Oberlaender, M., Broser, P. J., Sakmann, B., & Hippler, S. (2009). Shack-Hartmann wave front measurements in cortical tissue for deconvolution of large three-dimensional mosaic transmitted light brightfield micrographs. Journal of Microscopy, 233(2), 275–289.
Oberlaender, M., Boudewijns, Z. S., Kleele, T., Mansvelder, H. D., Sakmann, B., & de Kock, C. P. (2011). Three-dimensional axon morphologies of individual layer 5 neurons indicate cell type-specific intracortical pathways for whisker motion and touch. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(10), 4188–4193. doi:10.1073/pnas.1100647108.
Oberlaender, M., de Kock, C. P. J., Bruno, R. M., Ramirez, A., Meyer, H. S., Dercksen, V. J., et al. (2012a). Cell Type-Specific Three-Dimensional Structure of Thalamocortical Circuits in a Column of Rat Vibrissal Cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 22(10), 2375-2391 (New York, NY : 1991), doi:10.1093/cercor/bhr317.
Oberlaender, M., Ramirez, A., & Bruno, R. M. (2012b). Sensory experience restructures thalamocortical axons during adulthood. Neuron, 74(4), 648–655. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2012.03.022.
Parekh, R., & Ascoli, G. A. (2013). Neuronal morphology goes digital: a research hub for cellular and system neuroscience. Neuron, 77(6), 1017–1038. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.03.008.
Peng, H., Ruan, Z., Long, F., Simpson, J. H., & Myers, E. W. (2010). V3D enables real-time 3D visualization and quantitative analysis of large-scale biological image data sets. Nature Biotechnology, 28(4), 348–353. doi:10.1038/nbt.1612.
Peng, H., Long, F., Zhao, T., & Myers, E. (2011). Proof-editing is the bottleneck of 3D neuron reconstruction: the problem and solutions. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 103–105. doi:10.1007/s12021-010-9090-x.
Pinault, D. (1996). A novel single-cell staining procedure performed in vivo under electrophysiological control: morpho-functional features of juxtacellularly labeled thalamic cells and other central neurons with biocytin or Neurobiotin. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 65(2), 113–136.
Ragan, T., Kadiri, L. R., Venkataraju, K. U., Bahlmann, K., Sutin, J., Taranda, J., et al. (2012). Serial two-photon tomography for automated ex vivo mouse brain imaging. Nature Methods, 9(3), 255–258. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1854.
Schubert, D., Kotter, R., Luhmann, H. J., & Staiger, J. F. (2006). Morphology, electrophysiology and functional input connectivity of pyramidal neurons characterizes a genuine layer va in the primary somatosensory cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 16(2), 223–236.
Sigg, C., Weyerich, T., Botsch, M., & Gross, M. GPU-Based Ray-Casting of Quadratic Surfaces. In 3rd Eurographics/IEEE VGTC conference on Point-Based Graphics, Boston MA, 2006 (pp. 59–65).
Skiena, S. (1998). The algorithm design manual: Springer Verlag New York.
Svoboda, K. (2011). The past, present, and future of single neuron reconstruction. Neuroinformatics, 9(2-3), 97-99. doi:10.1007/s12021-011-9097-y.
Szeliski, R. (2006). Image alignment and stitching: a tutorial. Foundations and Trends in Computer Graphics and Vision, 2(1), 1–104.
Wearne, S. L., Rodriguez, A., Ehlenberger, D. B., Rocher, A. B., Henderson, S. C., & Hof, P. R. (2005). New techniques for imaging, digitization and analysis of three-dimensional neural morphology on multiple scales. Neuroscience, 136(3), 661–680. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.05.053.
Wills, G. J. (1996). Selection: 524,288 ways to say “this is interesting”. In IEEE Symposium on Information Visualization, (pp. 54–60)
Wong-Riley, M. (1979). Changes in the visual system of monocularly sutured or enucleated cats demonstrable with cytochrome oxidase histochemistry. Brain Research, 171(1), 11–28.
Zitova, B., & Flusser, J. (2003). Image registration methods: a survey. Image and Vision Computing, 21(11), 977–1000. doi:10.1016/S0262-8856(03)00137-9.
Acknowledgments
We thank Bert Sakmann and Philip J. Broser for advice and assistance during early stages of the project; Wolfgang Holler and Britta Weber for their contribution to the Filament Editor; Marianne Krabi and Jonas Hörsch for assisting with the analysis functionality; Norbert Lindow for providing the LineRayCaster. Randy M. Bruno and Christiaan P.J. de Kock for supplying biocytin-labeled neurons; Lothar Baltruschat, Richard Smith, Kevin Pels, and Ariel Lee for proof-editing; Hans-Joachim Wagner and the entire staff of the Anatomy Institute of the University of Tuebingen for their generous support. Funding was provided by the Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience, Tuebingen (funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF; FKZ: 01GQ1002)) (MO), by the Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, Tuebingen (MO), by the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience, Jupiter (MO), by the Werner Reichardt Center for Integrative Neuroscience, Tuebingen (MO), by the Zuse Institute Berlin (VJD, HCH) and the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology, Martinsried (VJD). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author Contributions
Conceived and designed the project: MO. Developed the Filament Editor and associated functionalities: VJD. Analyzed the data and wrote the paper: VJD, HCH, MO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 26 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dercksen, V.J., Hege, HC. & Oberlaender, M. The Filament Editor: An Interactive Software Environment for Visualization, Proof-Editing and Analysis of 3D Neuron Morphology. Neuroinform 12, 325–339 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-013-9213-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-013-9213-2