Abstract
Purpose
The current study investigated the correlation between dietary iron intake and diabetic kidney disease among diabetic adults.
Methods
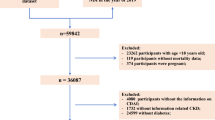
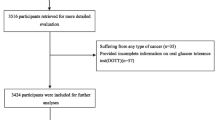
This cross-sectional study enrolled 8118 participants who suffered from diabetes from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999–2018. Dietary iron intake was obtained from 24 h recall interviews, and diabetic kidney disease was defined as eGFR < 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 or albumin creatinine ratio (ACR) ≥ 30 mg/g. Three weighted logistic regression models were utilized to investigate odd ratio (OR) and 95% CIs for diabetic kidney disease. Stratified analyses were performed by gender, age, BMI, HbA1c, hypertension status, and smoking status, and diabetes types.
Results
Among 8118 participants (51.6% male, mean age 61.3 years), 40.7% of participants suffered from diabetic kidney disease. With the adjustment of potential covariates, we found that ≥ 12.59 mg of dietary iron was related to a lower risk of diabetic kidney disease (OR = 0.78, 95% CI: 0.63 to 0.96; OR = 0.79, 95% CI: 0.63 to 0.98). In stratified analyses, higher iron intake was negatively related to diabetic kidney disease, especially among those who were male, < 60 years, those with hypertension, those with HbA1c < 7.0%, and those who were ex-smokers. The result remained robust in sensitivity analyses.
Conclusion
We found that ≥ 12.59 mg of dietary iron is associated with a lower risk of diabetic kidney disease, especially in those who were male, younger, heavier weight, have better blood sugar control, and those who were ex-smokers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.K. Ali, J. Pearson-Stuttard, E. Selvin, E.W. Gregg, Interpreting global trends in type 2 diabetes complications and mortality. Diabetologia 65, 3–13 (2022)
M. Neuenschwander, A. Ballon, K.S. Weber, T. Norat, D. Aune, L. Schwingshackl, S. Schlesinger, Role of diet in type 2 diabetes incidence: umbrella review of meta-analyses of prospective observational studies. BMJ 366, l2368 (2019)
M. Morales, X. Xue, Targeting iron metabolism in cancer therapy. Theranostics 11, 8412–8429 (2021)
J. He, A. Fang, S. Yu, X. Shen, K. Li, Dietary Nonheme, Heme, and total iron intake and the risk of diabetes in adults: results from the china health and nutrition survey. Diabetes Care 43, 776–784 (2020)
Z. Shi, X. Hu, B. Yuan, X. Pan, H.E. Meyer, G. Holmboe-Ottesen, Association between serum ferritin, hemoglobin, iron intake, and diabetes in adults in Jiangsu, China. Diabetes Care 29, 1878–1883 (2006)
X. Wang, X. Fang, W. Zheng, J. Zhou, Z. Song, M. Xu, J. Min, F. Wang, Genetic support of a causal relationship between iron status and Type 2 diabetes: a mendelian randomization study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 106, e4641–e4651 (2021)
Y. Huang, D. Cao, Z. Chen, B. Chen, J. Li, R. Wang, J. Guo, Q. Dong, C. Liu, Q. Wei, L. Liu, Iron intake and multiple health outcomes: umbrella review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 63, 2910–2927 (2023).
S. Rajpathak, J. Ma, J. Manson, W.C. Willett, F.B. Hu, Iron intake and the risk of type 2 diabetes in women: a prospective cohort study. Diabetes Care 29, 1370–1376 (2006)
A. Reunanen, H. Takkunen, P. Knekt, R. Seppänen, A. Aromaa, Body iron stores, dietary iron intake and coronary heart disease mortality. J. Intern. Med. 238, 223–230 (1995)
A.G.R. Mainous, B. Wells, P.J. Carek, J.M. Gill, M.E. Geesey, The mortality risk of elevated serum transferrin saturation and consumption of dietary iron. Ann. Fam. Med. 2, 139–144 (2004)
Johnson C.L., Paulose-Ram R., Ogden C.L., Carroll M.D., Kruszon-Moran D., Dohrmann S.M., Curtin L.R. National health and nutrition examination survey: analytic guidelines, 1999–2010. Vital Health Stat. Series 2 161, 1–24 (2013)
Zipf G., Chiappa M., Porter K.S., Ostchega Y., Lewis B.G., Dostal J. National health and nutrition examination survey: plan and operations, 1999–2010. Vital Health Stat. Ser. 1, Program Collection Procedures 56, 1–37 (2013)
A.S. Levey, L.A. Stevens, C.H. Schmid, Y.L. Zhang, A.R. Castro, H.I. Feldman, J.W. Kusek, P. Eggers, F. Van Lente, T. Greene, J. Coresh, A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 150, 604–612 (2009)
I.H. de Boer, K. Khunti, T. Sadusky, K.R. Tuttle, J.J. Neumiller, C.M. Rhee, S.E. Rosas, P. Rossing, G. Bakris, Diabetes management in chronic kidney disease: a consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 102, 974–989 (2022)
S.C. DeShields, T.D. Cunningham, Comparison of osteoporosis in US adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 41, 1051–1060 (2018)
Johnson C.L., Paulose-Ram R., Ogden C.L., Carroll M.D., Kruszon-Moran D., Dohrmann S.M., Curtin L.R.: National health and nutrition examination survey: analytic guidelines, 1999-2010. Vital and health statistics. Series 2, Data Evaluation and Methods Research:1-24 (2013)
P. Trumbo, A.A. Yates, S. Schlicker, M. Poos, Dietary reference intakes: vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, vanadium, and zinc. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 101, 294–301 (2001)
D. Hirano, H. Unoki-Kubota, T. Imasawa, R. Yamamoto-Honda, H. Kajio, S. Yamashita, Y. Fukazawa, N. Seki, M. Noda, Y. Kaburagi, Independent risk factors of rapid glomerular filtration rate decline in patients with type 2 diabetes with preserved kidney function and normoalbuminuria: a multicenter cohort study. J. Diabetes Investig. 14, 874–882 (2023).
S.D. Mathias, S.I. Blum, V. Sikirica, K.L. Johansen, H.H. Colwell, T. Okoro, Symptoms and impacts in anemia of chronic kidney disease. J. Patient Rep. Outcom 4, 64 (2020)
A.R. Hizomi, F. Fakhri, T.M. Naeimi, F. Talebi, Z. Talebi, N. Rashidi, M. Zahedi, Prevalence of anemia and its associated factors among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a referral diabetic clinic in the north of Iran. Bmc Endocr. Disord. 23, 58 (2023)
Y. Wu, Y. Sun, Y. Wu, K. Zhang, Y. Chen, Predictive value of ferroptosis-related biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease: a prospective observational study. Acta Diabetol. 60, 507–516 (2023)
M. Mo, Y. Gao, L. Deng, Y. Liang, N. Xia, L. Pan, Association between iron metabolism and acute kidney injury in critically Ill patients with diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 13, 892811 (2022)
A.V. Harrison, F.R. Lorenzo, D.A. McClain, Iron and the pathophysiology of diabetes. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 85, 339–362 (2022).
M.C.F.D. Santos, C.P. Anderson, S. Neschen, K.B. Zumbrennen-Bullough, S.J. Romney, M. Kahle-Stephan, B. Rathkolb, V. Gailus-Durner, H. Fuchs, E. Wolf, J. Rozman, M.H. de Angelis, W.M. Cai, M. Rajan, J. Hu, P.C. Dedon, E.A. Leibold, Irp2 regulates insulin production through iron-mediated Cdkal1-catalyzed tRNA modification. Nat. Commun. 11, 296 (2020)
M. Yamanouchi, K. Furuichi, M. Shimizu, T. Toyama, Y. Yamamura, M. Oshima, S. Kitajima, A. Hara, Y. Iwata, N. Sakai, Y. Oba, S. Matsuoka, D. Ikuma, H. Mizuno, T. Suwabe, J. Hoshino, N. Sawa, Y. Yuzawa, H. Kitamura, Y. Suzuki, H. Sato, N. Uesugi, Y. Ueda, S. Nishi, H. Yokoyama, T. Nishino, K. Samejima, K. Kohagura, Y. Shibagaki, H. Makino, S. Matsuo, Y. Ubara, T. Wada, Serum hemoglobin concentration and risk of renal function decline in early stages of diabetic kidney disease: a nationwide, biopsy-based cohort study. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 37, 489–497 (2022)
P.J. Thompson, A. Shah, V. Ntranos, F. Van Gool, M. Atkinson, A. Bhushan, Targeted elimination of senescent beta cells prevents Type 1 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 29, 1045–1060 (2019)
Y. Wu, Y. Zhao, H.Z. Yang, Y.J. Wang, Y. Chen, HMGB1 regulates ferroptosis through Nrf2 pathway in mesangial cells in response to high glucose. Biosci. Rep. 41, BSR20202924 (2021)
A. Aregbesola, S. Voutilainen, J.K. Virtanen, J. Mursu, T.P. Tuomainen, Gender difference in type 2 diabetes and the role of body iron stores. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 54, 113–120 (2017)
L.R. Zacharski, D.L. Ornstein, S. Woloshin, L.M. Schwartz, Association of age, sex, and race with body iron stores in adults: analysis of NHANES III data. Am. Heart J. 140, 98–104 (2000)
K.T. Grubic, B. Curko-Cofek, Age-related changes and sex-related differences in brain iron metabolism. Nutrients 12, 2601 (2020).
C. Vecchi, G. Montosi, C. Garuti, E. Corradini, M. Sabelli, S. Canali, A. Pietrangelo, Gluconeogenic signals regulate iron homeostasis via hepcidin in mice. Gastroenterology 146, 1060–1069 (2014)
J.M. Fernandez-Real, D. McClain, M. Manco, Mechanisms linking glucose homeostasis and iron metabolism toward the onset and progression of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 38, 2169–2176 (2015)
P. Krisai, S. Leib, S. Aeschbacher, T. Kofler, M. Assadian, A. Maseli, J. Todd, J. Estis, M. Risch, L. Risch, D. Conen, Relationships of iron metabolism with insulin resistance and glucose levels in young and healthy adults. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 32, 31–37 (2016)
C.I. Cook, B.P. Yu, Iron accumulation in aging: modulation by dietary restriction. Mech. Ageing Dev. 102, 1–13 (1998)
C.E. Hughes, T.K. Coody, M.Y. Jeong, J.A. Berg, D.R. Winge, A.L. Hughes, Cysteine toxicity drives age-related mitochondrial decline by altering iron homeostasis. Cell 180, 296–310 (2020)
E.K. Batchelor, P. Kapitsinou, P.E. Pergola, C.P. Kovesdy, D.I. Jalal, Iron deficiency in chronic kidney disease: updates on pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 31, 456–468 (2020)
R.S. Zeidan, S.M. Han, C. Leeuwenburgh, R. Xiao, Iron homeostasis and organismal aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 72, 101510 (2021)
S.T. Lugg, A. Scott, D. Parekh, B. Naidu, D.R. Thickett, Cigarette smoke exposure and alveolar macrophages: mechanisms for lung disease. Thorax 77, 94–101 (2022)
A. Sampilvanjil, T. Karasawa, N. Yamada, T. Komada, T. Higashi, C. Baatarjav, S. Watanabe, R. Kamata, N. Ohno, M. Takahashi, Cigarette smoke extract induces ferroptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol-Heart C 318, H508–H518 (2020)
M. Takahashi, K. Mizumura, Y. Gon, T. Shimizu, Y. Kozu, S. Shikano, Y. Iida, M. Hikichi, S. Okamoto, K. Tsuya, A. Fukuda, S. Yamada, K. Soda, S. Hashimoto, S. Maruoka, Iron-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 643980 (2021)
Funding
This work was supported by research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Z.Z., 82270862, 81700730), (Y.J., 82370818, 82000785); the Guangzhou Science and Technology Project (Y.J.,2024A04J5098); and the National Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship, Southern Medical University (Z.Z., 202312121031, Y.J., S202312121167).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.W., Z.Z., Y.J., and Y.X. designed this study, Y.W., M.X., and J.C. performed the data extraction and statistical analysis. Y.T., H.L., L.L., Y.X., A.C., and H.J. validated the statistical analysis. Y.W. wrote the original draft of the manuscript, which was revised by Z.Z. Y.J. and Y.X. All authors made great contributions to the manuscript and approved it for submission. Z.Z. and Y.J. are the guarantors of this work and, as such, had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Xiao, M., Chen, J. et al. Association of dietary iron intake with diabetic kidney disease among individuals with diabetes. Endocrine (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-024-03819-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-024-03819-y