Abstract
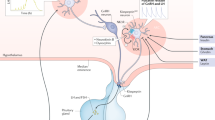
Neuroactive steroids are a type of steroid hormones produced within the nervous system or in peripheral glands and then transported to the brain to exert their neuromodulatory effects. Neuroactive steroids have pleiotropic effects, that include promoting myelination, neuroplasticity, and brain development. They also regulate important physiological functions, such as metabolism, feeding, reproduction, and stress response. The homoeostatic processes of metabolism and reproduction are closely linked and mutually dependent. Reproductive events, such as pregnancy, bring about significant changes in metabolism, and metabolic status may affect reproductive function in mammals. In females, the regulation of reproduction and energy balance is controlled by the fluctuations of oestradiol and progesterone throughout the menstrual cycle. Neurosteroids play a key role in the neuroendocrine control of reproduction. The synthesis of neuroestradiol and neuroprogesterone within the brain is a crucial process that facilitates the release of GnRH and LH, which in turn, regulate the transition from oestrogen-negative to oestrogen-positive feedback. In addition to their function in the reproductive system, oestrogen has a key role in the regulation of energy homoeostasis by acting at central and peripheral levels. The oestrogenic effects on body weight homoeostasis are primarily mediated by oestrogen receptors-α (ERα), which are abundantly expressed in multiple brain regions that are implicated in the regulation of food intake, basal metabolism, thermogenesis, and brown tissue distribution. The tight interplay between energy balance and reproductive physiology is facilitated by shared regulatory pathways, namely POMC, NPY and kisspeptin neurons, which are targets of oestrogen regulation and likely participate in different aspects of the joint control of energy balance and reproductive function. The aim of this review is to present a summary of the progress made in uncovering shared regulatory pathways that facilitate the tight coupling between energy balance and reproductive physiology, as well as their reciprocal interactions and the modulation induced by neurosteroids.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Sze, P.J. Brunton, Neurosteroids and early-life programming: an updated perspective. Curr. Opin. Endocr. Metab. Res. 25, 100367 (2022)
X. Liu, H. Shi, Regulation of estrogen receptor α expression in the hypothalamus by sex steroids: implication in the regulation of energy homeostasis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 1 (2015)
S. Giatti, S. Romano, M. Pesaresi, G. Cermenati, N. Mitro, D. Caruso, M.J. Tetel, L.M. Garcia-Segura, R.C. Melcangi, Neuroactive steroids and the peripheral nervous system: an update. Steroids 103, 23 (2015)
S.H. Mellon, L.D. Griffin, Neurosteroids: biochemistry and clinical significance. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 13, 35–43 (2002)
J. Luo, D. Liu, Does GPER really function as a g protein-coupled estrogen receptor in vivo? Front. Endocrinol. 11, 148 (2020)
J. Zhu, Y. Zhou, B. Jin, J. Shu, Role of estrogen in the regulation of central and peripheral energy homeostasis: from a menopausal perspective. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 14, 20420188231199359 (2023)
S.L. González, M.F. Coronel, M.C. Raggio, F. Labombarda, Progesterone receptor-mediated actions and the treatment of central nervous system disorders: an up-date of the known and the challenge of the unknown. Steroids 153, 108525 (2020)
P. Thomas, Membrane progesterone receptors (mPRs, PAQRs): review of structural and signaling characteristics. Cells 11, 1785 (2022)
D.S. Reddy, Neurosteroids. in Prog. Brain Res. (Elsevier, 2010), pp. 113–137.
S.H. Luquet, H. Vaudry, R. Granata, Neuroendocrine control of feeding behavior. Front. Endocrinol. 10, 399 (2019)
N. Geary, L. Asarian, K.S. Korach, D.W. Pfaff, S. Ogawa, Deficits in E2-dependent control of feeding, weight gain, and cholecystokinin satiation in ER-α null mice. Endocrinology 142, 4751 (2001)
G.C. Parker, M.E. McKee, C. Bishop, D.V. Coscina, Whole-body metabolism varies across the estrous cycle in Sprague–Dawley rats. Physiol. Behav. 74, 399 (2001)
N.H. Rogers, J.W. Perfield, K.J. Strissel, M.S. Obin, A.S. Greenberg, Reduced energy expenditure and increased inflammation are early events in the development of ovariectomy-induced obesity. Endocrinology 150, 2161 (2009)
M.E.E. Jones, A.W. Thorburn, K.L. Britt, K.N. Hewitt, N.G. Wreford, J. Proietto, O.K. Oz, B.J. Leury, K.M. Robertson, S. Yao, E.R. Simpson, Aromatase-deficient (ArKO) mice have a phenotype of increased adiposity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 97, 12735 (2000)
P.A. Heine, J.A. Taylor, G.A. Iwamoto, D.B. Lubahn, P.S. Cooke, Increased adipose tissue in male and female estrogen receptor-α knockout mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 97, 12729 (2000)
Y. Xu, T.P. Nedungadi, L. Zhu, N. Sobhani, B.G. Irani, K.E. Davis, X. Zhang, F. Zou, L.M. Gent, L.D. Hahner, S.A. Khan, C.F. Elias, J.K. Elmquist, D.J. Clegg, Distinct hypothalamic neurons mediate estrogenic effects on energy homeostasis and reproduction. Cell Metab. 14, 453 (2011)
S. Musatov, W. Chen, D.W. Pfaff, M.G. Kaplitt, S. Ogawa, RNAi-mediated silencing of estrogen receptor α in the ventromedial nucleus of hypothalamus abolishes female sexual behaviors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 103, 10456 (2006)
K. Sano, M.C. Tsuda, S. Musatov, T. Sakamoto, S. Ogawa, Differential effects of site‐specific knockdown of estrogen receptor α in the medial amygdala, medial preoptic area, and ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus on sexual and aggressive behavior of male mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 37, 1308 (2013)
T. Khodai, S.M. Luckman, Ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus neurons under the magnifying glass. Endocrinology 162, bqab141 (2021)
M. López, M. Tena-Sempere, Estrogens and the control of energy homeostasis: a brain perspective. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 26, 411 (2015)
D. Atasoy, J.N. Betley, H.H. Su, S.M. Sternson, Deconstruction of a neural circuit for hunger. Nature 488, 172 (2012)
P. Sweeney, L.E. Gimenez, C.C. Hernandez, R.D. Cone, Targeting the central melanocortin system for the treatment of metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 19, 507 (2023)
F.S.J. De Souza, S. Nasif, R. López-Leal, D.H. Levi, M.J. Low, M. Rubinsten, The estrogen receptor α colocalizes with proopiomelanocortin in hypothalamic neurons and binds to a conserved motif present in the neuron-specific enhancer nPE2. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 660, 181 (2011)
K. Saito, X. Cao, Y. He, Y. Xu, Progress in the molecular understanding of central regulation of body weight by estrogens: estrogenic regulation of body weight. Obesity 23, 919 (2015)
L.E. Olofsson, A.A. Pierce, A.W. Xu, Functional requirement of AgRP and NPY neurons in ovarian cycle-dependent regulation of food intake. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 106, 15932 (2009)
A. Gouveia, R. de Oliveira Beleza, SM. Steculorum, AgRP neuronal activity across feeding-related behaviours. Eur J Neurosci 54, 7458 (2021)
L. Dye, J.E. Blundell, Implications for weight regulation. Hum. Reprod. 12, 1142 (1997)
E. Holmberg, J. Sjöstedt, E. Malinina, M. Johansson, S. Turkmen, G. Ragagnin, A. Lundqvist, M. Löfgren, L. Jaukkuri, M. Bixo, T. Bäckström, Implications for weight regulation. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 48, 70 (2018)
E. Holmberg, M. Johansson, T. Bäckström, M. Löfgren, D. Haage, Repeated allopregnanolone exposure induces weight gain in schedule fed rats on high fat diet. Physiol. Behav. 140, 1 (2015)
A. Lundqvist, H. Sandström, T. Bäckström, The relationship between weight gain during pregnancy and allopregnanolone levels: a longitudinal study. Endocr. Connect. 6, 253 (2017)
B. Meister, Neurotransmitters in key neurons of the hypothalamus that regulate feeding behavior and body weight. Physiol. Behav. 92, 263 (2007)
Q. Tong, C.-P. Ye, J.E. Jones, J.K. Elmquist, B.B. Lowell, Synaptic release of GABA by AgRP neurons is required for normal regulation of energy balance. Nat. Neurosci. 11, 998 (2008)
H. Hedström, T. Bäckström, M. Bixo, S. Nyberg, M. Wang, I. Gideonsson, S. Turkmen, Women with polycystic ovary syndrome have elevated serum concentrations of and altered GABAA receptor sensitivity to allopregnanolone. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 83, 643 (2015)
S. Turkmen, L. Andreen, Y. Cengiz, Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery on eating behaviour and allopregnanolone levels in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 31, 301 (2015)
T.L. Stincic, J. Qiu, A.M. Connors, M.J. Kelly, O.K. Rønnekleiv, Arcuate and preoptic kisspeptin neurons exhibit differential projections to hypothalamic nuclei and exert opposite postsynaptic effects on hypothalamic paraventricular and dorsomedial nuclei in the female mouse. Eneuro 8, ENEURO.0093 (2021)
H. Stevenson, S. Bartram, M.M. Charalambides, S. Murthy, T. Petitt, A. Pradeep, O. Vineall, I. Abaraonye, A. Lancaster, K. Koysombat, B. Patel, A. Abbara, Kisspeptin-neuron control of LH pulsatility and ovulation. Front. Endocrinol. 13, 951938 (2022)
M.A. Mittelman-Smith, H. Williams, S.J. Krajewski-Hall, J. Lai, P. Ciofi, N.T. McMullen, N.E. Rance, Arcuate kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons mediate the estrogen suppression of gonadotropin secretion and body weight. Endocrinology 153, 2800 (2012)
B.P. Kenealy, K.L. Keen, J.P. Garcia, L.K. Kohlenberg, E. Terasawa, STX, a novel nonsteroidal estrogenic compound, induces rapid action in primate GnRH neuronal calcium dynamics and peptide release. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 114, 13804 (2017)
B.P. Kenealy, A. Kapoor, K.A. Guerriero, K.L. Keen, J.P. Garcia, J.R. Kurian, T.E. Ziegler, E. Terasawa, Neuroestradiol in the hypothalamus contributes to the regulation of gonadotropin releasing hormone release. J. Neurosci. 33, 19051 (2013)
E. Terasawa, Neuroestradiol in regulation of GnRH release. Horm. Behav. 104, 138 (2018)
B.P. Kenealy, K.L. Keen, J.P. Garcia, D.J. Richter, E. Terasawa, Prolonged infusion of estradiol benzoate into the stalk median eminence stimulates release of GnRH and kisspeptin in ovariectomized female rhesus macaques. Endocrinology 156, 1804 (2015)
R.S. Legro, R.G. Brzyski, M.P. Diamond, C. Coutifaris, W.D. Schlaff, P. Casson, G.M. Christman, H. Huang, Q. Yan, R. Alvero, D.J. Haisenleder, K.T. Barnhart, G.W. Bates, R. Usadi, S. Lucidi, V. Baker, J.C. Trussell, S.A. Krawetz, P. Snyder, D. Ohl, N. Santoro, E. Eisenberg, H. Zhang, Letrozole versus clomiphene for infertility in the polycystic ovary syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 371, 119 (2014)
M. P. Diamond, R. S. Legro, C. Coutifaris, R. Alvero, R. D. Robinson, P. Casson, G. M. Christman, J. Ager, H. Huang, K. R. Hansen, V. Baker, R. Usadi, A. Seungdamrong, G. W. Bates, R. M. Rosen, D. Haisenleder, S. A. Krawetz, K. Barnhart, J. C. Trussell, D. Ohl, Y. Jin, N. Santoro, E. Eisenberg, and H. Zhang, Letrozole, Gonadotropin, or Clomiphene for Unexplained Infertility. N. Engl. J. Med. 373, 1230 (2015).
P.E. Micevych, V. Chaban, J. Ogi, P. Dewing, J.K.H. Lu, K. Sinchak, Estradiol stimulates progesterone synthesis in hypothalamic astrocyte cultures. Endocrinology 148, 782 (2007)
M.A. Mittelman-Smith, A.M. Wong, P.E. Micevych, Estrogen and progesterone integration in an in vitro model of RP3V kisspeptin neurons. Neuroendocrinology 106, 101 (2018)
M.A. Mohr, L.A. Esparza, P. Steffen, P.E. Micevych, A.S. Kauffman, Progesterone receptors in AVPV kisspeptin neurons are sufficient for positive feedback induction of the LH surge. Endocrinology 162, bqab161 (2021)
J. Kuo, N. Hamid, G. Bondar, E.R. Prossnitz, P. Micevych, Membrane estrogen receptors stimulate intracellular calcium release and progesterone synthesis in hypothalamic astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 30, 12950 (2010)
P. Micevych, K. Sinchak, The neurosteroid progesterone underlies estrogen positive feedback of the LH surge. Front. Endocrinol. 2, 90 (2011)
T. Chuon, M. Feri, C. Carlson, S. Ondrejik, P.E. Micevych, K. Sinchak, Progesterone receptor‐Src kinase signaling pathway mediates neuroprogesterone induction of the luteinizing hormone surge in female rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 34, e13071 (2022)
K. Sinchak, M.A. Mohr, P.E. Micevych, Hypothalamic astrocyte development and physiology for neuroprogesterone induction of the luteinizing hormone surge. Front. Endocrinol. 11, 420 (2020)
A.S. Kauffman, Neuroendocrine mechanisms underlying estrogen positive feedback and the LH surge. Front. Neurosci. 16, 953252 (2022)
C.A. Cornil, On the role of brain aromatase in females: why are estrogens produced locally when they are available systemically? J. Comp. Physiol. A 204, 31 (2018)
T.L. Stincic, M.J. Kelly, Estrogenic regulation of reproduction and energy homeostasis by a triumvirate of hypothalamic arcuate neurons. J. Neuroendocrinol. 34, e13145 (2022)
S.L. Padilla, J. Qiu, C.C. Nestor, C. Zhang, A.W. Smith, B.B. Whiddon, O.K. Rønnekleiv, M.J. Kelly, R.D. Palmiter, AgRP to Kiss1 neuron signaling links nutritional state and fertility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114, 2413 (2017)
C. Ohlsson, N. Hellberg, P. Parini, O. Vidal, M. Bohlooly, M. Rudling, M.K. Lindberg, M. Warner, B. Angelin, J.-Å. Gustafsson, Biochem. obesity and disturbed lipoprotein profile in estrogen receptor-α-deficient male mice. Biophys. Res. Commun. 278, 640 (2000)
E. Haas, I. Bhattacharya, E. Brailoiu, M. Damjanović, G.C. Brailoiu, X. Gao, L. Mueller-Guerre, N.A. Marjon, A. Gut, R. Minotti, M.R. Meyer, K. Amann, E. Ammann, A. Perez-Dominguez, M. Genoni, D.J. Clegg, N.J. Dun, T.C. Resta, E.R. Prossnitz, M. Barton, Regulatory role of g protein–coupled estrogen receptor for vascular function and obesity. Circ. Res. 104, 288 (2009)
S. Liu, C. Le May, W.P.S. Wong, R.D. Ward, D.J. Clegg, M. Marcelli, K.S. Korach, F. Mauvais-Jarvis, Importance of extranuclear estrogen receptor-α and membrane G protein–coupled estrogen receptor in pancreatic islet survival. Diabetes 58, 2292 (2009)
G. Sharma, C. Hu, J.L. Brigman, G. Zhu, H.J. Hathaway, E.R. Prossnitz, GPER deficiency in male mice results in insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and a proinflammatory state. Endocrinology 154, 4136 (2013)
Q. Gao, M.J. Wolfgang, S. Neschen, K. Morino, T.L. Horvath, G.I. Shulman, X.Y. Fu, Disruption of neural signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 causes obesity, diabetes, infertility, and thermal dysregulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 101, 4661 (2004)
K. Saito, T. Matsuzaki, T. Iwasa, M. Miyado, H. Saito, T. Hasegawa, K. Homma, E. Inoue, Y. Miyashiro, T. Kubota, M. Irahara, T. Ogata, M. Fukami, PI3K in the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus mediates estrogenic actions on energy expenditure in female mice. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 158, 31 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rasic-Markovic, A., Djuric, E., Skrijelj, D. et al. Neuroactive steroids in the neuroendocrine control of food intake, metabolism, and reproduction. Endocrine (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-024-03755-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-024-03755-x