Abstract
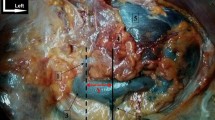
The adrenal gland is a retroperitoneal organ with intimate relationships with neighboring organs but also with the large retroperitoneal vessels. Our aim was to study the vascular relationships of the adrenal gland with the large abdominal vessels. Our work is an anatomical dissection of 80 fresh cadaveric adrenals. The subjects didn’t have a history of retroperitoneal surgery. Dissection conditions were similar to those in the living. All measurements were made in situ. On the right side, the average distance between the adrenal gland and the renal vein (DR) was 13 mm (0–20). In one case, the adrenal gland laid directly on the right renal vein (DR = 0). The average length L, over which the right adrenal gland entered behind the inferior vena cava (IVC), was 8 mm (0–12). In 4 cases, the right adrenal was lateral to the IVC and in 6 cases the length L exceeded 10 mm. On the left side, the mean distance DL, separating the adrenal gland from the left renal vein was 8 mm with extremes ranging from 0 mm to 18 mm. In eleven cases, the adrenal gland laid directly on the left renal vein. The right adrenal gland has a close relationship with the IVC and is often located behind it. This close relationship helps to explain the increased incidence of IVC lesions during surgery. The left adrenal gland has an intimate relationship with the left renal vein and often lies on top of it. This explains the risk of injury to the left renal pedicle during left adrenal surgery.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
References
M. Barczynski, A. Konturek, W. Nowak, Randomized clinical trial of posterior retroperitoneoscopic adrenalectomy versus lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy with a 5-year follow-up. Ann. Surg. 260, 740–748 (2014)
V.A. Constantinides, I. Christakis, P. Touska, F.F. Palazzo, Systematic review and meta-analysis of retroperitoneoscopic versus laparoscopic adrenalectomy. Br. J. Surg. 99, 1639–1648 (2012)
G. Conzo, E. Tartaglia, C. Gambardella et al. Minimally invasive approach for adrenal lesions: systematic review of laparoscopic versus retroperitoneoscopic adrenalectomy and assessment of risk factors for complications. Int J. Surg. 28, 118–123 (2016)
J.M. Duclos, Chirurgie de la glande surrénale. Encycl Med chir. (Elsevier Masson, Paris, 2003), Techniques chirurgicales - Urologie ; 41–496, 22p
P. Koenig, G.P. Haber, I.S. Gill, Surrénalectomie coelioscopique robotisée. Encycl Méd Chir. (Elsevier Masson, Paris, 2007), Techniques chirurgicales – Urologie ; 41-496-A, 7p
C.C. Capelouto, R.G. Moore, S.G. Silverman, L.R. Kavoussi, Retro-peritoneoscopy: anatomical rationale for direct retroperitoneal access. J. Urol. 152, 2008–2010 (1994)
J.F. Henry, F. Sebag, M. Iacobone, J. Hubbard, S. Maweja, Leçons retenues après 274 surrénalectomies laparoscopiques. Ann. Chir. 127, 512–519 (2002)
A. Saadi, S. Mokadem, M. Chakroun et al. A cadaveric anatomical study of the adrenals: Relationship with the posterior abdominal wall muscles revisited. Morphologie 105, 210–216 (2021a)
A. Saadi, S. Mokadem, M. Chakroun et al. Variations anatomiques du drainage veineux de la glande surrénale droite. Prog. Urol. 31, 854 (2021b)
L. Salomon, M. Soulié, F. Saint, P. Mouly, P. Plante, C.C. Abbou, Retroperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: a safe and reproducible technique. Prog. Urol. 11, 438–443 (2001)
A.S. Azzi, N. Driessens, Diagnostic des pathologies surrénaliennes: mise au point d’un incidentalome surrénalien. Rev. Med Brux. 38, 325–333 (2017)
F. William, J.R. Young, The incidentally discovered adrenal mass. N. Engl. J. Med 356, 601–610 (2007)
A.M. Meraney, A. Abd-El Samee, I.S. Gill, Vascular and bowel complications during retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery. J. Urol. 168, 1941–1944 (2002)
S. Permpongkosol, R.E. Link, S. Li-Ming et al. Complications of 2,775 urological laparoscopic procedures: 1993 to 2005. J. Urol. 177, 580–585 (2007)
R.T. Strebel, M. Müntener, T. Sulser, Intraoperative complications of laparoscopic adrenalectomy. World J. Urol. 26, 555–560 (2008)
M.K. Walz, P.F. Alesina, F.A. Wenger et al. Posterior retroperitoneoscopic adrenalectomy—results of 560 procedures in 520 patients. Surgery 140, 943–948 (2006)
E. Damien, V. Vallee, P. Tauzin-Fin, P. Ballanger, Morbidity of unilateral and bilateral laparoscopic adrenalectomy according to the indication. Report of a series of 100 consecutive cases. Prog. Urol. 15, 626–631 (2005)
R.R. Indupur, R.B. Nerli, M.N. Reddy, S.N. Siddappa, R. Thakkar, Laparoscopic adrenalectomy for large pheochromocytoma. BJU int 100, 1126–1129 (2007)
A.W. Kim, R.M. Quiros, J.B. Maxhimer, A.R. El-Ganzouri, R.A. Prinz, Outcome of laparoscopic adrenalectomy for pheochromocytomas vs aldosteronomas. Arch. Surg. 139, 526–529 (2004)
P. Cougard, L. Osmak, P. Goudet, Right laparoscopic adrenalectomy. Ann. Chir. 128, 339–343 (2003)
J. Hureau, G. Hidden, A.T.T. Minh, Vascularisation des glandes surrénales. Anat. Clin. 2, 127–146 (1979)
A. Saadi, S. Mokadem, M. Chakroun et al. A cadaveric anatomical study: anatomy and anatomical variations of left adrenal vein. Surg. Radio. Anat. 44, 689–695 (2022)
M. Siebert, Y. Robert, R. Didier et al. Anatomical variations of the venous drainage from the left adrenal gland: an anatomical study. World J. Surg. 41, 991–996 (2017)
T. Matsuura, K. Takase, H. Ota et al. Radiologic anatomy of the right adrenal vein: preliminary experience with MDCT. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 191, 402–408 (2008)
O.A. Castillo, A. Rodríguez-Carlin, J. López-Vallejo, V. Borgna, Complications associated with laparoscopic adrenalectomy: description and standardized assessment. Actas Urol. Esp. 38, 445–450 (2014)
F. Corcione, C. Esposito, D. Cuccurullo et al. Vena cava injury. A serious complication during laparoscopic right adrenalectomy. Surg. Endosc. 15, 218 (2001)
D. Mutter, M.H. Wheeler, J. Marescaux, Laparoscopic management of operative vena cava injury. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutan Tech. 9, 303–305 (1999)
F. Tissier, C. Hoang, Anatomie, embryologie et histologie de la surrenale. Méd Chir. (Elsevier Masson, Paris, 2007), Endocrinologie-nutrition; 10-014-A-10, 6p (35)
M.F. Kalady, R. Mckinlay, J.A. Olson et al. Laparoscopic adrenalectomy for pheochromocytoma: a comparison to aldosteronoma and incidentaloma. Surg. Endosc. 18, 621–625 (2004)
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank those who donated their bodies to science so that anatomical research could be performed. Results from such research can potentially increase mankind’s overall knowledge that can then improve patient care. Therefore, these donors and their families deserve our highest gratitude.
Author’s contributions
Study conception and Design: A.S. and S.M. Acquisition of data: A.S., M.A.B., S.Z., S.M., H.B., A.H. and M.B. Analysis and interpretation of data : A.S., M.A.B., S.M. and A.H. Drafting of manuscript: A.S. and S.M. Critical revision of the manuscript: A.S., H.A., A.B., M.C., M.A. and R.B.S. Administrative support: H.A., A.B., M.A., M.C. and R.B.S. Final approval of manuscript : All Authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saadi, A., Mokadem, S., Bedoui, M.A. et al. A cadaveric anatomical study of the adrenals: vascular relationship. Endocrine 83, 483–487 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-023-03585-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-023-03585-3