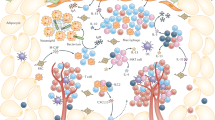
Abstract
Purpose
This review will focus on the immune cells in adipose tissue microenvironment and their regulatory roles in metabolic homeostasis of adipose tissue and even the whole body under physiological and obese conditions.
Methods
This review used PubMed searches of current literature to examine adipose tissue immune cells and cytokines, as well as the complex interactions between them.
Results
Aside from serving as a passive energy depot, adipose tissue has shown specific immunological function. Adipose tissue microenvironment is enriched with a large number of immune cells and cytokines, whose physiological regulation plays a crucial role for metabolic homeostasis. However, obesity causes pro-inflammatory alterations in these adipose tissue immune cells, which have detrimental effects on metabolism and increase the susceptibility of individuals to the obesity related diseases.
Conclusions
Adipose tissue microenvironment is enriched with various immune cells and cytokines, which regulate metabolic homeostasis of adipose tissue and even the whole body, whether under physiological or obese conditions. Targeting key immune cells and cytokines in adipose tissue microenvironment for obesity treatment becomes an attractive research point.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.S. Hotamisligil, N.S. Shargill, B.M. Spiegelman, Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 259, 87–91 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7678183
H. Xu, G.T. Barnes, Q. Yang, G. Tan, D. Yang, C.J. Chou, J. Sole, A. Nichols, J.S. Ross, L.A. Tartaglia, H. Chen, Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 112, 1821–1830 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI19451
S.P. Weisberg, D. McCann, M. Desai, M. Rosenbaum, R.L. Leibel, A.W. Ferrante, Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Invest. 112, 1796–1808 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI19246
A. Schäffler, J. Schölmerich, B. Salzberger, Adipose tissue as an immunological organ: toll-like receptors, C1q/TNFs and CTRPs. Trends Immunol. 28, 393–399 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2007.07.003
R.W. Grant, V.D. Dixit, Adipose tissue as an immunological organ. Obesity (Silver Spring) 23, 512–518 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.21003
The Lancet Public Health: Obesity prevention: changing perspectives. Lancet Public Health 8, e161 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-2667(23)00033-6
A. Kohlgruber, L. Lynch, Adipose tissue inflammation in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 15, 92 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-015-0670-x
A. Sakers, M.K. De Siqueira, P. Seale, C.J. Villanueva, Adipose-tissue plasticity in health and disease. Cell 185, 419–446 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.016
L. Ranvier, Du dévelopment et de l’accroissement desvaiseaux sanguins. Arch. Physiol. Norm. Pathol. 6, 429–446 (1874)
C. Bénézech, N.-T. Luu, J.A. Walker, A.A. Kruglov, Y. Loo, K. Nakamura, Y. Zhang, S. Nayar, L.H. Jones, A. Flores-Langarica, A. McIntosh, J. Marshall, F. Barone, G. Besra, K. Miles, J.E. Allen, M. Gray, G. Kollias, A.F. Cunningham, D.R. Withers, K.M. Toellner, N.D. Jones, M. Veldhoen, S.A. Nedospasov, A.N.J. McKenzie, J.H. Caamaño, Inflammation-induced formation of fat-associated lymphoid clusters. Nat. Immunol. 16, 819–828 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3215
J. Rangel-Moreno, J.E. Moyron-Quiroz, D.M. Carragher, K. Kusser, L. Hartson, A. Moquin, T.D. Randall, Omental milky spots develop in the absence of lymphoid tissue-inducer cells and support B and T cell responses to peritoneal antigens. Immunity 30, 731–743 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2009.03.014
C.N. Lumeng, Innate immune activation in obesity. Mol. Asp. Med. 34, 12–29 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2012.10.002
N. Esser, S. Legrand-Poels, J. Piette, A.J. Scheen, N. Paquot, Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 105, 141–150 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2014.04.006
C.N. Lumeng, J.L. Bodzin, A.R. Saltiel, Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Invest. 117, 175–184 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI29881
C. Bogdan, Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2, 907–916 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1001-907
H.-J. Kim, T. Higashimori, S.-Y. Park, H. Choi, J. Dong, Y.-J. Kim, H.-L. Noh, Y.-R. Cho, G. Cline, Y.-B. Kim, J.K. Kim, Differential effects of interleukin-6 and -10 on skeletal muscle and liver insulin action in vivo. Diabetes 53, 1060–1067 (2004). https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.53.4.1060
M. Blüher, M. Fasshauer, A. Tönjes, J. Kratzsch, M.R. Schön, R. Paschke, Association of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, interleukin-10 and adiponectin plasma concentrations with measures of obesity, insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 113, 534–537 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-872851
K.D. Nguyen, Y. Qiu, X. Cui, Y.P.S. Goh, J. Mwangi, T. David, L. Mukundan, F. Brombacher, R.M. Locksley, A. Chawla, Alternatively activated macrophages produce catecholamines to sustain adaptive thermogenesis. Nature 480, 104–108 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10653
D. Wu, A.B. Molofsky, H.-E. Liang, R.R. Ricardo-Gonzalez, H.A. Jouihan, J.K. Bando, A. Chawla, R.M. Locksley, Eosinophils sustain adipose alternatively activated macrophages associated with glucose homeostasis. Science 332, 243–247 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1201475
Y. Qiu, K.D. Nguyen, J.I. Odegaard, X. Cui, X. Tian, R.M. Locksley, R.D. Palmiter, A. Chawla, Eosinophils and type 2 cytokine signaling in macrophages orchestrate development of functional beige fat. Cell 157, 1292–1308 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.066
A.J. Knights, E.J. Vohralik, P.J. Houweling, E.S. Stout, L.J. Norton, S.J. Alexopoulos, J.J. Yik, H. Mat Jusoh, E.M. Olzomer, K.S. Bell-Anderson, K.N. North, K.L. Hoehn, M. Crossley, K.G.R. Quinlan, Eosinophil function in adipose tissue is regulated by Krüppel-like factor 3 (KLF3). Nat. Commun. 11, 2922 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16758-9
W.R. Bolus, K.R. Peterson, M.J. Hubler, A.J. Kennedy, M.L. Gruen, A.H. Hasty, Elevating adipose eosinophils in obese mice to physiologically normal levels does not rescue metabolic impairments. Mol. Metab. 8, 86–95 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2017.12.004
H. Sunadome, H. Matsumoto, Y. Izuhara, T. Nagasaki, Y. Kanemitsu, Y. Ishiyama, C. Morimoto, T. Oguma, I. Ito, K. Murase, S. Muro, T. Kawaguchi, Y. Tabara, K. Chin, F. Matsuda, T. Hirai, Correlation between eosinophil count, its genetic background and body mass index: The Nagahama Study. Allergol. Int. 69, 46–52 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alit.2019.05.012
K. Moussa, P. Gurung, B. Adams-Huet, S. Devaraj, I. Jialal, Increased eosinophils in adipose tissue of metabolic syndrome. J. Diabetes Complications 33, 535–538 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2019.05.010
A.B. Molofsky, J.C. Nussbaum, H.-E. Liang, S.J. Van Dyken, L.E. Cheng, A. Mohapatra, A. Chawla, R.M. Locksley, Innate lymphoid type 2 cells sustain visceral adipose tissue eosinophils and alternatively activated macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 210, 535–549 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20121964
J.R. Brestoff, B.S. Kim, S.A. Saenz, R.R. Stine, L.A. Monticelli, G.F. Sonnenberg, J.J. Thome, D.L. Farber, K. Lutfy, P. Seale, D. Artis, Group 2 innate lymphoid cells promote beiging of white adipose tissue and limit obesity. Nature 519, 242–246 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14115
A.M. Miller, D.L. Asquith, A.J. Hueber, L.A. Anderson, W.M. Holmes, A.N. McKenzie, D. Xu, N. Sattar, I.B. McInnes, F.Y. Liew, Interleukin-33 induces protective effects in adipose tissue inflammation during obesity in mice. Circ. Res. 107, 650–658 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.218867
L. Lynch, M. Nowak, B. Varghese, J. Clark, A.E. Hogan, V. Toxavidis, S.P. Balk, D. O’Shea, C. O’Farrelly, M.A. Exley, Adipose tissue invariant NKT cells protect against diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorder through regulatory cytokine production. Immunity 37, 574–587 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2012.06.016
L. Lynch, D. O’Shea, D.C. Winter, J. Geoghegan, D.G. Doherty, C. O’Farrelly, Invariant NKT cells and CD1d(+) cells amass in human omentum and are depleted in patients with cancer and obesity. Eur. J. Immunol. 39, 1893–1901 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200939349
L. Lynch, X. Michelet, S. Zhang, P.J. Brennan, A. Moseman, C. Lester, G. Besra, E.E. Vomhof-Dekrey, M. Tighe, H.-F. Koay, D.I. Godfrey, E.A. Leadbetter, D.B. Sant’Angelo, U. von Andrian, M.B. Brenner, Regulatory iNKT cells lack expression of the transcription factor PLZF and control the homeostasis of T(reg) cells and macrophages in adipose tissue. Nat. Immunol. 16, 85–95 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3047
L. Lynch, Adipose invariant natural killer T cells. Immunology 142, 337–346 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12269
L. Lynch, A.E. Hogan, D. Duquette, C. Lester, A. Banks, K. LeClair, D.E. Cohen, A. Ghosh, B. Lu, M. Corrigan, D. Stevanovic, E. Maratos-Flier, D.J. Drucker, D. O’Shea, M. Brenner, iNKT cells induce FGF21 for thermogenesis and are required for maximal weight loss in GLP1 therapy. Cell Metab. 24, 510–519 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.08.003
M. Brigl, M.B. Brenner, CD1: antigen presentation and T cell function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22, 817–890 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.22.012703.104608
A.C. Kohlgruber, S.T. Gal-Oz, N.M. LaMarche, M. Shimazaki, D. Duquette, H.-F. Koay, H.N. Nguyen, A.I. Mina, T. Paras, A. Tavakkoli, U. von Andrian, A.P. Uldrich, D.I. Godfrey, A.S. Banks, T. Shay, M.B. Brenner, L. Lynch, γδ T cells producing interleukin-17A regulate adipose regulatory T cell homeostasis and thermogenesis. Nat. Immunol. 19, 464–474 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-018-0094-2
T. Mahlakõiv, A.-L. Flamar, L.K. Johnston, S. Moriyama, G.G. Putzel, P.J. Bryce, D. Artis, Stromal cells maintain immune cell homeostasis in adipose tissue via production of interleukin-33. Sci. Immunol. 4, eaax0416 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.aax0416
M.-W. Lee, J.I. Odegaard, L. Mukundan, Y. Qiu, A.B. Molofsky, J.C. Nussbaum, K. Yun, R.M. Locksley, A. Chawla, Activated type 2 innate lymphoid cells regulate beige fat biogenesis. Cell 160, 74–87 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.12.011
D. Kolodin, N. van Panhuys, C. Li, A.M. Magnuson, D. Cipolletta, C.M. Miller, A. Wagers, R.N. Germain, C. Benoist, D. Mathis, Antigen- and cytokine-driven accumulation of regulatory T cells in visceral adipose tissue of lean mice. Cell Metab. 21, 543–557 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.03.005
A. Vasanthakumar, K. Moro, A. Xin, Y. Liao, R. Gloury, S. Kawamoto, S. Fagarasan, L.A. Mielke, S. Afshar-Sterle, S.L. Masters, S. Nakae, H. Saito, J.M. Wentworth, P. Li, W. Liao, W.J. Leonard, G.K. Smyth, W. Shi, S.L. Nutt, S. Koyasu, A. Kallies, The transcriptional regulators IRF4, BATF and IL-33 orchestrate development and maintenance of adipose tissue-resident regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 16, 276–285 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3085
S. Winer, Y. Chan, G. Paltser, D. Truong, H. Tsui, J. Bahrami, R. Dorfman, Y. Wang, J. Zielenski, F. Mastronardi, Y. Maezawa, D.J. Drucker, E. Engleman, D. Winer, H.-M. Dosch, Normalization of obesity-associated insulin resistance through immunotherapy. Nat. Med. 15, 921–929 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2001
M. Feuerer, L. Herrero, D. Cipolletta, A. Naaz, J. Wong, A. Nayer, J. Lee, A.B. Goldfine, C. Benoist, S. Shoelson, D. Mathis, Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters. Nat. Med. 15, 930–939 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2002
M.M. Tiemessen, A.L. Jagger, H.G. Evans, M.J.C. van Herwijnen, S. John, L.S. Taams, CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induce alternative activation of human monocytes/macrophages. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 19446–19451 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0706832104
D. Medrikova, T.P. Sijmonsma, K. Sowodniok, D.M. Richards, M. Delacher, C. Sticht, N. Gretz, T. Schafmeier, M. Feuerer, S. Herzig, Brown adipose tissue harbors a distinct sub-population of regulatory T cells. PloS One 10, e0118534 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0118534
T. Gnad, S. Scheibler, I. von Kügelgen, C. Scheele, A. Kilić, A. Glöde, L.S. Hoffmann, L. Reverte-Salisa, P. Horn, S. Mutlu, A. El-Tayeb, M. Kranz, W. Deuther-Conrad, P. Brust, M.E. Lidell, M.J. Betz, S. Enerbäck, J. Schrader, G.G. Yegutkin, C.E. Müller, A. Pfeifer, Adenosine activates brown adipose tissue and recruits beige adipocytes via A2A receptors. Nature 516, 395–399 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13816
P.J. Schuler, Z. Saze, C.-S. Hong, L. Muller, D.G. Gillespie, D. Cheng, M. Harasymczuk, M. Mandapathil, S. Lang, E.K. Jackson, T.L. Whiteside, Human CD4+ CD39+ regulatory T cells produce adenosine upon co-expression of surface CD73 or contact with CD73+ exosomes or CD73+ cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 177, 531–543 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12354
N. Baumgarth, The double life of a B-1 cell: self-reactivity selects for protective effector functions. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 34–46 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2901
L. Shen, M.H.Y. Chng, M.N. Alonso, R. Yuan, D.A. Winer, E.G. Engleman, B-1a lymphocytes attenuate insulin resistance. Diabetes 64, 593–603 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-0554
S. Nishimura, I. Manabe, S. Takaki, M. Nagasaki, M. Otsu, H. Yamashita, J. Sugita, K. Yoshimura, K. Eto, I. Komuro, T. Kadowaki, R. Nagai, Adipose natural regulatory B cells negatively control adipose tissue inflammation. Cell Metab. 18, 759–766 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.09.017
W.V. Trim, L. Lynch, Immune and non-immune functions of adipose tissue leukocytes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 22, 371–386 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-021-00635-7
A. Hruby, F.B. Hu, The epidemiology of obesity: a big picture. PharmacoEconomics 33, 673–689 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-014-0243-x
T. Kelly, W. Yang, C.-S. Chen, K. Reynolds, J. He, Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int. J. Obes. 2005 32, 1431–1437 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.102
S.M. Reilly, A.R. Saltiel, Adapting to obesity with adipose tissue inflammation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 13, 633–643 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2017.90
S.U. Amano, J.L. Cohen, P. Vangala, M. Tencerova, S.M. Nicoloro, J.C. Yawe, Y. Shen, M.P. Czech, M. Aouadi, Local proliferation of macrophages contributes to obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation. Cell Metab. 19, 162–171 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.11.017
D.Y. Oh, H. Morinaga, S. Talukdar, E.J. Bae, J.M. Olefsky, Increased macrophage migration into adipose tissue in obese mice. Diabetes 61, 346–354 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2337/db11-0860
H. Kanda, S. Tateya, Y. Tamori, K. Kotani, K. Hiasa, R. Kitazawa, S. Kitazawa, H. Miyachi, S. Maeda, K. Egashira, M. Kasuga, MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 1494–1505 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI26498
S. Cinti, G. Mitchell, G. Barbatelli, I. Murano, E. Ceresi, E. Faloia, S. Wang, M. Fortier, A.S. Greenberg, M.S. Obin, Adipocyte death defines macrophage localization and function in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. J. Lipid Res. 46, 2347–2355 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M500294-JLR200
R.M. Pirzgalska, E. Seixas, J.S. Seidman, V.M. Link, N.M. Sánchez, I. Mahú, R. Mendes, V. Gres, N. Kubasova, I. Morris, B.A. Arús, C.M. Larabee, M. Vasques, F. Tortosa, A.L. Sousa, S. Anandan, E. Tranfield, M.K. Hahn, M. Iannacone, N.J. Spann, C.K. Glass, A.I. Domingos, Sympathetic neuron-associated macrophages contribute to obesity by importing and metabolizing norepinephrine. Nat. Med. 23, 1309–1318 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4422
D.A. Jaitin, L. Adlung, C.A. Thaiss, A. Weiner, B. Li, H. Descamps, P. Lundgren, C. Bleriot, Z. Liu, A. Deczkowska, H. Keren-Shaul, E. David, N. Zmora, S.M. Eldar, N. Lubezky, O. Shibolet, D.A. Hill, M.A. Lazar, M. Colonna, F. Ginhoux, H. Shapiro, E. Elinav, I. Amit, Lipid-associated macrophages control metabolic homeostasis in a Trem2-dependent manner. Cell 178, 686–698.e14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.054
N.C. Winn, E.M. Wolf, J.N. Garcia, A.H. Hasty, Exon 2-mediated deletion of Trem2 does not worsen metabolic function in diet-induced obese mice. J. Physiol. 600, 4485–4501 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1113/JP283684
D. Patsouris, P.-P. Li, D. Thapar, J. Chapman, J.M. Olefsky, J.G. Neels, Ablation of CD11c-positive cells normalizes insulin sensitivity in obese insulin resistant animals. Cell Metab. 8, 301–309 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2008.08.015
K.T. Uysal, S.M. Wiesbrock, M.W. Marino, G.S. Hotamisligil, Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-alpha function. Nature 389, 610–614 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/39335
J.M. Wentworth, G. Naselli, W.A. Brown, L. Doyle, B. Phipson, G.K. Smyth, M. Wabitsch, P.E. O’Brien, L.C. Harrison, Pro-inflammatory CD11c+CD206+ adipose tissue macrophages are associated with insulin resistance in human obesity. Diabetes 59, 1648–1656 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2337/db09-0287
L.H. Jackson-Jones, P. Smith, J.R. Portman, M.S. Magalhaes, K.J. Mylonas, M.M. Vermeren, M. Nixon, B.E.P. Henderson, R. Dobie, S. Vermeren, L. Denby, N.C. Henderson, D.J. Mole, C. Bénézech, Stromal cells covering omental fat-associated lymphoid clusters trigger formation of neutrophil aggregates to capture peritoneal contaminants. Immunity 52, 700–715.e6 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2020.03.011
V. Elgazar-Carmon, A. Rudich, N. Hadad, R. Levy, Neutrophils transiently infiltrate intra-abdominal fat early in the course of high-fat feeding. J. Lipid Res. 49, 1894–1903 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M800132-JLR200
Y. Watanabe, Y. Nagai, H. Honda, N. Okamoto, T. Yanagibashi, M. Ogasawara, S. Yamamoto, R. Imamura, I. Takasaki, H. Hara, M. Sasahara, M. Arita, S. Hida, S. Taniguchi, T. Suda, K. Takatsu, Bidirectional crosstalk between neutrophils and adipocytes promotes adipose tissue inflammation. FASEB J. 33, 11821–11835 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201900477RR
J. Nijhuis, S.S. Rensen, Y. Slaats, F.M.H. van Dielen, W.A. Buurman, J.W.M. Greve, Neutrophil activation in morbid obesity, chronic activation of acute inflammation. Obesity (Silver Spring) 17, 2014–2018 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2009.113
E. Brotfain, N. Hadad, Y. Shapira, E. Avinoah, A. Zlotnik, L. Raichel, R. Levy, Neutrophil functions in morbidly obese subjects. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 181, 156–163 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12631
S. Talukdar, D.Y. Oh, G. Bandyopadhyay, D. Li, J. Xu, J. McNelis, M. Lu, P. Li, Q. Yan, Y. Zhu, J. Ofrecio, M. Lin, M.B. Brenner, J.M. Olefsky, Neutrophils mediate insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet through secreted elastase. Nat. Med. 18, 1407–1412 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2885
M.M. Altintas, A. Azad, B. Nayer, G. Contreras, J. Zaias, C. Faul, J. Reiser, A. Nayer, Mast cells, macrophages, and crown-like structures distinguish subcutaneous from visceral fat in mice. J. Lipid Res. 52, 480–488 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M011338
A. Divoux, S. Moutel, C. Poitou, D. Lacasa, N. Veyrie, A. Aissat, M. Arock, M. Guerre-Millo, K. Clément, Mast cells in human adipose tissue: link with morbid obesity, inflammatory status, and diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 97, E1677–E1685 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2012-1532
J. Liu, A. Divoux, J. Sun, J. Zhang, K. Clément, J.N. Glickman, G.K. Sukhova, P.J. Wolters, J. Du, C.Z. Gorgun, A. Doria, P. Libby, R.S. Blumberg, B.B. Kahn, G.S. Hotamisligil, G.-P. Shi, Genetic deficiency and pharmacological stabilization of mast cells reduce diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Nat. Med. 15, 940–945 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.1994
Y. Zhou, X. Yu, H. Chen, S. Sjöberg, J. Roux, L. Zhang, A.-H. Ivoulsou, F. Bensaid, C.-L. Liu, J. Liu, J. Tordjman, K. Clement, C.-H. Lee, G.S. Hotamisligil, P. Libby, G.-P. Shi, Leptin deficiency shifts mast cells toward anti-inflammatory actions and protects mice from obesity and diabetes by polarizing M2 macrophages. Cell Metab. 22, 1045–1058 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.09.013
J. Wang, G.-P. Shi, Mast cell stabilization: novel medication for obesity and diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 27, 919–924 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.1272
D.A. Gutierrez, S. Muralidhar, T.B. Feyerabend, S. Herzig, H.-R. Rodewald, Hematopoietic kit deficiency, rather than lack of mast cells, protects mice from obesity and insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 21, 678–691 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.04.013
S. Nishimura, I. Manabe, M. Nagasaki, K. Eto, H. Yamashita, M. Ohsugi, M. Otsu, K. Hara, K. Ueki, S. Sugiura, K. Yoshimura, T. Kadowaki, R. Nagai, CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat. Med. 15, 914–920 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.1964
C. Duffaut, J. Galitzky, M. Lafontan, A. Bouloumié, Unexpected trafficking of immune cells within the adipose tissue during the onset of obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 384, 482–485 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.05.002
U. Kintscher, M. Hartge, K. Hess, A. Foryst-Ludwig, M. Clemenz, M. Wabitsch, P. Fischer-Posovszky, T.F.E. Barth, D. Dragun, T. Skurk, H. Hauner, M. Blüher, T. Unger, A.-M. Wolf, U. Knippschild, V. Hombach, N. Marx, T-lymphocyte infiltration in visceral adipose tissue: a primary event in adipose tissue inflammation and the development of obesity-mediated insulin resistance. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28, 1304–1310 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.165100
K.J. Strissel, J. DeFuria, M.E. Shaul, G. Bennett, A.S. Greenberg, M.S. Obin, T-cell recruitment and Th1 polarization in adipose tissue during diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice. Obesity (Silver Spring) 18, 1918–1925 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2010.1
M. Moysidou, S. Karaliota, E. Kodela, M. Salagianni, Y. Koutmani, A. Katsouda, K. Kodella, P. Tsakanikas, S. Ourailidou, E. Andreakos, N. Kostomitsopoulos, D. Skokos, A. Chatzigeorgiou, K.-J. Chung, S. Bornstein, M.W. Sleeman, T. Chavakis, K.P. Karalis, CD8+ T cells in beige adipogenesis and energy homeostasis. JCI Insight 3, e95456 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.95456
H. Yang, Y.-H. Youm, B. Vandanmagsar, A. Ravussin, J.M. Gimble, F. Greenway, J.M. Stephens, R.L. Mynatt, V.D. Dixit, Obesity increases the production of proinflammatory mediators from adipose tissue T cells and compromises TCR repertoire diversity: implications for systemic inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Immunol. 185, 1836–1845 (2010). https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1000021
W.J. McDonnell, J.R. Koethe, S.A. Mallal, M.A. Pilkinton, A. Kirabo, M.K. Ameka, M.A. Cottam, A.H. Hasty, A.J. Kennedy, High CD8 T-cell receptor clonality and altered CDR3 properties are associated with elevated isolevuglandins in adipose tissue during diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 67, 2361–2376 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2337/db18-0040
S. Tsai, X. Clemente-Casares, X.S. Revelo, S. Winer, D.A. Winer, Are obesity-related insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes autoimmune diseases. Diabetes 64, 1886–1897 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1488
F.C. McGillicuddy, E.H. Chiquoine, C.C. Hinkle, R.J. Kim, R. Shah, H.M. Roche, E.M. Smyth, M.P. Reilly, Interferon gamma attenuates insulin signaling, lipid storage, and differentiation in human adipocytes via activation of the JAK/STAT pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 31936–31944 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.061655
J. Park, J.Y. Huh, J. Oh, J.I. Kim, S.M. Han, K.C. Shin, Y.G. Jeon, S.S. Choe, J. Park, J.B. Kim, Activation of invariant natural killer T cells stimulates adipose tissue remodeling via adipocyte death and birth in obesity. Genes Dev. 33, 1657–1672 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.329557.119
K. Ohmura, N. Ishimori, Y. Ohmura, S. Tokuhara, A. Nozawa, S. Horii, Y. Andoh, S. Fujii, K. Iwabuchi, K. Onoé, H. Tsutsui, Natural killer T cells are involved in adipose tissues inflammation and glucose intolerance in diet-induced obese mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 30, 193–199 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.198614
J.Y. Huh, Y.J. Park, J.B. Kim, Adipocyte CD1d determines adipose inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. Adipocyte 7, 129–136 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/21623945.2018.1440928
J.Y. Huh, J. Park, J.I. Kim, Y.J. Park, Y.K. Lee, J.B. Kim, Deletion of CD1d in adipocytes aggravates adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. Diabetes 66, 835–847 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2337/db16-1122
P. Mehta, A.M. Nuotio-Antar, C.W. Smith, γδ T cells promote inflammation and insulin resistance during high fat diet-induced obesity in mice. J. Leukoc. Biol. 97, 121–134 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.3A0414-211RR
J.M. Olefsky, C.K. Glass, Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 72, 219–246 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135846
M.S.H. Akash, K. Rehman, A. Liaqat, Tumor necrosis factor-alpha: role in development of insulin resistance and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Cell. Biochem. 119, 105–110 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26174
D.A. Winer, S. Winer, L. Shen, P.P. Wadia, J. Yantha, G. Paltser, H. Tsui, P. Wu, M.G. Davidson, M.N. Alonso, H.X. Leong, A. Glassford, M. Caimol, J.A. Kenkel, T.F. Tedder, T. McLaughlin, D.B. Miklos, H.-M. Dosch, E.G. Engleman, B cells promote insulin resistance through modulation of T cells and production of pathogenic IgG antibodies. Nat. Med. 17, 610–617 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2353
A. Fleischman, S.E. Shoelson, R. Bernier, A.B. Goldfine, Salsalate improves glycemia and inflammatory parameters in obese young adults. Diabetes Care 31, 289–294 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc07-1338
A.B. Goldfine, R. Silver, W. Aldhahi, D. Cai, E. Tatro, J. Lee, S.E. Shoelson, Use of salsalate to target inflammation in the treatment of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Clin. Transl. Sci. 1, 36–43 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-8062.2008.00026.x
A.B. Goldfine, V. Fonseca, K.A. Jablonski, L. Pyle, M.A. Staten, S.E. Shoelson,TINSAL-T2D (Targeting Inflammation Using Salsalate in Type 2 Diabetes) Study Team, The effects of salsalate on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 152, 346–357 (2010). https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-152-6-201003160-00004
E. Faghihimani, A. Aminorroaya, H. Rezvanian, P. Adibi, F. Ismail-Beigi, M. Amini, Reduction of insulin resistance and plasma glucose level by salsalate treatment in persons with prediabetes. Endocr. Pract. 18, 826–833 (2012). https://doi.org/10.4158/EP12064.OR
A.B. Goldfine, P.R. Conlin, F. Halperin, J. Koska, P. Permana, D. Schwenke, S.E. Shoelson, P.D. Reaven, A randomised trial of salsalate for insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk factors in persons with abnormal glucose tolerance. Diabetologia 56, 714–723 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-012-2819-3
S. Koppaka, S. Kehlenbrink, M. Carey, W. Li, E. Sanchez, D.-E. Lee, H. Lee, J. Chen, E. Carrasco, P. Kishore, K. Zhang, M. Hawkins, Reduced adipose tissue macrophage content is associated with improved insulin sensitivity in thiazolidinedione-treated diabetic humans. Diabetes 62, 1843–1854 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2337/db12-0868
D.H. Solomon, E. Massarotti, R. Garg, J. Liu, C. Canning, S. Schneeweiss, Association between disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and diabetes risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. JAMA 305, 2525–2531 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2011.878
F. Ofei, S. Hurel, J. Newkirk, M. Sopwith, R. Taylor, Effects of an engineered human anti-TNF-alpha antibody (CDP571) on insulin sensitivity and glycemic control in patients with NIDDM. Diabetes 45, 881–885 (1996). https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.45.7.881
J.H. Huh, H.M. Kim, E.S. Lee, M.H. Kwon, B.R. Lee, H.-J. Ko, C.H. Chung, Dual CCR2/5 antagonist attenuates obesity-induced insulin resistance by regulating macrophage recruitment and M1/M2 status. Obesity (Silver Spring) 26, 378–386 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.22103
N.A. Di Prospero, E. Artis, P. Andrade-Gordon, D.L. Johnson, N. Vaccaro, L. Xi, P. Rothenberg, CCR2 antagonism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 16, 1055–1064 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.12309
S.K. Biswas, Metabolic reprogramming of immune cells in cancer progression. Immunity 43, 435–449 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2015.09.001
C. Jing, T. Castro-Dopico, N. Richoz, Z.K. Tuong, J.R. Ferdinand, L.S.C. Lok, K.W. Loudon, G.D. Banham, R.J. Mathews, Z. Cader, S. Fitzpatrick, K.R. Bashant, M.J. Kaplan, A. Kaser, R.S. Johnson, M.P. Murphy, R.M. Siegel, M.R. Clatworthy, Macrophage metabolic reprogramming presents a therapeutic target in lupus nephritis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117, 15160–15171 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2000943117
P. García-González, G. Ubilla-Olguín, D. Catalán, K. Schinnerling, J.C. Aguillón, Tolerogenic dendritic cells for reprogramming of lymphocyte responses in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 15, 1071–1080 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2016.07.032
A.D. Hildreth, F. Ma, Y.Y. Wong, R. Sun, M. Pellegrini, T.E. O’Sullivan, Single-cell sequencing of human white adipose tissue identifies new cell states in health and obesity. Nat. Immunol. 22, 639–653 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-021-00922-4
I. Magalhaes, K. Pingris, C. Poitou, S. Bessoles, N. Venteclef, B. Kiaf, L. Beaudoin, J. Da Silva, O. Allatif, J. Rossjohn, L. Kjer-Nielsen, J. McCluskey, S. Ledoux, L. Genser, A. Torcivia, C. Soudais, O. Lantz, C. Boitard, J. Aron-Wisnewsky, E. Larger, K. Clément, A. Lehuen, Mucosal-associated invariant T cell alterations in obese and type 2 diabetic patients. J. Clin. Invest. 125, 1752–1762 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI78941
C.E. Macdougall, E.G. Wood, J. Loschko, V. Scagliotti, F.C. Cassidy, M.E. Robinson, N. Feldhahn, L. Castellano, M.-B. Voisin, F. Marelli-Berg, C. Gaston-Massuet, M. Charalambous, M.P. Longhi, Visceral adipose tissue immune homeostasis is regulated by the crosstalk between adipocytes and dendritic cell subsets. Cell Metab. 27, 588–601.e4 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.02.007
Funding
This work was supported by the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS) (2022-I2M-2-002); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.82270913); the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No.7222137); the National Key Clinical Specialty Capacity Improvement Project; the National Key Program of Clinical Science (WBYZ2011-873) and the PUMCH Foundation (pumch-2013-020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.J. performed the literature search and data analysis, and drafted the primary manuscript. F.G. designed and supervised the project, and critically revised the primary manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Gong, F. Immune cells in adipose tissue microenvironment under physiological and obese conditions. Endocrine 83, 10–25 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-023-03521-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-023-03521-5