Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the relationship between estimated glucose disposal rate (eGDR) and bone turnover markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Materials and methods
This is a cross-sectional study, which recruited 549 patients with T2DM. The eGDRs of patients were calculated based on the presence of hypertension, glycated hemoglobin, and body mass index. All patients were divided into high-eGDR group and low-eGDR group using the median of eGDR as the boundary. The patients were further divided into two subgroups: males and postmenopausal females.
Results
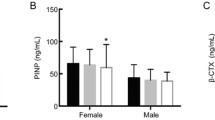
The lower the eGDR, the more severe was insulin resistance. The levels of osteocalcin (OC), type I collagen carboxyl-terminal peptide (β-CTX), and type I procollagen amino-terminal peptide (PINP) were significantly lower in the low-eGDR group than those in the high-eGDR group. The eGDR was positively correlated with OC, β-CTX, and PINP in all patients, and in the male subgroups. In the postmenopausal female subgroup, there was no correlation between eGDR and OC, β-CTX, or PINP. In addition, this positive correlation remained after adjusting for other factors in multilinear regression analysis.
Conclusion
Our study was the first to demonstrate that eGDR is positively correlated with bone turnover markers in patients with T2DM. This correlation was observed among the male patients with T2DM but not among postmenopausal female patients with T2DM.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Alaei-Shahmiri, M.E. Khamseh, K. Manhoei, H. Yadegari, H. Kazemi et al. The optimal vitamin D cut-off value associated with hyperglycemia in an Iranian population. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 19, 5–12 (2020)
H. Chang-Quan, D. Bi-Rong, H. Ping, L. Zhen-Chan, Insufficient renal 1-alpha hydroxylase and bone homeostasis in aged rats with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 26, 561–568 (2008)
R. Nishtala, N. Kietsiriroje, Estimated glucose disposal rate demographics and clinical characteristics of young adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional pilot study. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 17, 1479164120952321 (2020)
K.V. Williams, J.R. Erbey, D. Becker, S. Arslanian, T.J. Orchard, Can clinical factors estimate insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes? Diabetes 49, 626–632 (2000)
L.L. O’Mahoney, N. Kietsiriroje, Estimated glucose disposal rate as a candidate biomarker for thrombotic biomarkers in T1D: a pooled analysis. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 44, 2417–2426 (2021)
J.J. Chillarón, A. Goday, J.A. Flores-Le-Roux, D. Benaiges, M.J. Carrera et al. Estimated glucose disposal rate in assessment of the metabolic syndrome and microvascular complications in patients with type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 94, 3530–3534 (2009)
A. Zabala, V. Darsalia, M. Lind, A.M. Svensson, S. Franzén et al. Estimated glucose disposal rate and risk of stroke and mortality in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study. Cardiovascular Diabetol. 20, 202 (2021)
T. Nyström, M.J. Holzmann, B. Eliasson, A.M. Svensson, J. Kuhl et al. Estimated glucose disposal rate and long-term survival in type 2 diabetes after coronary artery bypass grafting. Heart Vessels 32, 269–278 (2017)
P. Vestergaard, Discrepancies in bone mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes–a meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 18, 427–444 (2007)
K. Hygum, J. Starup-Linde, T. Harsløf, P. Vestergaard, B.L. Langdahl, MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: diabetes mellitus, a state of low bone turnover – a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 176, R137–r157 (2017)
J.Y. Lee, N.K. Lee, Up-regulation of cyclinD1 and Bcl2A1 by insulin is involved in osteoclast proliferation. Life Sci. 114, 57–61 (2014)
K. Fulzele, R.C. Riddle, D.J. DiGirolamo, X. Cao, C. Wan et al. Insulin receptor signaling in osteoblasts regulates postnatal bone acquisition and body composition. Cell 142, 309–319 (2010)
K.T. Tonks, C.P. White, J.R. Center, D. Samocha-Bonet, J.R. Greenfield, Bone turnover is suppressed in insulin resistance, independent of adiposity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 102, 1112–1121 (2017)
M. Tencerova, M. Okla, M. Kassem, Insulin signaling in bone marrow adipocytes. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 17, 446–454 (2019)
V.V. Shanbhogue, J.S. Finkelstein, M.L. Bouxsein, E.W. Yu, Association between insulin resistance and bone structure in nondiabetic postmenopausal women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 101, 3114–3122 (2016)
E.M. Dennison, H.E. Syddall, A. Aihie Sayer, S. Craighead, D.I. Phillips et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with increased axial bone density in men and women from the Hertfordshire Cohort Study: evidence for an indirect effect of insulin resistance? Diabetologia 47, 1963–1968 (2004)
S. Huang, M. Kaw, M.T. Harris, N. Ebraheim, M.F. McInerney et al. Decreased osteoclastogenesis and high bone mass in mice with impaired insulin clearance due to liver-specific inactivation to CEACAM1. Bone 46, 1138–1145 (2010)
S.K. Kunutsor, T.A. Apekey, J.A. Laukkanen, Association of serum total osteocalcin with type 2 diabetes and intermediate metabolic phenotypes: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational evidence. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 30, 599–614 (2015)
S. Yano, T. Nabika, A. Nagai, T. Hamano, M. Yamasaki et al. Interrelationship between glucose metabolism and undercarboxylated osteocalcin: a cross-sectional study in a community-dwelling population. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 24, 489–495 (2015)
S.W. Lee, H.H. Jo, M.R. Kim, J.H. Kim, Y.O. You, Association between osteocalcin and metabolic syndrome in postmenopausal women. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 292, 673–681 (2015)
W.W. Hu, Y.H. Ke, J.W. He, W.Z. Fu, Y.J. Liu et al. Serum osteocalcin levels are inversely associated with plasma glucose and body mass index in healthy Chinese women. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 35, 1521–1526 (2014)
G.S. Kim, Y. Jekal, H.S. Kim, J.A. Im, J.Y. Park et al. Reduced serum total osteocalcin is associated with central obesity in Korean children. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 8, e201–e298 (2014)
K. Mori, M. Emoto, K. Motoyama, E. Lee, S. Yamada et al. Undercarboxylated osteocalcin does not correlate with insulin resistance as assessed by euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp technique in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 4, 53 (2012)
X.Y. Ma, F.Q. Chen, H. Hong, X.J. Lv, M. Dong et al. The relationship between serum osteocalcin concentration and glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus – the role of osteocalcin in energy metabolism. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 66, 110–116 (2015)
K.M. Bador, L.D. Wee, S.A. Halim, M.F. Fadi, P. Santhiran et al. Serum osteocalcin in subjects with metabolic syndrome and central obesity. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 10, S42–S45 (2016)
Q. Wang, B. Zhang, Y. Xu, H. Xu, N. Zhang, The relationship between serum osteocalcin concentration and glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 842598 (2013)
H. Guo, C. Wang, B. Jiang, S. Ge, J. Cai et al. Association of insulin resistance and β-cell function with bone turnover biomarkers in dysglycemia patients. Front. Endocrinol. 12, 554604 (2021)
Z. Feldbrin, M. Shargorodsky, Bone remodelling markers in hypertensive patients with and without diabetes mellitus: link between bone and glucose metabolism. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 31, 752–757 (2015)
G.M. Reaven, Pathophysiology of insulin resistance in human disease. Physiological Rev. 75, 473–486 (1995)
A. Fraser, R. Harris, N. Sattar, S. Ebrahim, G. Davey Smith et al. Alanine aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyltransferase, and incident diabetes: the British Women’s Heart and Health Study and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 32, 741–750 (2009)
A.J. Hanley, L.E. Wagenknecht, A. Festa, R.B. D’Agostino Jr., S.M. Haffner, Alanine aminotransferase and directly measured insulin sensitivity in a multiethnic cohort: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. Diabetes Care 30, 1819–1827 (2007)
L. Aguirre, N. Napoli, D. Waters, C. Qualls, D.T. Villareal et al. Increasing adiposity is associated with higher adipokine levels and lower bone mineral density in obese older adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 99, 3290–3297 (2014)
F.L. Bilotta, B. Arcidiacono, S. Messineo, M. Greco, E. Chiefari et al. Insulin and osteocalcin: further evidence for a mutual cross-talk. Endocrine 59, 622–632 (2018)
L. Wang, T. Li, J. Liu, X. Wu, H. Wang et al. Association between glycosylated hemoglobin A1c and bone biochemical markers in type 2 diabetic postmenopausal women: a cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 19, 31 (2019)
W. Wang, X. Zhang, J. Zheng, J. Yang, High glucose stimulates adipogenic and inhibits osteogenic differentiation in MG-63 cells through cAMP/protein kinase A/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 338, 115–122 (2010)
P. Lakatos, B. Szili, B. Bakos, I. Takacs, Z. Putz et al. Thyroid hormones, glucocorticoids, insulin, and bone. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 262, 93–120 (2020)
M. Alikhani, Z. Alikhani, C. Boyd, C.M. MacLellan, M. Raptis et al. Advanced glycation end products stimulate osteoblast apoptosis via the MAP kinase and cytosolic apoptotic pathways. Bone 40, 345–353 (2007)
L.F. Liu, W.J. Shen, Z.H. Zhang, L.J. Wang, F.B. Kraemer, Adipocytes decrease Runx2 expression in osteoblastic cells: roles of PPARγ and adiponectin. J. Cell. Physiol. 225, 837–845 (2010)
P. Vestergaard, Diabetes and osteoporosis – cause for concern? Front. Endocrinol. 5, 53 (2014)
C. Ma, K.T. Tonks, J.R. Center, D. Samocha-Bonet, J.R. Greenfield, Complex interplay among adiposity, insulin resistance and bone health. Clin. Obes. 8, 131–139 (2018)
S. Rathinavelu, C. Guidry-Elizondo, J. Banu, Molecular modulation of osteoblasts and osteoclasts in type 2. Diabetes 2018, 6354787 (2018)
K. Baek, H.R. Hwang, H.J. Park, A. Kwon, A.S. Qadir et al. TNF-α upregulates sclerostin expression in obese mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Cell. Physiol. 229, 640–650 (2014)
V. Boschert, M. van Dinther, S. Weidauer, K. van Pee, E.M. Muth et al. Mutational analysis of sclerostin shows importance of the flexible loop and the cystine-knot for Wnt-signaling inhibition. PloS One 8, e81710 (2013)
Z. Yao, L. Xing, C. Qin, E.M. Schwarz, B.F. Boyce, Osteoclast precursor interaction with bone matrix induces osteoclast formation directly by an interleukin-1-mediated autocrine mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 9917–9924 (2008)
C. Conte, S. Epstein, N. Napoli, Insulin resistance and bone: a biological partnership. Acta Diabetol. 55, 305–314 (2018)
Y. Bao, X. Ma, R. Yang, F. Wang, Y. Hao et al. Inverse relationship between serum osteocalcin levels and visceral fat area in Chinese men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 98, 345–351 (2013)
S. Muruganandan, C.J. Sinal, The impact of bone marrow adipocytes on osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. IUBMB Life 66, 147–155 (2014)
X.G. Han, D.W. Wang, Z.G. Bi, F. Gao, Regulatory effect of estrogen receptor-α-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway on osteoblast proliferation. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 30, 381–387 (2016)
J.A. Im, B.P. Yu, J.Y. Jeon, S.H. Kim, Relationship between osteocalcin and glucose metabolism in postmenopausal women. Clin. Chim. Acta 396, 66–69 (2008)
Y.C. Hwang, I.K. Jeong, K.J. Ahn, H.Y. Chung, Circulating osteocalcin level is associated with improved glucose tolerance, insulin secretion and sensitivity independent of the plasma adiponectin level. Osteoporos. Int. 23, 1337–1342 (2012)
P.D. Sarkar, A.B. Choudhury, Relationships between serum osteocalcin levels versus blood glucose, insulin resistance and markers of systemic inflammation in central Indian type 2 diabetic patients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 17, 1631–1635 (2013)
M. Zhou, X. Ma, H. Li, X. Pan, J. Tang et al. Serum osteocalcin concentrations in relation to glucose and lipid metabolism in Chinese individuals. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 161, 723–729 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Z.L., X.P., Y.J., X.Z., and C.D. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Z.L. Writing (review and editing) was performed by S.C. and C.Q.; all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent to participate
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Hebei General Hospital (Date May 8, 2020/No. 202027).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Qi, C., Pan, X. et al. The relationship between estimated glucose disposal rate and bone turnover markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 77, 242–251 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-022-03090-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-022-03090-z