Abstract
Purpose
Cushing’s syndrome (CS) is a rare and severe disease caused by sustained hypercortisolism. The clinical manifestations of CS can be atypical in the elderly, and the diagnosis in these patients is often missed. Infectious Purpura Fulminans (PF) is a life-threating, thrombotic form of disseminated intravascular coagulation with high mortality. To our knowledge, PF occurring in a patient with CS has not been reported previously.
Methods
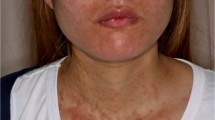
We described an 84-year-old female presented with severe infection, but normal temperature. She suffered from a variety of diseases especially personality change. Physical examination revealed thin skin, general edema, and multiple scattered ecchymosis. Combined with obviously elevated serum cortisol (36.85 ug/dl) and adenoma revealed by adrenal CT scanning, endogenous CS was diagnosed. During hospitalization, the patient developed serious subcutaneous hemorrhage on the right thigh and back. The skin biopsy showed multiple small vessel thrombosis suggesting that the patient developed the rare complication of CS, Purpura Fulminans (PF).
Results
Chronic hypercortisolism can cause immune suppression, low-grade inflammation, endothelial damage, and a hypercoagulable state, which together increased susceptibility of PF. Fluid resuscitation, antibiotics, infusion of blood product, and debridement were effective treatment measures when CS complicated with infectious PF.
Conclusion
Severe subcutaneous hemorrhage due to PF could occur in the patients of CS, especially in the elderly. Clinicians should be alert to the diagnosis of CS in older adults with cognitive decline and personality change.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Newell-Price, X. Bertagna, A.B. Grossman, L.K. Nieman, Cushing’s syndrome. Lancet 367, 1605–1617 (2006)
L.T. Braun, M. Reincke, What is the role of medical therapy in adrenal-dependent Cushing’s syndrome? Best. Pract. Res Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 34, 101376 (2020)
P. Javanmard, D. Duan, E.B. Geer, Mortality in patients with endogenous Cushing’s syndrome. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 47, 313–333 (2018)
V. Hasenmajer, E. Sbardella, F. Sciarra, M. Minnetti, A.M. Isidori, M.A. Venneri, The immune system in Cushing’s syndrome. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 31, 655–669 (2020)
M.E. Colling, P.K. Bendapudi, Purpura Fulminans: mechanism and management of dysregulated hemostasis. Transfus. Med. Rev. 32, 69–76 (2018)
A. Lacroix, R.A. Feelders, C.A. Stratakis, L.K. Nieman, Cushing’s syndrome. Lancet 386, 913–927 (2015)
L.K. Nieman, B.M. Biller, J.W. Findling, J. Newell-Price, M.O. Savage, P.M. Stewart et al. The diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 1526–1540 (2008)
F. Ferraù, M. Korbonits. (eds.) Metabolic syndrome consequent to endocrine disorders. Front. Horm. Res. 49, 85–103 (2018)
C.A. Stratakis, Skin manifestations of Cushing’s syndrome. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 17, 283–286 (2016)
T. Kugai, H. Nakagawa, Evolution of Purpura Fulminans. N. Engl. J. Med. 376, 2182 (2017)
Funding
This work was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81870470) and Discipline Promotion Plan of Xijing Hospital (no. XJZT18MDT11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.L. and G.C.: collecting data, writing-reviewing, and editing. F.J.: participate in disease discussions. X.N.: supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We here assure that whole or partial data of the paper has not been submitted for the dual publication elsewhere, authors of the paper have no competing interests, and all the authors have read and approved the paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Cao, G., Jin, F. et al. Rare complication of cushing’s syndrome in the elderly: a case report. Endocrine 74, 281–284 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02844-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02844-5