Abstract
Purpose
We elucidate the effect of Growth differentiation factor-15(GDF-15)/adiponectin ratio in improving the assessment value for odds of type 2 diabetes.
Methods
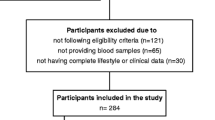
Cross-sectional design. A total of 405 participants (135 patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, 135 age- and sex-matched participants with prediabetes, and 135 healthy controls) were collected from Guangzhou and Dongguan, China. The serum GDF-15 and adiponectin levels were measured by ELISA and latex-enhanced immunoturbidimetry. Logistic regression analysis and restricted cubic splines were used to evaluate the associations between diabetes and the indicators.
Results
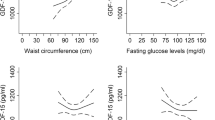
The low level of adiponectin and high GDF-15/adiponectin ratio were significantly associated with increased odds of type 2 diabetes, but not for GDF-15. Three clusters were identified based on the K-means clustering analysis. Compared to the lowest quartiles of adiponectin, the OR and 95% CI of the highest adiponectin with type 2 diabetes was 0.24 (0.07–0.74, p trend = 0.004) after adjusting for sex, age, BMI, and DBP only in cluster 1. After adjusting for confounding factors, subjects with the highest GDF-15/adiponectin ratio quartiles had 3.9 times (OR = 3.85, 95% CI = 0.76–24.25) and 3.8 times (OR = 3.80, 95% CI = 1.02–14.68) higher odds of type 2 diabetes in cluster 2 and cluster 3, respectively. The association between the GDF-15/adiponectin ratio and type 2 diabetes was attenuated, but still remarkable (OR = 3.18, 95% CI = 1.11–10.18), in cluster 1.
Conclusions
Higher GDF-15/adiponectin ratio is independently associated with increased odds of type 2 diabetes for all study populations, suggesting that the GDF-15/adiponectin ratio may be a better indicator of type 2 diabetes.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article or in the data repositories listed in References.
Abbreviations
- FPG:
-
Fasting plasma glucose
- GDF-15:
-
Growth differentiation factor-15
- HC:
-
Hip circumference
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triglycerides
- WC:
-
Waist circumference
References
P. Saeedi, I. Petersohn, P. Salpea, B. Malanda, S. Karuranga, N. Unwin, S. Colagiuri, L. Guariguata, A.A. Motala, K. Ogurtsova, J.E. Shaw, D. Bright, R. Williams; IDF Diabetes Atlas Committee, Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 157, 107843 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
K. Unsicker, B. Spittau, K. Krieglstein, The multiple facets of the TGF-beta family cytokine growth/differentiation factor-15/macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24(4), 373–384 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.05.003
L. Scheja, J. Heeren, The endocrine function of adipose tissues in health and cardiometabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 15(9), 507–524 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-019-0230-6
A.P. Coll, M. Chen, P. Taskar, D. Rimmington, S. Patel, J.A. Tadross, I. Cimino, M. Yang, P. Welsh, S. Virtue, D.A. Goldspink, E.L. Miedzybrodzka, A.R. Konopka, R.R. Esponda, J.T. Huang, Y.C.L. Tung, S. Rodriguez-Cuenca, R.A. Tomaz, H.P. Harding, A. Melvin, G.S.H. Yeo, D. Preiss, A. Vidal-Puig, L. Vallier, K.S. Nair, N.J. Wareham, D. Ron, F.M. Gribble, F. Reimann, N. Sattar, D.B. Savage, B.B. Allan, S. O’Rahilly, GDF15 mediates the effects of metformin on body weight and energy balance. Nature 578(7795), 444–448 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1911-y
S.L. Au Yeung, S. Luo, C.M. Schooling, The impact of GDF-15, a biomarker for metformin, on the risk of coronary artery disease, breast and colorectal cancer, and type 2 diabetes and metabolic traits: a Mendelian randomisation study. Diabetologia 62(9), 1638–1646 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-019-4913-2
A. Bidadkosh, S.P.H. Lambooy, H.J. Heerspink, M.J. Pena, R.H. Henning, H. Buikema, L.E. Deelman, Predictive properties of biomarkers GDF-15, NTproBNP, and hs-TnT for morbidity and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes with nephropathy. Diabetes Care 40(6), 784–792 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc16-2175
N. Pavo, R. Wurm, S. Neuhold, C. Adlbrecht, G. Vila, G. Strunk, M. Clodi, M. Resl, H. Brath, R. Prager, A. Luger, R. Pacher, M. Hulsmann, GDF-15 is associated with cancer incidence in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin. Chem. 62(12), 1612–1620 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2016.257212
M.Y. Shin, J.M. Kim, Y.E. Kang, M.K. Kim, K.H. Joung, J.H. Lee, K.S. Kim, H.J. Kim, B.J. Ku, M. Shong, Association between Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF15) and cardiovascular risk in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Korean Med. Sci. 31(9), 1413–1418 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.9.1413
M. Carstensen, C. Herder, E.J. Brunner, K. Strassburger, A.G. Tabak, M. Roden, D.R. Witte, Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 is increased in individuals before type 2 diabetes diagnosis but is not an independent predictor of type 2 diabetes: the Whitehall II study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 162(5), 913–917 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-09-1066
T. Kempf, A. Guba-Quint, J. Torgerson, M.C. Magnone, C. Haefliger, M. Bobadilla, K.C. Wollert, Growth differentiation factor 15 predicts future insulin resistance and impaired glucose control in obese nondiabetic individuals: results from the XENDOS trial. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 167(5), 671–678 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-12-0466
X. Bao, Y. Borne, I.F. Muhammad, J. Nilsson, L. Lind, O. Melander, K. Niu, M. Orho-Melander, G. Engstrom, Growth differentiation factor 15 is positively associated with incidence of diabetes mellitus: the Malmo Diet and Cancer-Cardiovascular Cohort. Diabetologia 62(1), 78–86 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-018-4751-7
H. Fang, R.L. Judd, Adiponectin regulation and function. Compr. Physiol. 8(3), 1031–1063 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c170046
S.G. Wannamethee, G.D. Lowe, A. Rumley, L. Cherry, P.H. Whincup, N. Sattar, Adipokines and risk of type 2 diabetes in older men. Diabetes Care 30(5), 1200–1205 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc06-2416
C. Herder, M. Peltonen, P.A. Svensson, M. Carstensen, P. Jacobson, M. Roden, L. Sjostrom, L. Carlsson, Adiponectin and bariatric surgery: associations with diabetes and cardiovascular disease in the Swedish Obese Subjects Study. Diabetes Care 37(5), 1401–1409 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc13-1362
S. Lindberg, J.S. Jensen, S.H. Pedersen, S. Galatius, J. Frystyk, A. Flyvbjerg, M. Bjerre, R. Mogelvang, Low adiponectin levels and increased risk of type 2 diabetes in patients with myocardial infarction. Diabetes Care 37(11), 3003–3008 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc14-0932
C. Herder, M. Carstensen, D.M. Ouwens, Anti-inflammatory cytokines and risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 15, 39–50 (2013).
C. Liu, X. Feng, Q. Li, Y. Wang, Q. Li, M. Hua, Adiponectin, TNF-alpha and inflammatory cytokines and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine 86, 100–109 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2016.06.028
A.E. Berezin, Diabetes mellitus related biomarker: The predictive role of growth-differentiation factor-15. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 10(Suppl 1), S154–S157 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2015.09.016
A.A. Ghadge, A.A. Khaire, A.A. Kuvalekar, Adiponectin: a potential therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 39, 151–158 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2018.01.004
J. Lu, Y. Zhang, X. Dong, J. Lu, C. Zhang, J. Liu, Q. Yu, H. Teng, Q. Yao, J. Yin, L. Qin, Association between MIC-1 and Type 2 diabetes: a combined analysis. Dis. Markers 2019, 7284691 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7284691
C. Huth, C. von Toerne, F. Schederecker, T. de Las Heras Gala, C. Herder, F. Kronenberg, C. Meisinger, W. Rathmann, W. Koenig, M. Waldenberger, M. Roden, A. Peters, S.M. Hauck, B. Thorand, Protein markers and risk of type 2 diabetes and prediabetes: a targeted proteomics approach in the KORA F4/FF4 study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 34(4), 409–422 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-018-0475-8
R.B. Goldberg, G.A. Bray, S.M. Marcovina, K.J. Mather, T.J. Orchard, L. Perreault, M. Temprosa, Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group, Non-traditional biomarkers and incident diabetes in the Diabetes Prevention Program: comparative effects of lifestyle and metformin interventions. Diabetologia 62(1), 58–69 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-018-4748-2
Z. Liu, S. Liang, S. Que, L. Zhou, S. Zheng, A. Mardinoglu, Meta-analysis of adiponectin as a biomarker for the detection of metabolic syndrome. Front. Physiol. 9, 1238 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01238
J.R. Kizer, A.M. Arnold, D. Benkeser, J.H. Ix, L. Djousse, S.J. Zieman, J.I. Barzilay, R.P. Tracy, C.S. Mantzoros, D.S. Siscovick, K.J. Mukamal, Total and high-molecular-weight adiponectin and risk of incident diabetes in older people. Diabetes Care 35(2), 415–423 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-1519
M.-F. Hivert, L.M. Sullivan, P. Shrader, C.S. Fox, D.M. Nathan, R.B. D'Agostino Sr, P.W.F. Wilson, B. Kowall, C. Herder, C. Meisinger, B. Thorand, W. Rathmann, J.B. Meigs, Insulin resistance influences the association of adiponectin levels with diabetes incidence in two population-based cohorts: the Cooperative Health Research in the Region of Augsburg (KORA) S4/F4 study and the Framingham Offspring Study. Diabetologia 54, 1019–1024 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-011-2067-y
Q. Ding, T. Mracek, P. Gonzalez-Muniesa, K. Kos, J. Wilding, P. Trayhurn, C. Bing, Identification of macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 in adipose tissue and its secretion as an adipokine by human adipocytes. Endocrinology 150(4), 1688–1696 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2008-0952
V.W. Tsai, H.P. Zhang, R. Manandhar, K.K.M. Lee-Ng, H. Lebhar, C.P. Marquis, Y. Husaini, A. Sainsbury, D.A. Brown, S.N. Breit, Treatment with the TGF-b superfamily cytokine MIC-1/GDF15 reduces the adiposity and corrects the metabolic dysfunction of mice with diet-induced obesity. Int J. Obes. 42(3), 561–571 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2017.258
C.M. Sena, A. Pereira, R. Fernandes, L. Letra, R.M. Seica, Adiponectin improves endothelial function in mesenteric arteries of rats fed a high-fat diet: role of perivascular adipose tissue. Br. J. Pharm. 174(20), 3514–3526 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13756
C.M. Kusminski, A.L. Ghaben, T.S. Morley, R.J. Samms, A.C. Adams, Y. An, J.A. Johnson, N. Joffin, T. Onodera, C. Crewe, W.L. Holland, R. Gordillo, P.E. Scherer, A novel model of diabetic complications: adipocyte mitochondrial dysfunction triggers massive beta-cell hyperplasia. Diabetes 69(3), 313–330 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2337/db19-0327
L. Qiao, J.S. Wattez, S. Lee, A. Nguyen, J. Schaack, W.W. Hay Jr, J. Shao, Adiponectin deficiency impairs maternal metabolic adaptation to pregnancy in mice. Diabetes 66(5), 1126–1135 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2337/db16-1096
H.K. Chung, D. Ryu, K.S. Kim, J.Y. Chang, Y.K. Kim, H.S. Yi, S.G. Kang, M.J. Choi, S.E. Lee, S.B. Jung, M.J. Ryu, S.J. Kim, G.R. Kweon, H. Kim, J.H. Hwang, C.H. Lee, S.J. Lee, C.E. Wall, M. Downes, R.M. Evans, J. Auwerx, M. Shong, Growth differentiation factor 15 is a myomitokine governing systemic energy homeostasis. J. Cell Biol. 216(1), 149–165 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201607110
I. Dostalova, T. Roubicek, M. Bartlova, M. Mraz, Z. Lacinova, D. Haluzikova, P. Kavalkova, M. Matoulek, M. Kasalicky, M. Haluzik, Increased serum concentrations of macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: the influence of very low calorie diet. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 161(3), 397–404 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-09-0417
J.H. Hong, H.K. Chung, H.Y. Park, K.H. Joung, J.H. Lee, J.G. Jung, K.S. Kim, H.J. Kim, B.J. Ku, M. Shong, GDF15 is a novel biomarker for impaired fasting glucose. Diabetes Metab. J. 38(6), 472–479 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.6.472
C.L. Cheung, K.C.B. Tan, P.C.M. Au, G.H.Y. Li, B.M.Y. Cheung, Evaluation of GDF15 as a therapeutic target of cardiometabolic diseases in human: a Mendelian randomization study. EBioMedicine 41, 85–90 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.02.021
D. Aguilar, M.L. Fernandez, Hypercholesterolemia induces adipose dysfunction in conditions of obesity and nonobesity. Adv. Nutr. 5(5), 497–502 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3945/an.114.005934
S.J. Gasparini, M.M. Swarbrick, S. Kim, L.J. Thai, H. Henneicke, L.L. Cavanagh, J. Tu, M.C. Weber, H. Zhou, M.J. Seibel, Androgens sensitise mice to glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance and fat accumulation. Diabetologia 62(8), 1463–1477 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-019-4887-0
L. Frederiksen, K. Hojlund, D.M. Hougaard, T.H. Mosbech, R. Larsen, A. Flyvbjerg, J. Frystyk, K. Brixen, M. Andersen, Testosterone therapy decreases subcutaneous fat and adiponectin in aging men. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 166(3), 469–476 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-11-0565
M.R. Bootcov, A.R. Bauskin, S.M. Valenzuela, A.G. Moore, M. Bansal, X.Y. He, H.P. Zhang, M. Donnellan, S. Mahler, K. Pryor, B.J. Walsh, R.C. Nicholson, W.D. Fairlie, S.B. Por, J.M. Robbins, S.N. Breit, MIC-1, a novel macrophage inhibitory cytokine, is a divergent member of the TGF-beta superfamily. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94(21), 11514–11519 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.21.11514
H. Yanai, H. Yoshida, Beneficial effects of adiponectin on glucose and lipid metabolism and atherosclerotic progression: mechanisms and perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20(5) (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051190
A. Kohlgruber, L. Lynch, Adipose tissue inflammation in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 15(11), 92 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-015-0670-x
F. Prattichizzo, V. De Nigris, R. Spiga, E. Mancuso, L. La Sala, R. Antonicelli, R. Testa, A.D. Procopio, F. Olivieri, A. Ceriello, Inflammageing and metaflammation: the yin and yang of type 2 diabetes. Ageing Res. Rev. 41, 1–17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2017.10.003
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the following sources: (1) National Key Research and Development Project of China (grants numbers 2016YFC0901204); (2) Science and Technique Development Special Fund Project of Guangdong Province (Social Development Field) (grants numbers 2017B020209002); (3) Provincial Science and Technology Applied Science and Technology R&D Special Fund Project (grants numbers 2016B020238001). The linguistic editing and proofreading have been performed by AJESCI during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: M.R., X.Z., and L.Y.; acquired the clinical data: H.L., Q.C., K.S., C.C., M.X., and Y.L.; performed the experiments: W.X., X.W., H.L., F.L., X.Z.; analyzed the data: L.Y., W.X., and X.W.; wrote the manuscript: W.X. and X.W. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and approved to submit the manuscript to Endocrine in its current form.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Xuan, W., You, L. et al. Associations of GDF-15 and GDF-15/adiponectin ratio with odds of type 2 diabetes in the Chinese population. Endocrine 72, 423–436 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02632-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02632-1