Abstract
Background
Mutations in DUOX2 are the frequent cause of congenital hypothyroidism (CH), a common neonatal metabolic disorder characterized by great phenotypic variability. CH can be traditionally subclassified into two subtypes: thyroid dysgenesis (TD) and thyroid dyshormonogenesis. The objectives of this study were to analyze the genetic data of two familial CH cases, to elucidate the pathogenesis from the perspective of genetics and to review and summarize the previous findings.
Methods
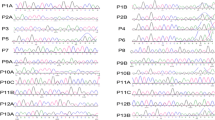
Targeted regions sequencing (TRS) technology covering all exons and intron-exon boundaries of 35 known and potential CH-related candidate target genes in combination with Sanger sequencing were performed to identify the likely pathogenic mutations of the six patients with familial CH.
Results
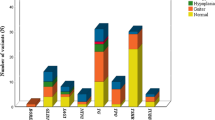
In family 1, two DUOX2 missense mutations, namely, c.1060C>T/p.R354W in exon 10 and c.3200C>T/p.S1067L in exon 25, were found. Patient 1 (P1), P2 and P3 were transient CH (TCH) patients with eutopic thyroid glands of normal size and function. In family 2, only the mutation c.3200C>T/p.S1067L was identified. P4, P5, and P6 were diagnosed with permanent CH (PCH), which requires lifelong levothyroxine (L-T4) treatment. Furthermore, both P4 and P5 harbored properly located thyroid glands, whereas P6 had a mildly reduced gland. P1, P3, P6, and other family members carrying monoallelic or biallelic DUOX2 mutations showed no obvious abnormal clinical symptoms or signs, while P2, P4, and P5 showed umbilical hernias.
Conclusions
The present study suggests that the phenotypic features resulting from DUOX2 mutations vary greatly. The p.R354W and p.S1067L alterations or the combination of the two alterations in DUOX2 are probably only predisposing to CH and DUOX2 may be involved in the morphogenesis of the human thyroid gland. Simultaneously, the compensation of DUOX1 for the loss of DUOX2, undetectable pathogenic mutations, the effects of environmental factors, epigenetic mechanisms and the involvement of multiple genes cannot be excluded in the explanation of these genetic results.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.M. Maciel, E.T. Kimura, C.R. Nogueira, G.M. Mazeto, P.K. Magalhaes, M.L. Nascimento, S. Nesi-Franca, S.E. Vieira, Congenital hypothyroidism: recommendations of the Thyroid Department of the Brazilian Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metab. 57(3), 184–192 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1590/s0004-27302013000300004
A.J. Wassner, Pediatric hypothyroidism: diagnosis and treatment. Paediatr. Drugs 19(4), 291–301 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40272-017-0238-0
C. Fu, S. Zhang, J. Su, S. Luo, H. Zheng, J. Wang, H. Qin, Y. Chen, Y. Shen, X. Hu, X. Fan, J. Luo, B. Xie, R. Chen, S. Chen, Mutation screening of DUOX2 in Chinese patients with congenital hypothyroidism. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 38(11), 1219–1224 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-015-0382-8
S. Liu, W. Han, Y. Zang, H. Zang, F. Wang, P. Jiang, H. Wei, X. Liu, Y. Wang, X. Ma, Y. Ge, Identification of two missense mutations in DUOX1 (p.R1307Q) and DUOXA1 (p.R56W) that can cause congenital hypothyroidism through impairing H2O2 generation. Front Endocrinol. 10, 526 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00526
H. Cangul, V.N. Bas, Y. Saglam, M. Kendall, T.G. Barrett, E.R. Maher, Z. Aycan, A nonsense thyrotropin receptor gene mutation (R609X) is associated with congenital hypothyroidism and heart defects. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 27(11–12), 1101–1105 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1515/jpem-2014-0025
A. Carvalho, P. Hermanns, A.L. Rodrigues, I. Sousa, J. Anselmo, H. Bikker, R. Cabral, C. Pereira-Duarte, L. Mota-Vieira, J. Pohlenz, A new PAX8 mutation causing congenital hypothyroidism in three generations of a family is associated with abnormalities in the urogenital tract. Thyroid 23(9), 1074–1078 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2012.0649
D.A. Fisher, J.H. Dussault, T.P. Foley Jr, A.H. Klein, S. LaFranchi, P.R. Larsen, M.L. Mitchell, W.H. Murphey, P.G. Walfish, Screening for congenital hypothyroidism: results of screening one million North American infants. J. Pediatr. 94(5), 700–705 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80133-x
A.J. Wassner, Congenital Hypothyroidism. Clin. Perinatol. 45(1), 1–18 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clp.2017.10.004
F. Sun, J.X. Zhang, C.Y. Yang, G.Q. Gao, W.B. Zhu, B. Han, L.L. Zhang, Y.Y. Wan, X.P. Ye, Y.R. Ma, M.M. Zhang, L. Yang, Q.Y. Zhang, W. Liu, C.C. Guo, G. Chen, S.X. Zhao, K.Y. Song, H.D. Song, The genetic characteristics of congenital hypothyroidism in China by comprehensive screening of 21 candidate genes. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 178(6), 623–633 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-17-1017
M. Hashemipour, S. Hovsepian, A. Ansari, M. Keikha, P. Khalighinejad, N. Niknam, Screening of congenital hypothyroidism in preterm, low birth weight and very low birth weight neonates: a systematic review. Pediatr. Neonatol. 59(1), 3–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedneo.2017.04.006
E. Medda, M.C. Vigone, A. Cassio, F. Calaciura, P. Costa, G. Weber, T. de Filippis, G. Gelmini, M. Di Frenna, S. Caiulo, R. Ortolano, D. Rotondi, M. Bartolucci, R. Gelsomino, S. De Angelis, M. Gabbianelli, L. Persani, A. Olivieri, Neonatal screening for congenital hypothyroidism: what can we learn from discordant twins? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 104(12), 5765–5779 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2019-00900
A.J. Wassner, R.S. Brown, Congenital hypothyroidism: recent advances. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 22(5), 407–412 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1097/MED.0000000000000181
S. Liu, X. Wang, H. Zou, Y. Ge, F. Wang, Y. Wang, S. Yan, H. Xia, M. Xing, Identification and characterization of novel PAX8 mutations in Congenital Hypothyroidism(CH) in a Chinese population. Oncotarget 8(5), 8707–8716 (2017). https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14419
F. Wang, K. Lu, Z. Yang, S. Zhang, W. Lu, L. Zhang, S. Liu, S. Yan, Genotypes and phenotypes of congenital goitre and hypothyroidism caused by mutations in dual oxidase 2 genes. Clin. Endocrinol. 81(3), 452–457 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.12469
H. Grasberger, S. Refetoff, Genetic causes of congenital hypothyroidism due to dyshormonogenesis. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 23(4), 421–428 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1097/MOP.0b013e32834726a4
H. Ohye, M. Sugawara, Dual oxidase, hydrogen peroxide and thyroid diseases. Exp. Biol. Med. 235(4), 424–433 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1258/ebm.2009.009241
S. Liu, W. Zhang, L. Zhang, H. Zou, K. Lu, Q. Li, H. Xia, S. Yan, X. Ma, Genetic and functional analysis of two missense DUOX2 mutations in congenital hypothyroidism and goiter. Oncotarget 9(4), 4366–4374 (2018). https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10525
M.M.L. Kizys, R.A. Louzada, M. Mitne-Neto, J.R. Jara, G.K. Furuzawa, D.P. de Carvalho, M.R. Dias-da-Silva, S. Nesi-Franca, C. Dupuy, R.M.B. Maciel, DUOX2 mutations are associated with congenital hypothyroidism with ectopic thyroid gland. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 102(11), 4060–4071 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2017-00832
C. Lof, K. Patyra, T. Kuulasmaa, J. Vangipurapu, H. Undeutsch, H. Jaeschke, T. Pajunen, A. Kero, H. Krude, H. Biebermann, G. Kleinau, P. Kuhnen, K. Rantakari, P. Miettinen, T. Kirjavainen, J.P. Pursiheimo, T. Mustila, J. Jaaskelainen, M. Ojaniemi, J. Toppari, J. Ignatius, M. Laakso, J. Kero, Detection of novel gene variants associated with congenital hypothyroidism in a Finnish patient cohort. Thyroid 26(9), 1215–1224 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2016.0016
L. Fugazzola, M. Muzza, G. Weber, P. Beck-Peccoz, L. Persani, DUOXS defects: genotype-phenotype correlations. Ann. Endocrinol. 72(2), 82–86 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ando.2011.03.004
S.M. Park, V.K. Chatterjee, Genetics of congenital hypothyroidism. J. Med. Genet. 42(5), 379–389 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.2004.024158
C. Peters, A.S.P. van Trotsenburg, N. Schoenmakers, Diagnosis of endocrine disease: congenital hypothyroidism: update and perspectives. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 179(6), R297–R317 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-18-0383
A. Carre, A. Stoupa, D. Kariyawasam, M. Gueriouz, C. Ramond, T. Monus, J. Leger, S. Gaujoux, F. Sebag, N. Glaser, D. Zenaty, P. Nitschke, C. Bole-Feysot, L. Hubert, S. Lyonnet, R. Scharfmann, A. Munnich, C. Besmond, W. Taylor, M. Polak, Mutations in BOREALIN cause thyroid dysgenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 26(3), 599–610 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddw419
L.P. Fernandez, A. Lopez-Marquez, P. Santisteban, Thyroid transcription factors in development, differentiation and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 11(1), 29–42 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2014.186
G. Szinnai, Genetics of normal and abnormal thyroid development in humans. Best. Pract. Res Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 28(2), 133–150 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2013.08.005
A. Stoupa, R. Chaabane, M. Gueriouz, C. Raynaud-Ravni, P. Nitschke, C. Bole-Feysot, M. Mnif, L. Ammar Keskes, M. Hachicha, N. Belguith, M. Polak, A. Carre, Thyroid hypoplasia in congenital hypothyroidism associated with thyroid peroxidase mutations. Thyroid 28(7), 941–944 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2017.0502
Y. Maruo, H. Takahashi, I. Soeda, N. Nishikura, K. Matsui, Y. Ota, Y. Mimura, A. Mori, H. Sato, Y. Takeuchi, Transient congenital hypothyroidism caused by biallelic mutations of the dual oxidase 2 gene in Japanese patients detected by a neonatal screening program. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93(11), 4261–4267 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-0856
V. Varela, C.M. Rivolta, S.A. Esperante, L. Gruneiro-Papendieck, A. Chiesa, H.M. Targovnik, Three mutations (p.Q36H, p.G418fsX482, and g.IVS19-2A>C) in the dual oxidase 2 gene responsible for congenital goiter and iodide organification defect. Clin. Chem. 52(2), 182–191 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2005.058321
L. Persani, G. Rurale, T. de Filippis, E. Galazzi, M. Muzza, L. Fugazzola, Genetics and management of congenital hypothyroidism. Best. Pract. Res Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 32(4), 387–396 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2018.05.002
L. Sindhuja, D. Dayal, K.S. Sodhi, N. Sachdeva, A. Bhattacharya, Thyroid dysfunction and developmental anomalies in first degree relatives of children with thyroid dysgenesis. World J. Pediatr. 12(2), 215–218 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-015-0061-z
G. Dufort, S. Larrivee-Vanier, D. Eugene, X. De Deken, B. Seebauer, K. Heinimann, S. Levesque, S. Gravel, G. Szinnai, G. Van Vliet, J. Deladoey, Wide spectrum of DUOX2 deficiency: from life-threatening compressive goiter in infancy to lifelong euthyroidism. Thyroid 29(7), 1018–1022 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2018.0461
M. Tan, Y. Huang, X. Jiang, P. Li, C. Tang, X. Jia, Q. Chen, W. Chen, H. Sheng, Y. Feng, D. Wu, L. Liu, The prevalence, clinical, and molecular characteristics of congenital hypothyroidism caused by DUOX2 mutations: a population-based cohort study in Guangzhou. Horm. Metab. Res. 48(9), 581–588 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-112224
H. Grasberger, Defects of thyroidal hydrogen peroxide generation in congenital hypothyroidism. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 322(1-2), 99–106 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2010.01.029
J.C. Moreno, H. Bikker, M.J. Kempers, A.S. van Trotsenburg, F. Baas, J.J. de Vijlder, T. Vulsma, C. Ris-Stalpers, Inactivating mutations in the gene for thyroid oxidase 2 (THOX2) and congenital hypothyroidism. N. Engl. J. Med. 347(2), 95–102 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa012752
X. Fan, C. Fu, Y. Shen, C. Li, S. Luo, Q. Li, J. Luo, J. Su, S. Zhang, X. Hu, R. Chen, X. Gu, S. Chen, Next-generation sequencing analysis of twelve known causative genes in congenital hypothyroidism. Clin. Chim. Acta 468, 76–80 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2017.02.009
M. Hashemipour, M. Ghasemi, S. Hovsepian, K. Heiydari, A. Sajadi, R. Hadian, M. Mansourian, N. Mirshahzadeh, R. Kelishadi, M. Dalvi, Etiology of congenital hypothyroidism in Isfahan: Does it different? Adv. Biomed. Res. 3, 21 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4103/2277-9175.124658
D.V. Bann, Q. Jin, K.E. Sheldon, K.R. Houser, L. Nguyen, J.I. Warrick, M.J. Baker, J.R. Broach, G.S. Gerhard, D. Goldenberg, Genetic variants implicate dual oxidase-2 in familial and sporadic nonmedullary thyroid cancer. Cancer Res. 79(21), 5490–5499 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-19-0721
Y. Watanabe, R.J. Bruellman, R.S. Ebrhim, M.A. Abdullah, A.M. Dumitrescu, S. Refetoff, R.E. Weiss, Congenital hypothyroidism due to oligogenic mutations in two sudanese families. Thyroid 29(2), 302–304 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2018.0295
Y. Maruo, K. Nagasaki, K. Matsui, Y. Mimura, A. Mori, M. Fukami, Y. Takeuchi, Natural course of congenital hypothyroidism by dual oxidase 2 mutations from the neonatal period through puberty. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 174(4), 453–463 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1530/eje-15-0959
M. Satoh, K. Aso, S. Ogikubo, A. Yoshizawa-Ogasawara, T. Saji, Hypothyroidism caused by the combination of two heterozygous mutations: one in the TSH receptor gene the other in the DUOX2 gene. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 28(5-6), 657–661 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1515/jpem-2014-0078
A. Yoshizawa-Ogasawara, K. Abe, S. Ogikubo, S. Narumi, T. Hasegawa, M. Satoh, Transient congenital hypothyroidism caused by compound heterozygous mutations affecting the NADPH-oxidase domain of DUOX2. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 29(3), 363–371 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/jpem-2014-0479
R. Abu-Khudir, S. Larrivee-Vanier, J.D. Wasserman, J. Deladoey, Disorders of thyroid morphogenesis. Best. Pract. Res Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 31(2), 143–159 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2017.04.008
M. Tonacchera, G. De Marco, P. Agretti, L. Montanelli, C. Di Cosmo, A.C. Freitas Ferreira, A. Dimida, E. Ferrarini, H.E. Ramos, C. Ceccarelli, F. Brozzi, A. Pinchera, P. Vitti, Identification and functional studies of two new dual-oxidase 2 (DUOX2) mutations in a child with congenital hypothyroidism and a eutopic normal-size thyroid gland. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 94(11), 4309–4314 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2009-0426
M.C. Vigone, L. Fugazzola, I. Zamproni, A. Passoni, S. Di Candia, G. Chiumello, L. Persani, G. Weber, Persistent mild hypothyroidism associated with novel sequence variants of the DUOX2 gene in two siblings. Hum. Mutat. 26(4), 395 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.9372
M. Muzza, S. Rabbiosi, M.C. Vigone, I. Zamproni, V. Cirello, M.A. Maffini, K. Maruca, N. Schoenmakers, L. Beccaria, F. Gallo, S.M. Park, P. Beck-Peccoz, L. Persani, G. Weber, L. Fugazzola, The clinical and molecular characterization of patients with dyshormonogenic congenital hypothyroidism reveals specific diagnostic clues for DUOX2 defects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 99(3), E544–553 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2013-3618
N. Pfarr, E. Korsch, S. Kaspers, A. Herbst, A. Stach, C. Zimmer, J. Pohlenz, Congenital hypothyroidism caused by new mutations in the thyroid oxidase 2 (THOX2) gene. Clin. Endocrinol. 65(6), 810–815 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2006.02672.x
K.J. Park, H.K. Park, Y.J. Kim, K.R. Lee, J.H. Park, J.H. Park, H.D. Park, S.Y. Lee, J.W. Kim, DUOX2 mutations are frequently associated with congenital hypothyroidism in the Korean population. Ann. Lab. Med. 36(2), 145–153 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2016.36.2.145
Author contributions
L.L. wrote the manuscript. W.L. and L.Z. conducted the experiments. Fang W., Fengqi W., and M.G. acquired the data. X.W. analyzed the data. S.L. designed the study.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant number 2016YFC1000306).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Liu, W., Zhang, L. et al. Identification and analyzes of DUOX2 mutations in two familial congenital hypothyroidism cases. Endocrine 72, 147–156 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02437-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02437-8