Abstract
Purpose
Mutations in the gene HSD17B3 encoding the 17-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 3 enzyme cause testosterone insufficiency leading to XY disorders of sex development. In this study the clinical and molecular characteristics of three patients from consanguineous families are elucidated.
Methods
We identified three patients from two unrelated families with XY DSD and a novel homozygous HSD17B3:c. 673G>A mutation. The effect of the mutation on splicing was determined in RNA extracted from the testis of one patient.
Results
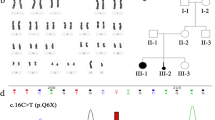
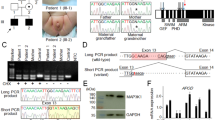
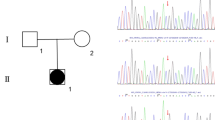
Three patients presented at ages 0.1, 8 and 0.7 years with ambiguous genitalia and an XY Karyotype. Endocrine workup showed normal cortisol and mineralocorticoid levels with a low testosterone/androstenedione ratio. Whole-exome sequencing, carried out in the first family, revealed a homozygous novel mutation in the HSD17B3 gene: c. 673G>A, p. V225M. The same mutation was found by Sanger sequencing in the third unrelated patient. Haplotype analysis of a 4 Mb region surrounding the HSD17B3 gene on chromosome 9 revealed that the mutation resides on the same allele in all three patients. The mutation, being the first nucleic acid on exon 10, affects splicing and causes exon 10 skipping in one of our patients’ testes.
Conclusion
The novel homozygous c. 673G>A, p. V225M mutation in the 17HSDB3 gene is likely a founder mutation and causes severe XY-DSD. It changes a conserved amino acid residue, and also alters 17HSDB3 gene transcription by causing skipping of exon 10, thereby contributing to an imbalance in the relevant protein isoforms and consequently, significant decreased 17HDSB3 enzymatic activity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Phelan, E. Williams, S. Cardamone, M. Lee, M. Creighton, G. Rumsby, G.S. Conway, Screening for mutation in 17 β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and androgen receptor in women presenting with partially virilized 46, XY disorders of sex development. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 172, 745–751 (2015)
A. Rosler, S. Silverstein, D.Abelovich, A (R80Q) mutation in 17 β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase Type 3 gene among Arabs of Israel is associated with pseudo hermaphroditism in males and normal asymptomatic females. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol 81, 1827–1831 (1996)
U. Goebelsmann, R. Horton, J.H. Mestman, J.J. Arce, Y. Nagata, R.M. Nakamura, I.H. Thorneycroft, D.R. Mishell, Male pseudo hermaphroditism due to testicular 17 β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 36, 867–878 (1973)
A. Rosler, A. Belanger, F. Labrie, Mechanisms of Androgen production in male pseudo hermaphroditism due to 17 β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 75, 773–778 (1992)
A. Boehmer, A.O. Brinkmann, L.A. Sandkuijl, D.J. Halley, F. Martinus, N.S. Andersson, F.H. De Jong, H. Kayserili, M.A. De Vroede, B.J. Otten et al. 17 β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-3 deficiency: diagnosis, phenotypic variability, population genetics, and worldwide distribution of ancient and de novo mutations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84, 4713–4721 (1999)
N. Moghrabi, I.A. Hughes, H.A. Dunaif, S. Andersson, Deleterious missense mutations and silent polymorphism in the human 17 β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 3 gene (HSD17B3). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 83, 2855–2860 (1998)
M.D. Omrani, T. Adamovic, U. Grandell, S. Saleh-Garhari, A. Nordenskjold, 17-β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3 deficiency in three adult Iranian siblings. J. Sex. Dev. 5, 273–276 (2011)
B. Ben Rhouma, N. Belguith, M. Feki Mnif, T. Kamoun, N. Charfi, M. Kamoun, F. Abdelhedi, M. Hachicha, H. Kamoun, M. Abid, F. Fakhfakh, A novel nonsense mutation in HSD17B3 gene in a Tunisian patient with sexual ambiguity. The. J. Sex. Med. 10, 2586–2589 (2013)
A. Alikasifoglu, D. Vuralli, O. Hiort, N. Gonc, A. Ozon, N. Kandemir, Severe undervirilization in a 46, XY case due to a novel mutation in HSD17B3 gene. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 7, 249–252 (2015)
R.T. Engeli, M. Tsachaki, H.A. Hassan, C.P. Sager, M.L. Essawi, Y.Z. Gad, Biochemical analysis of four missense mutations in the HSD17B3 gene associated with 46, XY disorders of sex development in Egyptian patients. The. J. Sex. Med. 14, 1165–1174 (2017)
S.A. Wudy, M.F. Hartmann, Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry profiling of steroids in times of molecular biology. Horm. Metab. Res. 36, 415–422 (2004)
ExAC Browser. http://exac.broadinstitute.org/. Accessed 19 Jul 2017
ClinVar. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/. Accessed 19 Jul 2017
dbSNP Home Page. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/SNP/. Accessed 19 Jul 2017
F. Pagani, F.E. Baralle, Genomic variants in exons and introns: identifying the splicing spoilers. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 389–396 (2004)
X. Jian, E. Boerwinkle, X. Liu, In silico prediction of splice-altering single nucleotide variants in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, 13534–13544 (2014)
Y.S. Lee, J.M.W. Kirk, R.G. Stanhope, D.I. Johnston, S. Harland, R.J. Auchus, S. Andersson, L.A. Hughest, Phenotypic variability in 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-3 deficiency and diagnostic pitfalls. Clin. Endocrinol. 67, 20–28 (2007)
R.L. Batista, M. Inacio, I.J.P. Arnold, N.L. Gomes, J.A. Diniz Faria, D.R. De Mores, E.M. Frade Coste, S. Dominice, B.B. Mendonca, Psychosexual aspects, effects of prenatal androgen exposure, and gender change in 46, XY disorders of sex development. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 104, 1160–1170 (2019)
D.J. Gross, H. Landau, G. Kohn, A. Farkas, E. Elrayyese, R. El-Shawwa, E.E. Lasch, A. Rosler, Male pseudo hermaphroditism due to 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency: gender reassignment in early infancy. Acta Endocrinol. 112, 238–246 (1986)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from Shaare Zedek medical Center (Mirsky fund, 2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levy-Khademi, F., Zeligson, S., Lavi, E. et al. The novel founder homozygous V225M mutation in the HSD17B3 gene causes aberrant splicing and XY-DSD. Endocrine 69, 650–654 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02327-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02327-z