Abstract
Purpose
Thyroid hormones (THs) have multiple effects on lipid synthesis, mobilization, and degradation, suggesting that THs may affect the development of dyslipidemia. However, prospective studies on the association between serum THs levels and incident dyslipidemia in euthyroid subjects are limited. Therefore, we conducted a cohort study (~5-year follow-up period, median: 3.0 years) to explore whether THs can affect incident dyslipidemia in a general euthyroid population aged 18 years old and over.
Methods
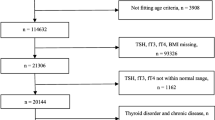
Dyslipidemia is characterized by elevated total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), or low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), or reduced high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). Serum free triiodothyronine (FT3), free thyroxine (FT4), and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) were determined by chemiluminescence immunoassay. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to assess the association between baseline FT3, FT4, TSH, and the risk of various dyslipidemias.
Results
During follow-up period, the incidence of elevated TC, TG, LDL-C, and reduced HDL-C was 29.3%, 20.7%, 24.8%, and 19.5%, respectively. After adjustment for multiple confounders, we found that per unit increase in FT3 concentrations were associated with decreased incidence of elevated TC and LDL-C, and the hazard ratios (95% confidence interval) were 0.87 (0.79–0.97) (P < 0.01) and 0.897 (0.808–0.995) (P = 0.04), respectively. We also found a weak positive association between TSH and incidence of reduced HDL-C (P = 0.02). However, we found no association between FT4 and incident dyslipidemia.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrated that low FT3 was associated with high dyslipidemia risk, especially for elevated TC and LDL-C, and that TSH had a weak positive effect on incidence of reduced HDL-C.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.G. Smith, Epidemiology of dyslipidemia and economic burden on the healthcare system. Am. J. Manag. Care 13(Suppl 3), S68–S71 (2007)
Y. Huang, L. Gao, X. Xie, S.C. Tan, Epidemiology of dyslipidemia in Chinese adults: meta-analysis of prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control. Popul. Health Metr. 12(1), 28 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12963-014-0028-7
R.H. Nelson, Hyperlipidemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Prim. Care 40(1), 195–211 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pop.2012.11.003
E.J. Benjamin, M.J. Blaha, S.E. Chiuve, M. Cushman, S.R. Das, R. Deo, S.D. de Ferranti, J. Floyd, M. Fornage, C. Gillespie, C.R. Isasi, M.C. Jimenez, L.C. Jordan, S.E. Judd, D. Lackland, J.H. Lichtman, L. Lisabeth, S. Liu, C.T. Longenecker, R.H. Mackey, K. Matsushita, D. Mozaffarian, M.E. Mussolino, K. Nasir, R.W. Neumar, L. Palaniappan, D.K. Pandey, R.R. Thiagarajan, M.J. Reeves, M. Ritchey, C.J. Rodriguez, G.A. Roth, W.D. Rosamond, C. Sasson, A. Towfighi, C.W. Tsao, M.B. Turner, S.S. Virani, J.H. Voeks, J.Z. Willey, J.T. Wilkins, J.H. Wu, H.M. Alger, S.S. Wong, P. Muntner, American Heart Association Statistics Committee, Stroke Statistics Subcommittee, Heart disease and stroke statistics—2017 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 135(10), e146–e603 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000485
A. Moran, D. Gu, D. Zhao, P. Coxson, Y.C. Wang, C.S. Chen, J. Liu, J. Cheng, K. Bibbins-Domingo, Y.M. Shen, J. He, L. Goldman, Future cardiovascular disease in china: markov model and risk factor scenario projections from the coronary heart disease policy model-china. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 3(3), 243–252 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.109.910711
European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation, Z. Reiner, A.L. Catapano, G. De Backer, I. Graham, M.R. Taskinen, O. Wiklund, S. Agewall, E. Alegria, M.J. Chapman, P. Durrington, S. Erdine, J. Halcox, R. Hobbs, J. Kjekshus, P.P. Filardi, G. Riccardi, R.F. Storey, D. Wood; E.S.C. Committee for Practice Guidelines, Committees, ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: the Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). Eur. Heart J. 32(14), 1769–1818 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehr158
E.N. Pearce, Hypothyroidism and dyslipidemia: modern concepts and approaches. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 6(6), 451–456 (2004)
C.V. Rizos, M.S. Elisaf, E.N. Liberopoulos, Effects of thyroid dysfunction on lipid profile. Open Cardiovasc. Med. J. 5, 76–84 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2174/1874192401105010076
D.J. Shin, T.F. Osborne, Thyroid hormone regulation and cholesterol metabolism are connected through Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein-2 (SREBP-2). J. Biol. Chem. 278(36), 34114–34118 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M305417200
I.M. Abreu, E. Lau, B. de Sousa Pinto, D. Carvalho, Subclinical hypothyroidism: to treat or not to treat, that is the question! A systematic review with meta-analysis on lipid profile. Endocr. Connect 6(3), 188–199 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1530/EC-17-0028
B.H.R. Wolffenbuttel, H. Wouters, S.N. Slagter, R.P. van Waateringe, A.C. Muller Kobold, J.V. van Vliet-Ostaptchouk, T.P. Links, M.M. van der Klauw, Thyroid function and metabolic syndrome in the population-based LifeLines cohort study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 17(1), 65 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-017-0215-1
S. Temizkan, B. Balaforlou, A. Ozderya, M. Avci, K. Aydin, S. Karaman, M. Sargin, Effects of thyrotrophin, thyroid hormones and thyroid antibodies on metabolic parameters in a euthyroid population with obesity. Clin. Endocrinol. 85(4), 616–623 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.13095
A. Roos, S.J. Bakker, T.P. Links, R.O. Gans, B.H. Wolffenbuttel, Thyroid function is associated with components of the metabolic syndrome in euthyroid subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92(2), 491–496 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2006-1718
G.L. Roef, E.R. Rietzschel, C.M. Van Daele, Y.E. Taes, M.L. De Buyzere, T.C. Gillebert, J.M. Kaufman, Triiodothyronine and free thyroxine levels are differentially associated with metabolic profile and adiposity-related cardiovascular risk markers in euthyroid middle-aged subjects. Thyroid 24(2), 223–231 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2013.0314
Y. Wang, Q. Yin, M. Xu, Q. Ni, W. Wang, Q. Wang, BMI modulates the effect of thyroid hormone on lipid profile in euthyroid adults. Int J. Endocrinol. 2017, 8591986 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8591986
B.O. Asvold, T. Bjoro, L.J. Vatten, Associations of TSH levels within the reference range with future blood pressure and lipid concentrations: 11-year follow-up of the HUNT study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 169(1), 73–82 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-13-0087
Y. Gu, H. Li, X. Bao, Q. Zhang, L. Liu, G. Meng, H. Wu, H. Du, H. Shi, Y. Xia, Q. Su, L. Fang, F. Yu, H. Yang, B. Yu, S. Sun, X. Wang, M. Zhou, Q. Jia, Q. Guo, H. Chang, G. Wang, G. Huang, K. Song, K. Niu, The relationship between thyroid function and the prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in euthyroid subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 102(2), 434–442 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2016-2965
National Cholesterol Education Program Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults, Third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation 106(25), 3143–3421 (2002)
K.G. Alberti, R.H. Eckel, S.M. Grundy, P.Z. Zimmet, J.I. Cleeman, K.A. Donato, J.C. Fruchart, W.P. James, C.M. Loria, S.C. Smith Jr.; International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention, Hational Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, American Heart Association, World Heart Federation, International Atherosclerosis Society, International Association for the Study of Obesity, Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 120(16), 1640–1645 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192644
A.P. Delitala, G. Fanciulli, G.M. Pes, M. Maioli, G. Delitala, Thyroid hormones, metabolic syndrome and its components. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 17(1), 56–62 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2174/1871530317666170320105221
R. Day, R.L. Gebhard, H.L. Schwartz, K.A. Strait, W.C. Duane, B.G. Stone, J.H. Oppenheimer, Time course of hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity and messenger ribonucleic acid, biliary lipid secretion, and hepatic cholesterol content in methimazole-treated hypothyroid and hypophysectomized rats after triiodothyronine administration: possible linkage of cholesterol synthesis to biliary secretion. Endocrinology 125(1), 459–468 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-125-1-459
L.H. Duntas, G. Brenta, The effect of thyroid disorders on lipid levels and metabolism. Med Clin. North Am. 96(2), 269–281 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2012.01.012
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge all the people that have contributed to this study.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81872611), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, Y., Meng, G., Zhang, Q. et al. Thyroid function and lipid profile in euthyroid adults: the TCLSIH cohort study. Endocrine 70, 107–114 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02312-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02312-6