Abstract
Purpose
To explore the relationship of phenotype and genotype of neonatal diabetes mellitus (NDM) in southwestern China.
Methods
Sixteen cases of NDM admitted to Children’s Hospital of Chongqing Medical University from May 2009 to May 2019 were included in this study. The clinical features of the included infants were retrospectively analyzed. Peripheral blood samples of the patients and their parents were collected for mutation detection.
Results
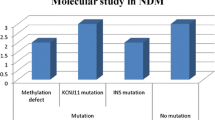
Among the 16 cases of NDM, 8 cases were permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM) (including 3 clinical syndromes), and 3 cases were transient neonatal diabetes mellitus (TNDM). Mutation detection was performed in six cases. The mutation genes and their loci were FOXP3 p.V408M, KCNJ11 p.C166Y, ABCC8 p.S830P, KCNJ11 p.I182T, KCNJ11 p.G334D, and ZFP57 p.R125X,412. ABCC8 p.S830P was the new found pathogenic site of gene mutation. According to the clinical features and follow-up results, one case was diagnosed as IPEX syndrome, two as DEND syndrome, two as simple PNDM, and one as TNDM. All the TNDM could spontaneously alleviate and then insulin was withdrawn. In PNDM, 75% of those with KATP channel gene mutation could be completely or partially converted to oral sulfonylureas treatment, however, the rest cases needed lifelong insulin replacement therapy.
Conclusion
The clinical manifestations and treatment regimens of patients with NDM vary according to the type of gene mutation. Even the same mutant genotype has differences in phenotype and response to treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Nagashima, D. Tanaka, N. Inagaki, Epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and genetic etiology of neonatal diabetes in Japan. Pediatr. Int. 59(2), 129–133 (2017)
E. Globa, N. Zelinska, D.J. Mackay, K.I. Temple, J.A. Houghton, A.T. Hattersley, S.E. Flanagan, S. Ellard, Neonatal diabetes in Ukraine: incidence, genetics, clinical phenotype and treatment. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 28(11–12), 1279–1286 (2015)
D. Iafusco, O. Massa, B. Pasquino, C. Colombo, L. Iughetti, C. Bizzarri, C. Mammi, D. Lo Presti, T. Suprani, R. Schiaffini, C.G. Nichols, L. Russo, V. Grasso, F. Meschi, R. Bonfanti, S. Brescianini, F. Barbetti, Minimal incidence of neonatal/infancy onset diabetes in Italy is 1:90,000 live births. Acta Diabetol. 49(5), 405–408 (2012)
A.L. Gloyn, E.R. Pearson, J.F. Antcliff, P. Proks, G.J. Bruining, A.S. Slingerland, N. Howard, S. Srinivasan, J.M. Silva, J. Molnes, E.L. Edghill, T.M. Frayling, I.K. Temple, D. Mackay, J.P. Shield, Z. Sumnik, A. van Rhijn, J.K. Wales, P. Clark, S. Gorman, J. Aisenberg, S. Ellard, P.R. Njolstad, F.M. Ashcroft, A.T. Hattersley, Activating mutations in the gene encoding the ATP-sensitive potassium-channel subunit Kir6.2 and permanent neonatal diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 350(18), 1838–1849 (2004)
M.B. Lemelman, L. Letourneau, S.A.W. Greeley, Neonatal diabetes mellitus: an update on diagnosis and management. Clin. Perinatol. 45(1), 41–59 (2018)
D. Ma, J.P. Shield, W. Dean, I. Leclerc, C. Knauf, R.R. Burcelin, G.A. Rutter, G. Kelsey, Impaired glucose homeostasis in transgenic mice expressing the human transient neonatal diabetes mellitus locus, TNDM. J. Clin. Invest. 114(3), 339–348 (2004)
D. Blum, H. Dorchy, T. Mouraux, E. Vamos, Y. Mardens, A. Kumps, C. De Prez, P. Heimann, B. Fowler, R. Baumgartner, Congenital absence of insulin cells in a neonate with diabetes mellitus and mutase-deficient methylmalonic acidaemia. Diabetologia 36(4), 352–357 (1993)
A. Touati, J. Errea-Dorronsoro, S. Nouri, Y. Halleb, A. Pereda, N. Mahdhaoui, A. Ghith, A. Saad, G. Perez de Nanclares, D. H’Mida Ben Brahim, Transient neonatal diabetes mellitus and hypomethylation at additional imprinted loci: novel ZFP57 mutation and review on the literature. Acta Diabetol. 56(3), 301–307 (2019)
M. Bak, S.E. Boonen, C. Dahl, J.M. Hahnemann, D.J. Mackay, Z. Tumer, K. Gronskov, I.K. Temple, P. Guldberg, N. Tommerup, Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of transient neonatal diabetes type 1 patients with mutations in ZFP57. BMC Med. Genet. 17, 29 (2016)
S. Quenneville, G. Verde, A. Corsinotti, A. Kapopoulou, J. Jakobsson, S. Offner, I. Baglivo, P.V. Pedone, G. Grimaldi, A. Riccio, D. Trono, In embryonic stem cells, ZFP57/KAP1 recognize a methylated hexanucleotide to affect chromatin and DNA methylation of imprinting control regions. Mol. Cell. 44(3), 361–372 (2011)
Y. Liu, H. Toh, H. Sasaki, X. Zhang, X. Cheng, An atomic model of Zfp57 recognition of CpG methylation within a specific DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 26(21), 2374–2379 (2012)
I. Baglivo, S. Esposito, L. De Cesare, A. Sparago, Z. Anvar, V. Riso, M. Cammisa, R. Fattorusso, G. Grimaldi, A. Riccio, P.V. Pedone, Genetic and epigenetic mutations affect the DNA binding capability of human ZFP57 in transient neonatal diabetes type 1. FEBS Lett. 587(10), 1474–1481 (2013)
E. Gole, S. Oikonomou, S. Ellard, E. De Franco, K. Karavanaki, A Novel KCNJ11 Mutation Associated with Transient Neonatal Diabetes. J. Clin. Res Pediatr. Endocrinol. 10(2), 175–178 (2018)
B. Piccini, C. Coviello, L. Drovandi, A. Rosangela, F. Monzali, E. Casalini, S. Giglio, S. Toni, C. Dani, Transient neonatal diabetes mellitus in a very preterm infant due to ABCC8 mutation. AJP Rep. 8(1), e39–e42 (2018)
F.H. Sansbury, S.E. Flanagan, J.A. Houghton, F.L. Shuixian Shen, A.M. Al-Senani, A.M. Habeb, M. Abdullah, A. Kariminejad, S. Ellard, A.T. Hattersley, SLC2A2 mutations can cause neonatal diabetes, suggesting GLUT2 may have a role in human insulin secretion. Diabetologia 55(9), 2381–2385 (2012)
T. Yorifuji, S. Higuchi, Y. Hosokawa, R. Kawakita, Chromosome 6q24-related diabetes mellitus. Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 27(2), 59–65 (2018)
L.E. Docherty, S. Kabwama, A. Lehmann, E. Hawke, L. Harrison, S.E. Flanagan, S. Ellard, A.T. Hattersley, J.P. Shield, S. Ennis, D.J. Mackay, I.K. Temple, Clinical presentation of 6q24 transient neonatal diabetes mellitus (6q24 TNDM) and genotype-phenotype correlation in an international cohort of patients. Diabetologia 56(4), 758–762 (2013)
L. Garcin, D. Kariyawasam, K. Busiah, A.L. Fauret-Amsellem, F. Le Bourgeois, L. Vaivre-Douret, H. Cave, M. Polak, J. Beltrand, Successful off-label sulfonylurea treatment of neonatal diabetes mellitus due to chromosome 6 abnormalities. Pediatr. Diabetes 19(4), 663–669 (2018)
J.L. Fu, T. Wang, X.H. Xiao, Relapsed 6q24-related transient neonatal diabetes mellitus successfully treated with sulfonylurea. Chin. Med J. 132(7), 846–848 (2019)
U. Neumann, C. Buhrer, O. Blankenstein, P. Kuhnen, K. Raile, Primary sulphonylurea therapy in a newborn with transient neonatal diabetes attributable to a paternal uniparental disomy 6q24 (UPD6). Diabetes Obes. Metab. 20(2), 474–475 (2018)
C. Reinauer, C. Bergmann, A. Jonasson, V. Soditt, E. Mayatepek, T. Meissner, S. Kummer, ZFP57-related transient neonatal diabetes responsive to oral sulfonylurea treatment. Klin. Padiatr. 231(4), 225–226 (2019)
K. Shimomura, Y. Maejima, KATP channel mutations and neonatal diabetes. Intern Med. 56(18), 2387–2393 (2017)
P. Proks, H. de Wet, F.M. Ashcroft, Molecular mechanism of sulphonylurea block of K(ATP) channels carrying mutations that impair ATP inhibition and cause neonatal diabetes. Diabetes 62(11), 3909–3919 (2013)
C.W. Lin, Y.W. Lin, F.F. Yan, J. Casey, M. Kochhar, E.B. Pratt, S.L. Shyng, Kir6.2 mutations associated with neonatal diabetes reduce expression of ATP-sensitive K+ channels: implications in disease mechanism and sulfonylurea therapy. Diabetes 55(6), 1738–1746 (2006)
A.P. Babenko, M. Polak, H. Cave, K. Busiah, P. Czernichow, R. Scharfmann, J. Bryan, L. Aguilar-Bryan, M. Vaxillaire, P. Froguel, Activating mutations in the ABCC8 gene in neonatal diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 355(5), 456–466 (2006)
X. Xiao, T. Wang, W. Li, H. Song, C. Gong, C. Diao, M. Yu, T. Yuan, Y. Zhang, X. Sun, Q. Zhang, K. Lu, H. Wang, O. Schmitz, T. Hansen, Transfer from insulin to sulfonylurea treatment in a chinese patient with permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus due to a KCNJ11 R201H mutation. Horm. Metab. Res. 41(7), 580–582 (2009)
T. Wang, M. Yu, C. Lu, H. Zhang, F. Ping, Q. Zhang, J. Xu, K. Feng, W. Li, J. Zheng, X. Wang, X. Xiao, Molecular and clinical features of 13 cases of ATP-sensitive potassium channel neonatal diabetes mellitus. Chin. J. Diabetes Mellit. 9(6), 350–355 (2017)
X. Li, A. Xu, H. Sheng, T.H. Ting, X. Mao, X. Huang, M. Jiang, J. Cheng, L. Liu, Early transition from insulin to sulfonylureas in neonatal diabetes and follow-up: experience from China. Pediatr. Diabetes 19(2), 251–258 (2018)
S.E. Flanagan, E.L. Edghill, A.L. Gloyn, S. Ellard, A.T. Hattersley, Mutations in KCNJ11, which encodes Kir6.2, are a common cause of diabetes diagnosed in the first 6 months of life, with the phenotype determined by genotype. Diabetologia 49(6), 1190–1197 (2006)
K. Balamurugan, B. Kavitha, Z. Yang, V. Mohan, V. Radha, S.L. Shyng, Functional characterization of activating mutations in the sulfonylurea receptor 1 (ABCC8) causing neonatal diabetes mellitus in Asian Indian children. Pediatr. Diabetes 20(4), 397–407 (2019)
R. Bacchetta, F. Barzaghi, M.G. Roncarolo, From IPEX syndrome to FOXP3 mutation: a lesson on immune dysregulation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1417(1), 5–22 (2018)
O. Rubio-Cabezas, J.A. Minton, R. Caswell, J.P. Shield, D. Deiss, Z. Sumnik, A. Cayssials, M. Herr, A. Loew, V. Lewis, S. Ellard, A.T. Hattersley, Clinical heterogeneity in patients with FOXP3 mutations presenting with permanent neonatal diabetes. Diabetes Care 32(1), 111–116 (2009)
T. Wang, M. Li, M. Yu, C. Lu, H. Zhang, F. Ping, Q. Zhang, C. Qi, J. Zheng, X. Wang, J. Fu, X. Xiao, Genetic and clinical features of 3 cases of neonatal diabetes mellitus caused by forkhead box P3 gene mutation. Chin. J. Diabetes Mellit. 9(10), 596–601 (2018)
S. Ma, R. Viola, L. Sui, V. Cherubini, F. Barbetti, D. Egli, Beta cell replacement after gene editing of a neonatal diabetes-causing mutation at the insulin locus. Stem Cell Rep. 11(6), 1407–1415 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the patients and their families for their invaluable contribution to this study and thank Juan Liu, MD, for her statistical assistance.
Author contributions
L.C. and H.W.: conceptualized and designed the study. L.C., Y.Z., P.D., and W.D.: collected and analyzed the data. L.C. and Q.H.: interpreted the mutation analysis. L.C. and Y.H.: drafted the original paper. H.W., Z.H., and M.Z.: reviewed and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Children’s Hospital of Chongqing Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, L., He, Y., Huang, Q. et al. Clinical features and partial proportional molecular genetics in neonatal diabetes mellitus: a retrospective analysis in southwestern China. Endocrine 69, 53–62 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02279-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02279-4